Instant payments provide real-time fund transfers, enabling users to send and receive money within seconds, contrasting with Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) systems that typically process transactions in batch cycles, often resulting in delays of several hours to days. Instant payments leverage continuously available infrastructure and immediate confirmation, enhancing user experience and operational efficiency for both retail and corporate banking sectors. Explore how adopting instant payments can revolutionize your banking operations and customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between instant payments and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is crucial for managing transaction speed, with instant payments providing real-time fund transfers while EFTs often process within hours to days. This knowledge helps individuals and businesses optimize cash flow and choose the appropriate payment method for urgent or routine transfers. Banks and financial institutions rely on this distinction to enhance customer service and operational efficiency. Instant payments typically involve technologies like RTP (Real-Time Payments) networks, whereas EFT includes methods such as ACH (Automated Clearing House) transfers.
Comparison Table
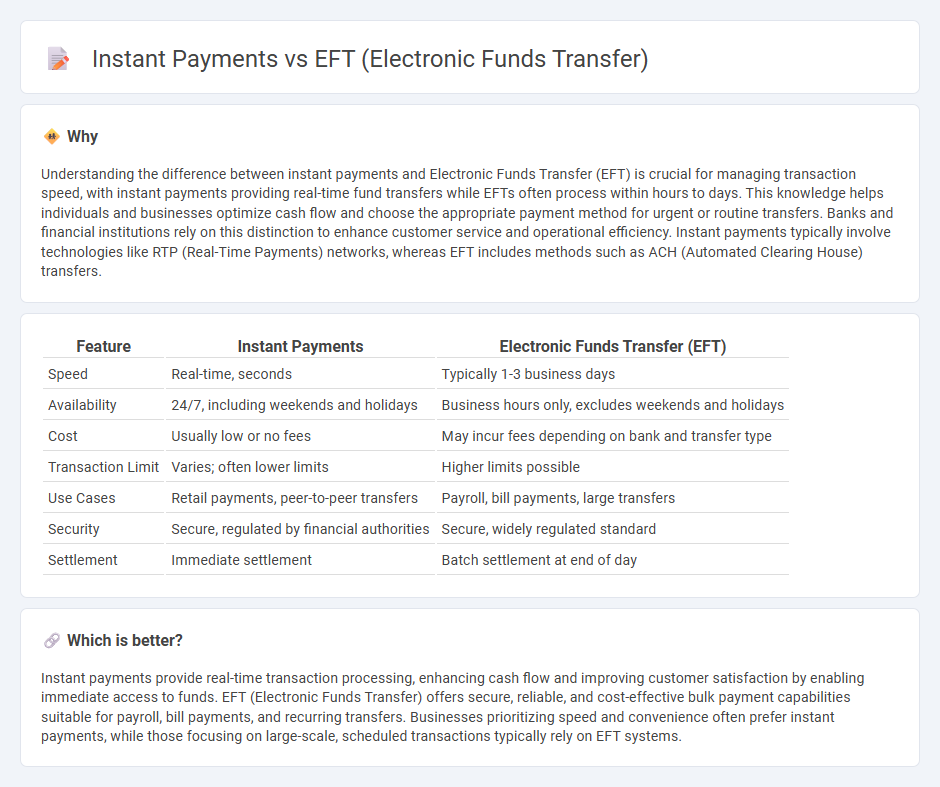
| Feature | Instant Payments | Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Real-time, seconds | Typically 1-3 business days |
| Availability | 24/7, including weekends and holidays | Business hours only, excludes weekends and holidays |
| Cost | Usually low or no fees | May incur fees depending on bank and transfer type |
| Transaction Limit | Varies; often lower limits | Higher limits possible |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, peer-to-peer transfers | Payroll, bill payments, large transfers |
| Security | Secure, regulated by financial authorities | Secure, widely regulated standard |
| Settlement | Immediate settlement | Batch settlement at end of day |
Which is better?
Instant payments provide real-time transaction processing, enhancing cash flow and improving customer satisfaction by enabling immediate access to funds. EFT (Electronic Funds Transfer) offers secure, reliable, and cost-effective bulk payment capabilities suitable for payroll, bill payments, and recurring transfers. Businesses prioritizing speed and convenience often prefer instant payments, while those focusing on large-scale, scheduled transactions typically rely on EFT systems.
Connection
Instant payments and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) are interconnected as both facilitate the rapid movement of funds between bank accounts through electronic systems. Instant payments enable real-time settlement of transactions, while traditional EFT processes may involve batch processing with delays ranging from minutes to days. The integration of instant payment technologies into EFT infrastructure enhances the speed, efficiency, and accessibility of banking transactions globally.
Key Terms
Settlement Speed
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) systems typically process transactions within one to three business days, reflecting a conventional settlement speed reliant on batch processing and bank working hours. Instant payments, leveraging real-time processing technology, complete settlements within seconds, enabling immediate fund availability and enhancing liquidity management for businesses and consumers. Explore the innovations driving faster payment settlements and their impact on financial ecosystems.
Clearing Process
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) typically involves a batch clearing process where transactions are grouped and settled at specific intervals, often resulting in delays of several hours to days. Instant payments utilize real-time clearing and settlement systems, enabling immediate fund availability and confirmation within seconds. Explore how evolving clearing technologies impact transaction speed and security in financial services.
Transaction Finality
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) transactions typically settle within one to three business days, allowing for reversals or disputes until finality is reached, whereas instant payments confirm transaction finality immediately, enabling irrevocable transfer of funds within seconds. The key advantage of instant payments lies in their real-time settlement, which reduces counterparty risk and enhances liquidity management compared to traditional EFT systems. Explore the differences in transaction finality and operational benefits to optimize your payment processing strategy.
Source and External Links
What is Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)? - EBANX - Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is a digital money movement from one bank account to another without paper documents, popular for its speed and simplicity in digital transactions.
What is Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)? - Modern Treasury - EFT is the digital transfer of money between bank accounts, reducing manual processing and enabling fast fund clearing typically within days.
EFT Payments Explained: A Business Guide On How They Work - EFTs include ACH, wire transfers, and real-time payments that offer businesses secure, efficient, and rapid electronic money transfers between banks, enhancing cash flow and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com