Green financing focuses specifically on funding projects that have a direct positive environmental impact, such as renewable energy, pollution reduction, and conservation efforts. Sustainable financing takes a broader approach, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support long-term economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental stewardship. Explore the key differences and benefits of both green and sustainable financing to make informed banking decisions.
Why it is important
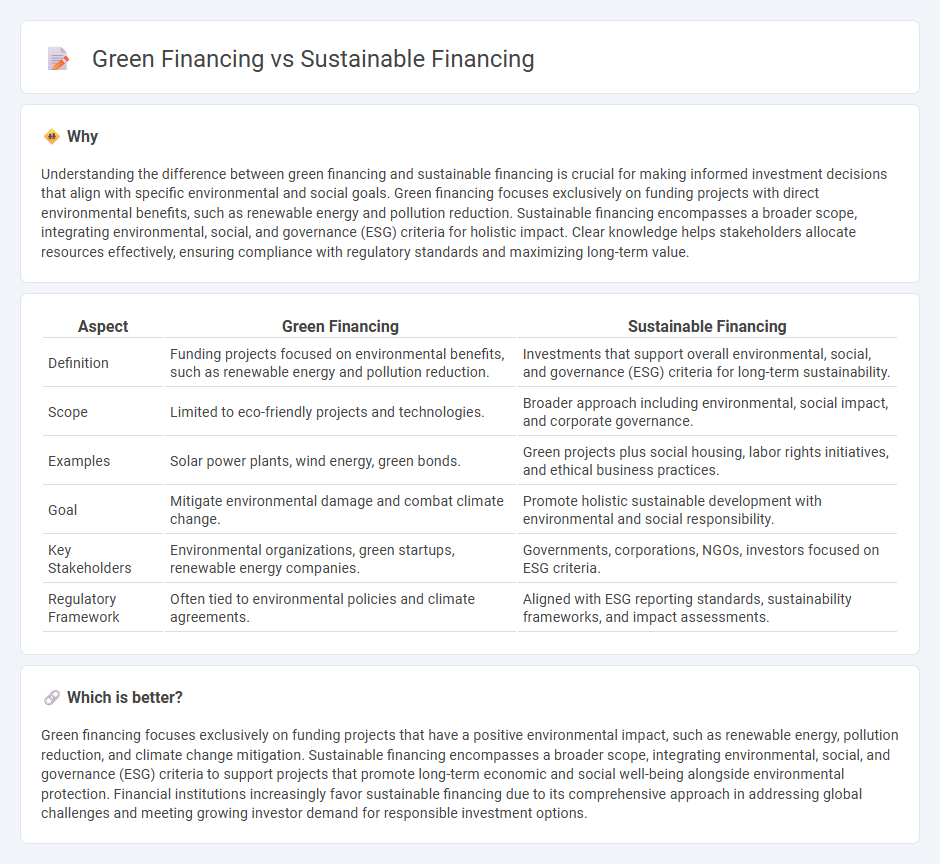
Understanding the difference between green financing and sustainable financing is crucial for making informed investment decisions that align with specific environmental and social goals. Green financing focuses exclusively on funding projects with direct environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction. Sustainable financing encompasses a broader scope, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria for holistic impact. Clear knowledge helps stakeholders allocate resources effectively, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and maximizing long-term value.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Financing | Sustainable Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Funding projects focused on environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction. | Investments that support overall environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria for long-term sustainability. |
| Scope | Limited to eco-friendly projects and technologies. | Broader approach including environmental, social impact, and corporate governance. |
| Examples | Solar power plants, wind energy, green bonds. | Green projects plus social housing, labor rights initiatives, and ethical business practices. |
| Goal | Mitigate environmental damage and combat climate change. | Promote holistic sustainable development with environmental and social responsibility. |
| Key Stakeholders | Environmental organizations, green startups, renewable energy companies. | Governments, corporations, NGOs, investors focused on ESG criteria. |
| Regulatory Framework | Often tied to environmental policies and climate agreements. | Aligned with ESG reporting standards, sustainability frameworks, and impact assessments. |
Which is better?
Green financing focuses exclusively on funding projects that have a positive environmental impact, such as renewable energy, pollution reduction, and climate change mitigation. Sustainable financing encompasses a broader scope, integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support projects that promote long-term economic and social well-being alongside environmental protection. Financial institutions increasingly favor sustainable financing due to its comprehensive approach in addressing global challenges and meeting growing investor demand for responsible investment options.
Connection
Green financing and sustainable financing are interconnected through their mutual goal of supporting environmentally responsible investments and projects. Both financing types prioritize funding initiatives that promote renewable energy, reduce carbon emissions, and enhance resource efficiency. Financial institutions increasingly integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to align green and sustainable financing with long-term ecological and economic resilience.
Key Terms
Sustainable Financing: ESG Integration, Social Bonds, Climate Risk Assessment
Sustainable financing encompasses a broad approach integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into investment decisions to promote responsible growth and social impact. It includes instruments like social bonds that fund projects benefiting communities, alongside rigorous climate risk assessments to mitigate environmental and financial risks. Explore more to understand how sustainable financing drives long-term value and resilience across sectors.
Green Financing: Green Bonds, Renewable Energy Investment, Carbon Footprint Reduction
Green financing specifically targets projects that positively impact the environment, including green bonds, which fund renewable energy investments such as solar and wind power, and initiatives aimed at carbon footprint reduction. This approach channels capital directly into sustainable infrastructure, promoting energy efficiency and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Explore how green financing drives global efforts toward a cleaner, more sustainable future.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Sustainable financing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to support projects that deliver long-term ecological and social benefits, ensuring comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA) guide investment decisions. Green financing specifically targets projects that provide direct environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction, often utilizing EIAs to measure and mitigate adverse environmental effects. Explore how Environmental Impact Assessments differentiate sustainable financing from green financing to enhance your understanding of investment strategies promoting environmental stewardship.
Source and External Links
Sustainable finance - Sustainable finance involves practices and products combining financial returns with environmental and social objectives, promoting growth aligned with climate and sustainability goals like the Paris Agreement and UN SDGs.
Overview of sustainable finance - European Commission - Sustainable finance integrates environmental, social, and governance factors into investment decisions and supports both green finance and transition finance for companies moving towards sustainability.
Sustainable Finance: Concepts and Practical ... - Sustainable finance aligns financial systems with sustainable development goals by embedding ESG considerations to support environmental preservation, social fairness, and economic growth as a practical response to climate and social challenges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com