Composable banking offers modular financial services through APIs, enabling banks to quickly customize and scale solutions. Neo banking operates entirely online, providing streamlined, customer-centric digital banking experiences without physical branches. Discover how these innovative approaches are reshaping the future of banking.
Why it is important
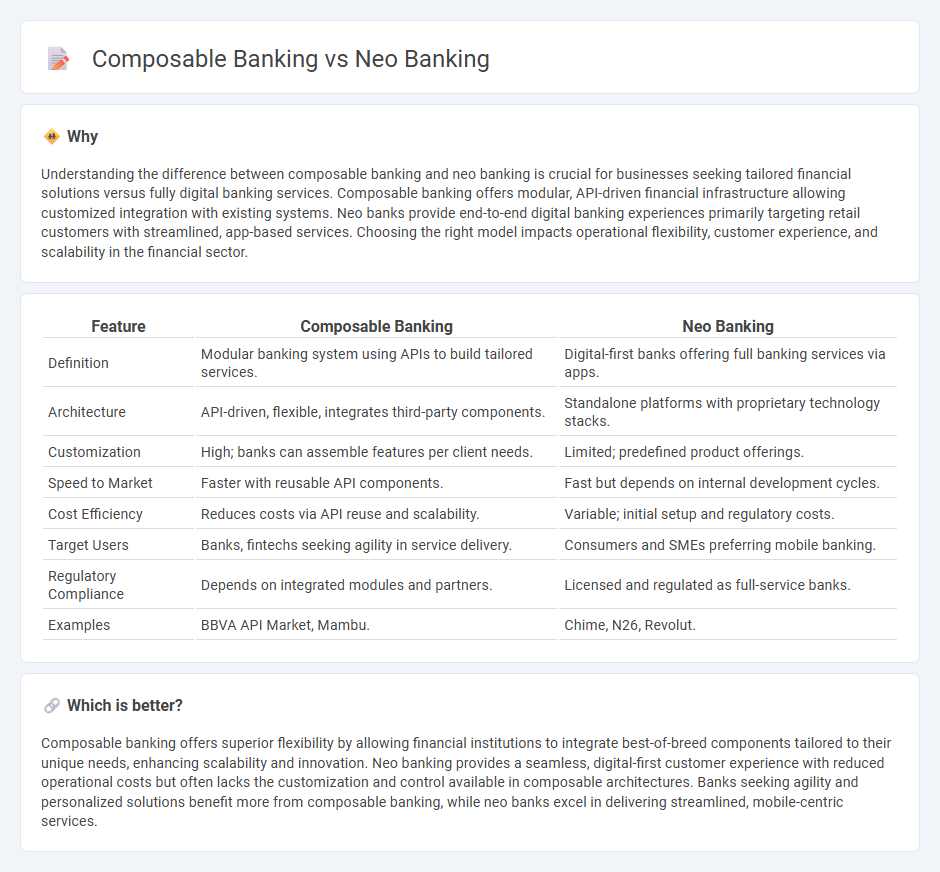
Understanding the difference between composable banking and neo banking is crucial for businesses seeking tailored financial solutions versus fully digital banking services. Composable banking offers modular, API-driven financial infrastructure allowing customized integration with existing systems. Neo banks provide end-to-end digital banking experiences primarily targeting retail customers with streamlined, app-based services. Choosing the right model impacts operational flexibility, customer experience, and scalability in the financial sector.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Composable Banking | Neo Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking system using APIs to build tailored services. | Digital-first banks offering full banking services via apps. |
| Architecture | API-driven, flexible, integrates third-party components. | Standalone platforms with proprietary technology stacks. |
| Customization | High; banks can assemble features per client needs. | Limited; predefined product offerings. |
| Speed to Market | Faster with reusable API components. | Fast but depends on internal development cycles. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces costs via API reuse and scalability. | Variable; initial setup and regulatory costs. |
| Target Users | Banks, fintechs seeking agility in service delivery. | Consumers and SMEs preferring mobile banking. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Depends on integrated modules and partners. | Licensed and regulated as full-service banks. |
| Examples | BBVA API Market, Mambu. | Chime, N26, Revolut. |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers superior flexibility by allowing financial institutions to integrate best-of-breed components tailored to their unique needs, enhancing scalability and innovation. Neo banking provides a seamless, digital-first customer experience with reduced operational costs but often lacks the customization and control available in composable architectures. Banks seeking agility and personalized solutions benefit more from composable banking, while neo banks excel in delivering streamlined, mobile-centric services.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs that enable Neo banking platforms to rapidly integrate financial services, customize user experiences, and scale efficiently. Neo banks utilize composable banking frameworks to assemble best-in-class fintech components, reducing time-to-market and enhancing agility in product innovation. This synergy drives personalized, seamless digital banking solutions tailored to evolving customer demands.
Key Terms
Digital-Only Platform
Neo banking operates as a fully digital-only platform offering streamlined financial services through intuitive mobile apps without physical branches. Composable banking leverages modular architecture, enabling banks to integrate best-of-breed components to customize and scale digital platforms swiftly. Explore how these evolving digital-only platforms transform customer experiences and operational agility.
Modular Architecture
Modular architecture in neo banking allows for agile, scalable financial services through discrete, interchangeable components, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. Composable banking extends this approach by enabling full customization of banking solutions via APIs, allowing institutions to assemble targeted, flexible products that respond quickly to market demands. Explore the unique benefits and use cases of modular versus composable banking to optimize your digital transformation strategy.
API Integration
Neo banking leverages API integration to offer seamless, user-centric digital financial services without traditional branch infrastructure. Composable banking builds on this by using modular, API-driven components to customize and rapidly scale banking solutions tailored to specific business needs. Explore the advantages of API integration in transforming modern banking strategies.
Source and External Links
Neo-Bank | Mendix Glossary - Provides an overview of neo-banks, also known as challenger banks, which are fintech organizations offering banking services online without physical locations.
Neobanks 101 | Stripe - Offers insights into how neobanks work, their digital interface, and how they generate revenue through transaction fees and other services.
What is a Neobank? | Statrys Blog - Explains what neobanks are, how they operate by partnering with traditional banks, and their advantages such as lower fees and specialized financial products.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com