Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledger technology to enable faster, transparent, and cross-border transactions with reduced intermediaries. ACH, or Automated Clearing House, processes electronic payments primarily within domestic networks, often involving batch processing with settlement delays. Explore the comparison between blockchain remittance and ACH to understand their advantages and applications in modern banking.
Why it is important
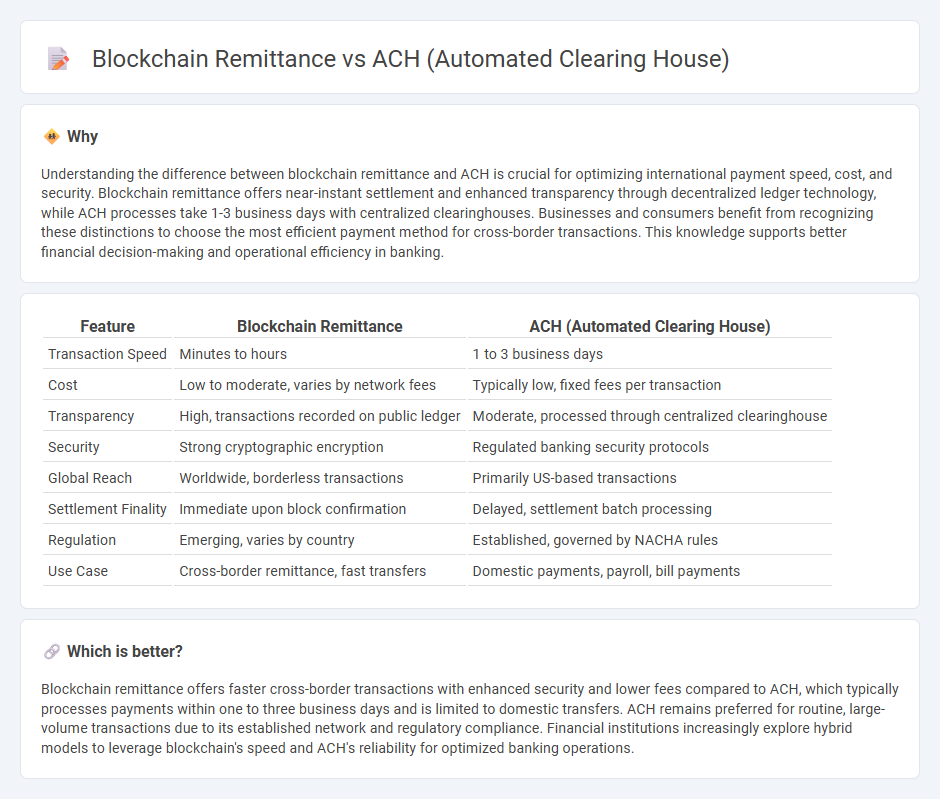
Understanding the difference between blockchain remittance and ACH is crucial for optimizing international payment speed, cost, and security. Blockchain remittance offers near-instant settlement and enhanced transparency through decentralized ledger technology, while ACH processes take 1-3 business days with centralized clearinghouses. Businesses and consumers benefit from recognizing these distinctions to choose the most efficient payment method for cross-border transactions. This knowledge supports better financial decision-making and operational efficiency in banking.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Remittance | ACH (Automated Clearing House) |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to hours | 1 to 3 business days |
| Cost | Low to moderate, varies by network fees | Typically low, fixed fees per transaction |
| Transparency | High, transactions recorded on public ledger | Moderate, processed through centralized clearinghouse |
| Security | Strong cryptographic encryption | Regulated banking security protocols |
| Global Reach | Worldwide, borderless transactions | Primarily US-based transactions |
| Settlement Finality | Immediate upon block confirmation | Delayed, settlement batch processing |
| Regulation | Emerging, varies by country | Established, governed by NACHA rules |
| Use Case | Cross-border remittance, fast transfers | Domestic payments, payroll, bill payments |
Which is better?
Blockchain remittance offers faster cross-border transactions with enhanced security and lower fees compared to ACH, which typically processes payments within one to three business days and is limited to domestic transfers. ACH remains preferred for routine, large-volume transactions due to its established network and regulatory compliance. Financial institutions increasingly explore hybrid models to leverage blockchain's speed and ACH's reliability for optimized banking operations.
Connection
Blockchain remittance innovates cross-border payments by using a decentralized ledger to enable faster, secure, and transparent transactions, reducing reliance on traditional financial intermediaries. ACH systems facilitate electronic funds transfers in the banking sector, primarily for domestic transactions, by batch-processing payments through a centralized network. Integration of blockchain technology with ACH could enhance the efficiency and security of remittance processes, streamlining settlement times and lowering operational costs for banks and customers alike.
Key Terms
Settlement Time
ACH transactions typically settle within 1-2 business days, leveraging batch processing through centralized banking systems. Blockchain remittances offer near real-time settlement by validating and recording transactions on a decentralized ledger, often within minutes. Explore the advantages of each method to determine the best solution for your remittance needs.
Intermediary Involvement
ACH transfers rely heavily on financial intermediaries like banks and clearinghouses to process and settle payments, which can introduce delays and fees. Blockchain remittance operates on a decentralized network that reduces or eliminates the need for intermediaries, enabling faster and often lower-cost cross-border transactions. Explore the advantages and challenges of both systems to better understand their impact on global remittance.
Transaction Transparency
ACH transactions process electronically through regulated banks, offering standard transparency with access to transaction details via bank statements and customer service. Blockchain remittance provides enhanced transaction transparency by recording each transfer on a decentralized, immutable ledger visible to all network participants, enabling real-time tracking and auditability. Discover how these transparency features impact security and efficiency in cross-border payments.
Source and External Links
ACH Payments 101 - ACH stands for Automated Clearing House, a U.S. financial network enabling banks and credit unions to electronically transfer money between accounts without paper checks or wire transfers, now offering same-day, next-day, or two-day processing options.
What is an ACH transaction? - An ACH transaction is an electronic money transfer between banks and credit unions, commonly used for direct deposits, monthly bill payments, and online payments, though processing times can vary and transactions may bounce if funds are insufficient.
Automated Clearing House - The ACH system is primarily used by federal agencies for electronic funds transfer, with regulations and operating rules defining the responsibilities of all parties involved and Nacha (a non-government organization) developing the industry rules financial institutions follow.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com