Composable banking enables financial institutions to build tailored banking solutions by integrating modular components and APIs, offering flexibility and scalability that traditional systems lack. Challenger banking refers to agile, digital-only banks that leverage advanced technology to disrupt conventional banking with innovative services and user-centric experiences. Explore deeper insights into how composable and challenger banking are revolutionizing the financial landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between composable banking and challenger banking is crucial for financial institutions to innovate effectively and meet evolving customer demands. Composable banking offers modular, customizable technology stacks enabling rapid integration and flexibility, while challenger banks are agile, digitally native financial services that compete with traditional banks through innovative customer experiences. This knowledge helps banks adopt the right strategy to enhance operational efficiency, scalability, and customer engagement. Choosing the appropriate model can drive competitive advantage and future-proof banking services.
Comparison Table
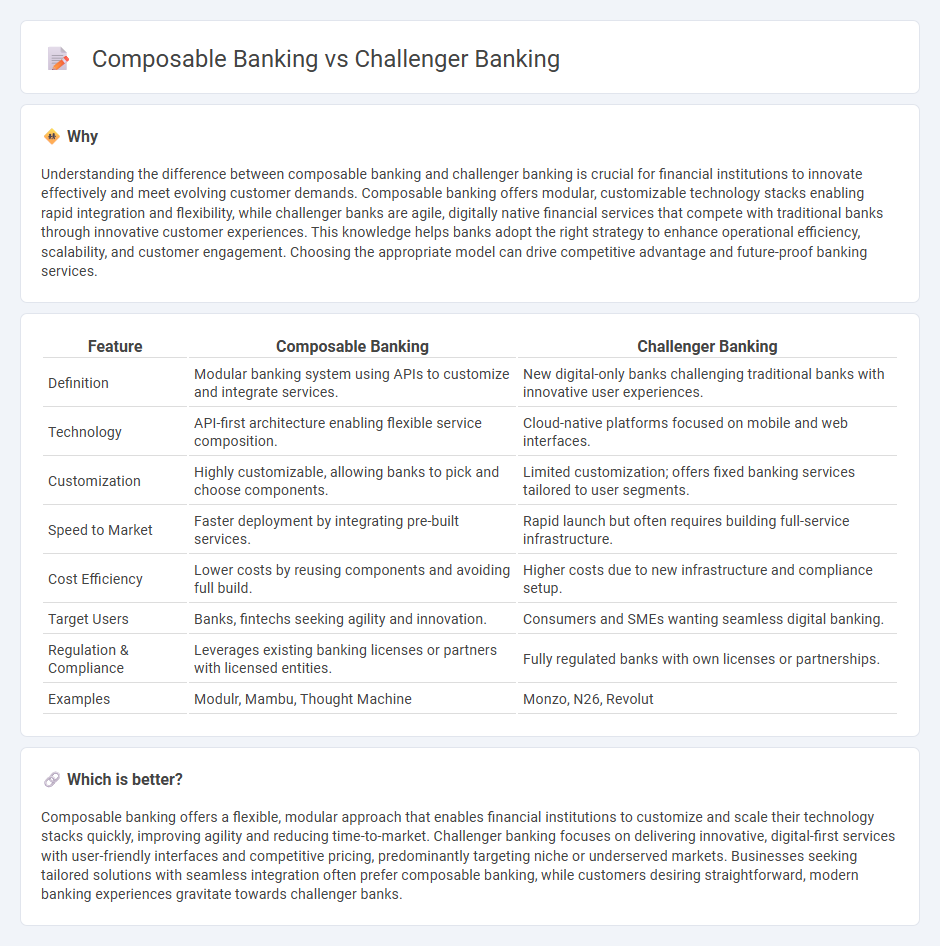
| Feature | Composable Banking | Challenger Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking system using APIs to customize and integrate services. | New digital-only banks challenging traditional banks with innovative user experiences. |
| Technology | API-first architecture enabling flexible service composition. | Cloud-native platforms focused on mobile and web interfaces. |
| Customization | Highly customizable, allowing banks to pick and choose components. | Limited customization; offers fixed banking services tailored to user segments. |
| Speed to Market | Faster deployment by integrating pre-built services. | Rapid launch but often requires building full-service infrastructure. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs by reusing components and avoiding full build. | Higher costs due to new infrastructure and compliance setup. |
| Target Users | Banks, fintechs seeking agility and innovation. | Consumers and SMEs wanting seamless digital banking. |
| Regulation & Compliance | Leverages existing banking licenses or partners with licensed entities. | Fully regulated banks with own licenses or partnerships. |
| Examples | Modulr, Mambu, Thought Machine | Monzo, N26, Revolut |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers a flexible, modular approach that enables financial institutions to customize and scale their technology stacks quickly, improving agility and reducing time-to-market. Challenger banking focuses on delivering innovative, digital-first services with user-friendly interfaces and competitive pricing, predominantly targeting niche or underserved markets. Businesses seeking tailored solutions with seamless integration often prefer composable banking, while customers desiring straightforward, modern banking experiences gravitate towards challenger banks.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs and microservices to enable rapid innovation, which directly supports the agile frameworks used by challenger banks. Challenger banks utilize composable banking architectures to quickly integrate new features, enhance customer experience, and maintain competitive agility in digital financial services. Both concepts drive disruption in traditional banking by promoting flexibility, customization, and seamless third-party integrations.
Key Terms
Digital-First Architecture
Challenger banking leverages digital-first architecture to deliver seamless, user-centric financial services through agile platforms designed for rapid innovation and customer engagement. Composable banking extends this by enabling modular integration of diverse banking components via APIs, facilitating highly customizable and scalable solutions tailored to specific business needs. Explore how combining these approaches can transform your digital banking strategy and accelerate innovation.
Modular Core Systems
Challenger banking emphasizes agile, customer-focused services built on modular core systems that enable rapid feature deployment and seamless integration with third-party APIs, enhancing user experience. Composable banking leverages modularity by assembling best-of-breed components into a flexible, scalable architecture tailored for continuous innovation and operational efficiency. Explore how modular core systems transform banking by combining agility with scalability to meet evolving market demands.
API Integration
Challenger banking leverages APIs to offer digital-first financial services, enhancing agility and customer experience by integrating third-party solutions quickly. Composable banking builds on this by providing a modular, API-driven architecture that allows banks to customize and scale their offerings seamlessly, ensuring higher flexibility and innovation speed. Explore how API integration differentiates these models and drives the future of digital banking.
Source and External Links
Challenger bank - Challenger banks are small, recently created retail banks that compete directly with longer-established banks, primarily in the UK.
Challenger Banks Explained: Trends and Opportunities - Challenger banks are digital-first financial institutions operating mainly via mobile apps and online platforms, offering lower fees and innovative services to challenge traditional banks, fueled by regulatory changes and technology advancements after the 2008 financial crisis.
Challenger Banks: What You Need to Know - Challenger banks focus on modern, digital, and customer-centric banking solutions, seeking to simplify money management and offer better mobile access, rate products, and fee transparency versus traditional banks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com