Central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) are government-backed digital assets issued by central banks, designed to provide a secure and regulated alternative to cash. Stablecoins are privately issued digital currencies pegged to assets like fiat money to maintain value stability while enabling faster transactions. Explore the key differences and implications of CBDCs and stablecoins for the future of digital finance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between central bank digital currency (CBDC) and stablecoins is crucial for recognizing their regulatory frameworks, trust levels, and underlying backing. CBDCs are issued and regulated by national governments to ensure monetary stability and financial security, while stablecoins are typically private-sector digital assets pegged to fiat currencies but lack direct government backing. This distinction impacts consumer protection, systemic risk, and the future of digital payments infrastructure. Knowledge of these differences guides informed decisions in banking, investment, and digital currency adoption.
Comparison Table
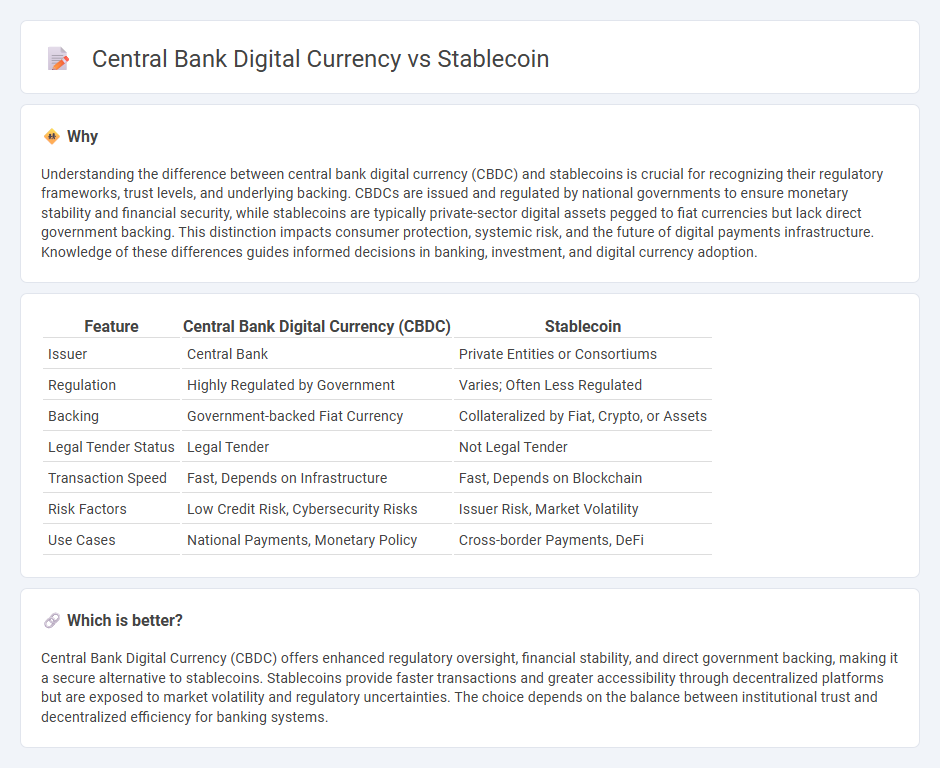
| Feature | Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) | Stablecoin |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Central Bank | Private Entities or Consortiums |
| Regulation | Highly Regulated by Government | Varies; Often Less Regulated |
| Backing | Government-backed Fiat Currency | Collateralized by Fiat, Crypto, or Assets |
| Legal Tender Status | Legal Tender | Not Legal Tender |
| Transaction Speed | Fast, Depends on Infrastructure | Fast, Depends on Blockchain |
| Risk Factors | Low Credit Risk, Cybersecurity Risks | Issuer Risk, Market Volatility |
| Use Cases | National Payments, Monetary Policy | Cross-border Payments, DeFi |
Which is better?
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) offers enhanced regulatory oversight, financial stability, and direct government backing, making it a secure alternative to stablecoins. Stablecoins provide faster transactions and greater accessibility through decentralized platforms but are exposed to market volatility and regulatory uncertainties. The choice depends on the balance between institutional trust and decentralized efficiency for banking systems.
Connection
Central bank digital currency (CBDC) and stablecoins are connected through their shared goal of providing digital forms of money that offer stability and efficiency in transactions. CBDCs are government-backed digital currencies issued by central banks, ensuring trust and regulatory oversight, while stablecoins are typically privately issued but maintain value stability by being pegged to assets like fiat currencies. Both forms aim to enhance payment systems by reducing transaction costs and increasing the speed and security of digital payments in the banking sector.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Stablecoins operate on decentralized blockchain networks, minimizing reliance on central authorities and enhancing transaction transparency. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are issued and regulated by sovereign governments, centralizing control and potentially impacting user privacy. Explore the nuances between stablecoins and CBDCs to understand their implications on decentralization.
Monetary Policy
Stablecoins, typically pegged to assets like the US dollar, aim to provide price stability and facilitate seamless digital transactions without direct influence on monetary policy. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), issued by national banks, serve as digital legal tender that enables governments to implement monetary policy more effectively through direct control of money supply and interest rates. Explore the nuances between stablecoins and CBDCs in shaping future monetary policy frameworks.
Legal Tender
Stablecoins are digital assets pegged to a reserve of fiat currencies or commodities but are not officially recognized as legal tender by governments, which limits their use for everyday transactions. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), issued and regulated by national monetary authorities, have legal tender status, enabling widespread acceptance for payments and debt settlement within the jurisdiction. Explore the legal implications and policy frameworks that shape the adoption and regulation of stablecoins and CBDCs.
Source and External Links
What is a stablecoin? - Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to assets like fiat currencies or gold to maintain a stable price, providing an alternative to volatile cryptocurrencies and enabling use in everyday transactions and blockchain finance services.
What is a stablecoin? - A stablecoin is a digital asset designed to maintain price stability by pegging its value to less volatile assets such as fiat currencies or gold, combining the security of cryptocurrencies with the stability needed for widespread adoption.
Stablecoin - Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies pegged to reference assets like fiat money or commodities aimed at maintaining value stability, though in practice some have failed to maintain their peg or adequate reserves.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com