Digital identity verification leverages biometric data and AI algorithms to confirm a user's identity swiftly and securely, reducing fraud risks in banking transactions. Smart card authentication relies on physical cards embedded with encrypted chips, enabling secure access and transaction authorization but can be susceptible to loss or theft. Explore the advantages and limitations of both methods to determine the best fit for modern banking security needs.
Why it is important
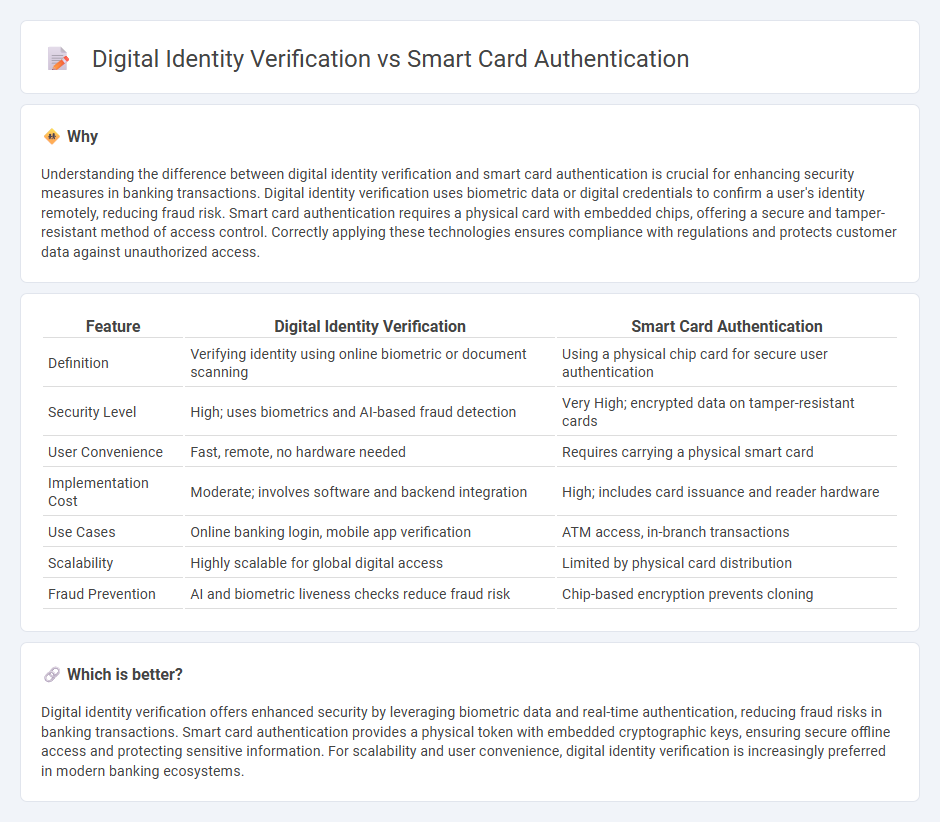
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and smart card authentication is crucial for enhancing security measures in banking transactions. Digital identity verification uses biometric data or digital credentials to confirm a user's identity remotely, reducing fraud risk. Smart card authentication requires a physical card with embedded chips, offering a secure and tamper-resistant method of access control. Correctly applying these technologies ensures compliance with regulations and protects customer data against unauthorized access.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Smart Card Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verifying identity using online biometric or document scanning | Using a physical chip card for secure user authentication |
| Security Level | High; uses biometrics and AI-based fraud detection | Very High; encrypted data on tamper-resistant cards |
| User Convenience | Fast, remote, no hardware needed | Requires carrying a physical smart card |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate; involves software and backend integration | High; includes card issuance and reader hardware |
| Use Cases | Online banking login, mobile app verification | ATM access, in-branch transactions |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for global digital access | Limited by physical card distribution |
| Fraud Prevention | AI and biometric liveness checks reduce fraud risk | Chip-based encryption prevents cloning |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification offers enhanced security by leveraging biometric data and real-time authentication, reducing fraud risks in banking transactions. Smart card authentication provides a physical token with embedded cryptographic keys, ensuring secure offline access and protecting sensitive information. For scalability and user convenience, digital identity verification is increasingly preferred in modern banking ecosystems.
Connection
Digital identity verification enhances banking security by confirming a customer's identity through biometric data or document authentication, which is seamlessly integrated with smart card authentication methods. Smart cards store encrypted digital certificates that interact with digital identity systems to provide multi-factor authentication and prevent fraud. This connection ensures secure transactions and compliance with regulatory standards in financial services.
Key Terms
EMV Chip Authentication
EMV chip authentication uses a secure embedded microprocessor in smart cards to verify transactions, ensuring robust protection against fraud by generating unique cryptographic codes for each interaction. Digital identity verification encompasses a broader range of technologies such as biometrics, document verification, and multi-factor authentication to confirm user identities across online platforms. Explore how EMV chip authentication enhances security in financial transactions and its role within the digital identity verification landscape.
Biometric Verification
Smart card authentication relies on physical cards embedded with secure chips to verify identity, ensuring high security through possession factor and sometimes integrating biometric data such as fingerprints for added protection. Digital identity verification primarily employs biometric verification methods like facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and iris recognition to authenticate users remotely, enhancing user convenience and reducing fraudulent access. Explore detailed insights on biometric verification's role in strengthening both smart card and digital identity authentication systems.
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Smart card authentication leverages embedded microchips to securely store user credentials, providing a robust layer of protection against identity fraud in KYC processes. Digital identity verification employs biometric data, document scanning, and AI-powered algorithms to validate user identity remotely, enhancing scalability and user convenience. Explore the latest advancements in both technologies to optimize your KYC compliance strategy.
Source and External Links
Understanding Smart Card Authentication - 1Kosmos - Smart card authentication uses an embedded chip on the card to verify identity via cryptographic challenges, providing highly secure user verification and reducing fraud risks by using standard protocols like ISO/IEC 7816 and 14443, commonly employed in banking and other sectors.
Chapter 1. Understanding smart card authentication - Red Hat - Smart card authentication in Red Hat Enterprise Linux can be configured to require smart cards exclusively or allow fallback to password, with options to lock the system on card removal, enhancing secure access management in various usage scenarios.
PKI Smart Card Authentication for Enterprise Security - SecureW2 - PKI smart cards strengthen enterprise security by providing strong identity verification, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and integration with protocols like 802.1X for secure network access and phishing prevention through hardware-protected private keys.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com