Digital identity verification leverages biometric data and advanced encryption to enhance security beyond traditional PIN and password methods, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. While PINs and passwords remain common authentication tools, they are increasingly vulnerable to hacking, phishing, and social engineering attacks. Explore how digital identity verification is revolutionizing banking security protocols for safer and more seamless user experiences.
Why it is important
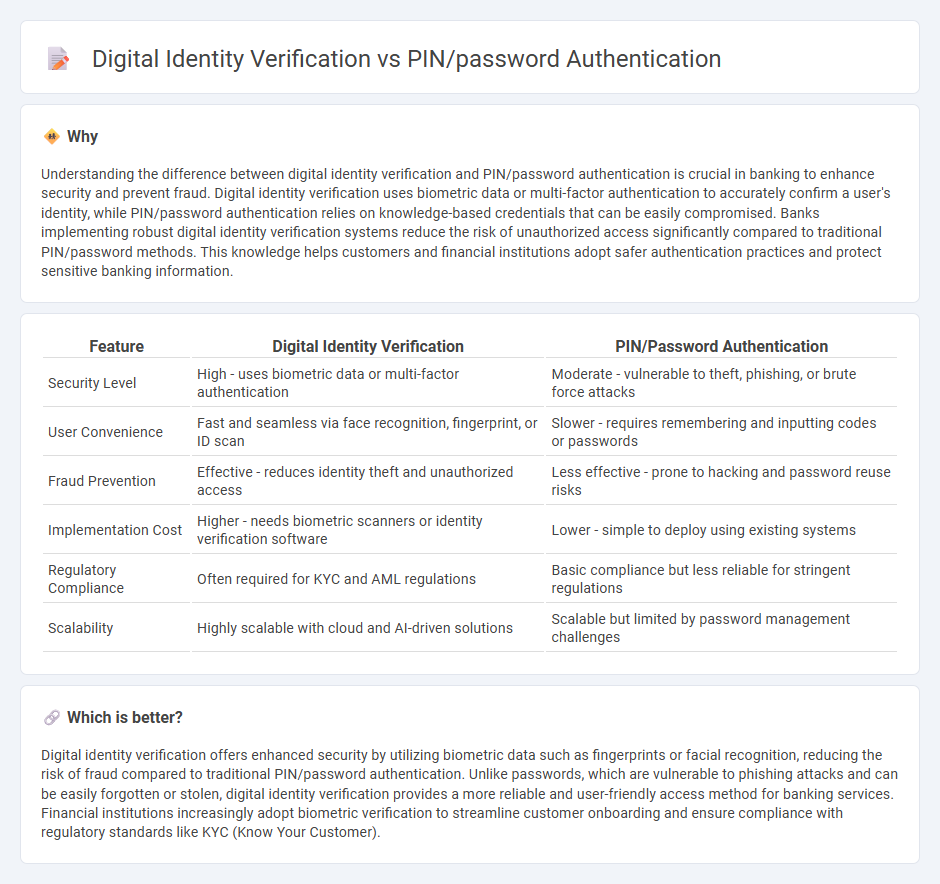
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and PIN/password authentication is crucial in banking to enhance security and prevent fraud. Digital identity verification uses biometric data or multi-factor authentication to accurately confirm a user's identity, while PIN/password authentication relies on knowledge-based credentials that can be easily compromised. Banks implementing robust digital identity verification systems reduce the risk of unauthorized access significantly compared to traditional PIN/password methods. This knowledge helps customers and financial institutions adopt safer authentication practices and protect sensitive banking information.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | PIN/Password Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | High - uses biometric data or multi-factor authentication | Moderate - vulnerable to theft, phishing, or brute force attacks |
| User Convenience | Fast and seamless via face recognition, fingerprint, or ID scan | Slower - requires remembering and inputting codes or passwords |
| Fraud Prevention | Effective - reduces identity theft and unauthorized access | Less effective - prone to hacking and password reuse risks |
| Implementation Cost | Higher - needs biometric scanners or identity verification software | Lower - simple to deploy using existing systems |
| Regulatory Compliance | Often required for KYC and AML regulations | Basic compliance but less reliable for stringent regulations |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cloud and AI-driven solutions | Scalable but limited by password management challenges |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification offers enhanced security by utilizing biometric data such as fingerprints or facial recognition, reducing the risk of fraud compared to traditional PIN/password authentication. Unlike passwords, which are vulnerable to phishing attacks and can be easily forgotten or stolen, digital identity verification provides a more reliable and user-friendly access method for banking services. Financial institutions increasingly adopt biometric verification to streamline customer onboarding and ensure compliance with regulatory standards like KYC (Know Your Customer).
Connection
Digital identity verification enhances banking security by confirming a customer's identity through biometrics or document validation before granting access. PIN and password authentication serve as a secondary layer, protecting accounts by requiring secret codes known only to the user. Together, these methods create a robust multi-factor authentication system that reduces fraud and unauthorized access in online banking.
Key Terms
PIN/password (Knowledge-based Authentication)
PIN/password authentication relies on knowledge-based authentication, requiring users to remember and input secret information for access, making it vulnerable to guessing, phishing, and credential theft. Despite widespread use due to simplicity, this method lacks robust security features such as biometric confirmation or device recognition, often leading to data breaches. Explore how digital identity verification enhances security beyond traditional PIN/password systems for better protection.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication leverages unique physiological traits such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans, providing a higher security level compared to traditional PIN or password methods that are vulnerable to theft or guessing. Digital identity verification systems increasingly integrate biometric data to enhance user verification accuracy and reduce fraud, especially in sectors like banking, healthcare, and government services. Explore the advancements in biometric authentication to understand how it revolutionizes digital identity verification and security protocols.
Know Your Customer (KYC)
PIN/password authentication relies on user-generated credentials that can be susceptible to theft and phishing attacks, posing risks in KYC processes. Digital identity verification employs biometric data, government-issued IDs, and AI-driven analysis to provide higher accuracy and reduce fraud during customer onboarding. Explore advanced digital identity solutions to enhance compliance and security in your KYC operations.
Source and External Links
What is PIN Authentication? - PIN authentication uses a short numeric code (typically 4-8 digits) for quick, local, and device-bound access, offering high phishing resistance and often works as part of multi-factor authentication.
Differences Between Password and PIN - A password is sent to a server for verification, while a PIN is used to unlock a hardware security chip (like TPM) on the local device, which then creates a secure credential for authentication with the server.
PIN Authentication Passkeys - A PIN-based passkey uses public-private key cryptography, with the private key stored locally on a secure hardware element, so a user's unique PIN unlocks access to their device's credentials, protecting against unauthorized use even if the device is compromised.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com