Crypto custody involves securing digital assets like cryptocurrencies using specialized wallets and encryption methods, while cash custody pertains to the physical safeguarding and management of paper money and coins within banking institutions. Crypto custody requires advanced cybersecurity protocols to prevent hacking, whereas cash custody focuses on physical security measures such as vaults and armored transportation. Explore more about how these distinct custodial methods impact asset security and institutional trust.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between crypto custody and cash custody is crucial for managing asset security and regulatory compliance in banking. Crypto custody involves safeguarding digital assets with private keys and blockchain technology, whereas cash custody pertains to the physical or electronic safeguarding of fiat money. Understanding these distinctions helps banks implement appropriate risk controls and adhere to financial regulations like KYC and AML guidelines. Proper knowledge ensures clients' assets are protected from cyber threats and fraud effectively.
Comparison Table
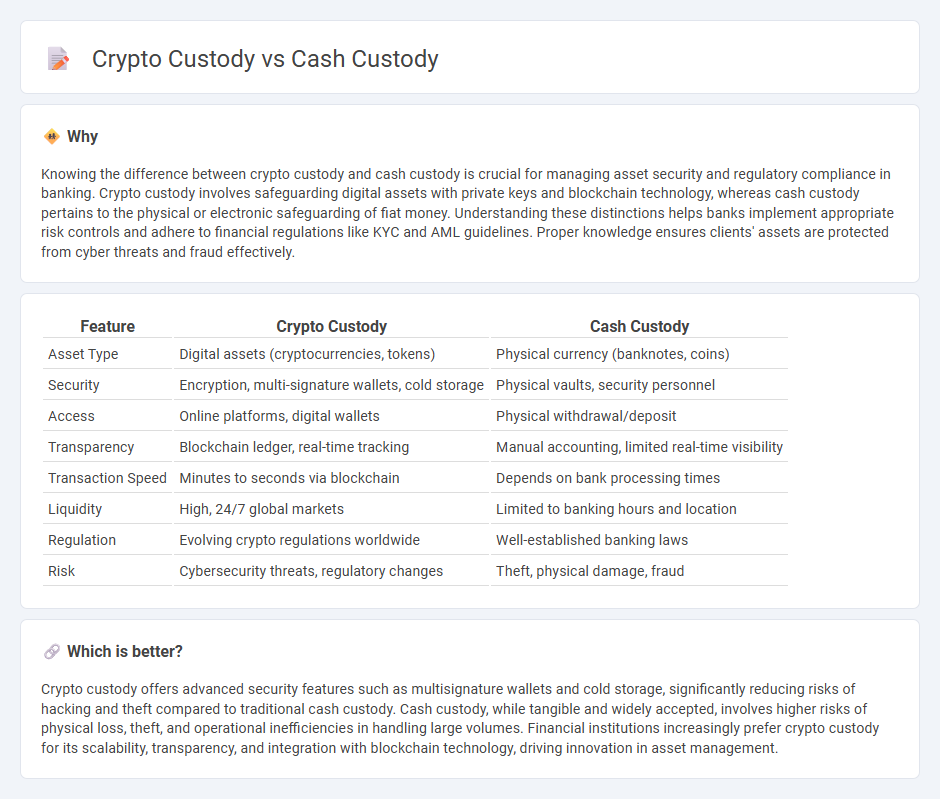
| Feature | Crypto Custody | Cash Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Digital assets (cryptocurrencies, tokens) | Physical currency (banknotes, coins) |
| Security | Encryption, multi-signature wallets, cold storage | Physical vaults, security personnel |
| Access | Online platforms, digital wallets | Physical withdrawal/deposit |
| Transparency | Blockchain ledger, real-time tracking | Manual accounting, limited real-time visibility |
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to seconds via blockchain | Depends on bank processing times |
| Liquidity | High, 24/7 global markets | Limited to banking hours and location |
| Regulation | Evolving crypto regulations worldwide | Well-established banking laws |
| Risk | Cybersecurity threats, regulatory changes | Theft, physical damage, fraud |
Which is better?
Crypto custody offers advanced security features such as multisignature wallets and cold storage, significantly reducing risks of hacking and theft compared to traditional cash custody. Cash custody, while tangible and widely accepted, involves higher risks of physical loss, theft, and operational inefficiencies in handling large volumes. Financial institutions increasingly prefer crypto custody for its scalability, transparency, and integration with blockchain technology, driving innovation in asset management.
Connection
Crypto custody and cash custody both involve safeguarding financial assets, with crypto custody focusing on securing digital currencies through cold storage and multi-signature wallets, while cash custody manages physical or digital fiat currency within banks or vaults. These custodial solutions intersect as financial institutions integrate crypto asset management into traditional banking services, enabling seamless asset conversion and enhanced security protocols. The convergence supports regulatory compliance, risk management, and customer trust across digital and traditional financial ecosystems.
Key Terms
Custodian
Cash custody involves traditional financial institutions acting as custodians, providing secure storage, insurance, and regulatory compliance for physical or electronic money. Crypto custody, managed by specialized custodians, employs advanced cryptographic technologies like multi-signature wallets and cold storage to safeguard digital assets from hacking and theft. Explore the differences and benefits of each custodian to optimize your asset protection strategy.
Private Key
Cash custody involves physical control and secured storage of tangible currency, while crypto custody centers on safeguarding private keys that grant access to digital assets on blockchain networks. Private keys must be stored in highly secure environments like hardware wallets or multi-signature wallets to prevent unauthorized access and potential loss of cryptocurrencies. Explore deeper into private key management techniques and security protocols to ensure optimal crypto asset protection.
Regulation
Cash custody is strictly governed by banking and financial regulations such as the Bank Secrecy Act and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) standards, ensuring depositor protection and fraud prevention. Crypto custody operates within evolving regulatory frameworks like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines and the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversight, emphasizing security, anti-money laundering (AML), and compliance with digital asset laws. Explore the complexities of both systems to understand how regulatory landscapes impact asset security and investor confidence.
Source and External Links
Custody Cash Account Definition - Law Insider - A Custody Cash Account is a segregated account maintained by a custodian for a client, allowing the client to demand withdrawal or for the custodian to manage payments or deliveries of the property held in the account under specific terms and conditions.
Understanding Custody: Bank and Brokerage Asset Safety - Cash in custody accounts is segregated from the bank's assets and held in trust, ensuring protection in case of bank failure, but not FDIC-insured if held in segregated cash accounts.
What is a bank custodian? What services do they provide? - Bank custodians physically hold and safeguard financial assets including cash, providing services like trade settlement, recordkeeping, and investing cash balances as instructed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com