Income streaming in banking involves generating steady revenue through consistent interest payments and fees from loan portfolios, enhancing predictable cash flows. Securitization income stems from the process of pooling assets like mortgages and selling them as securities, creating liquidity and diversifying revenue streams. Explore further to understand how these income models impact financial strategies and risk management in banking.
Why it is important
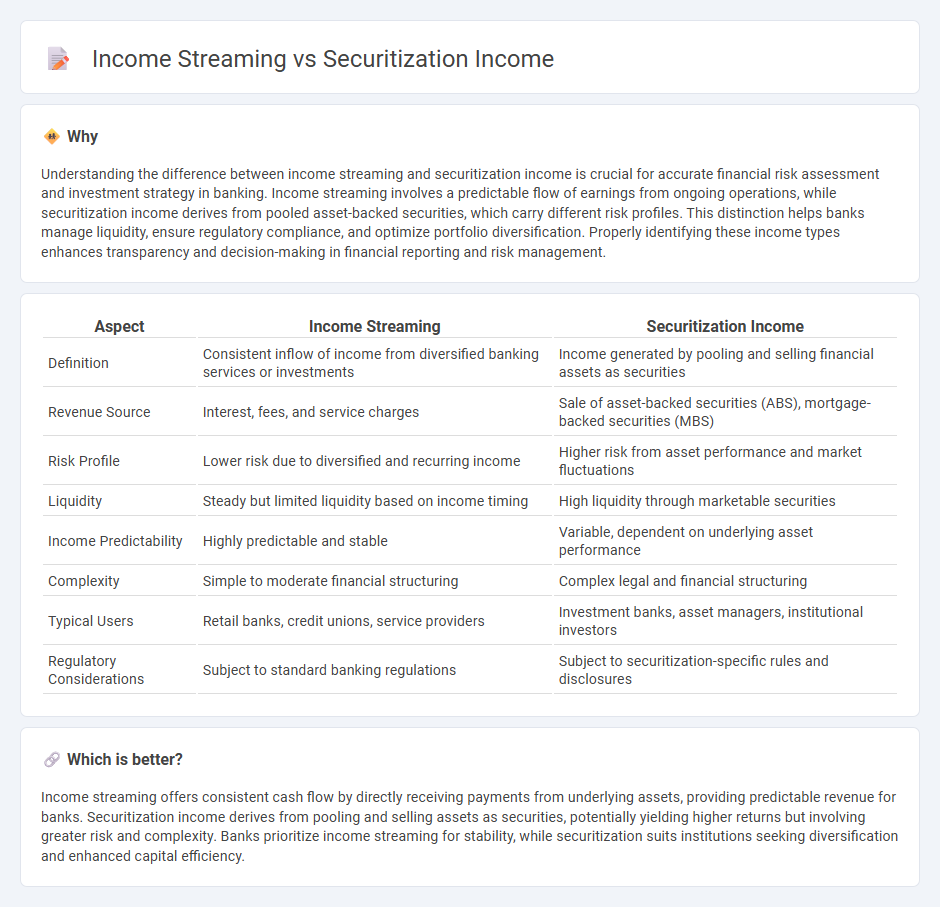
Understanding the difference between income streaming and securitization income is crucial for accurate financial risk assessment and investment strategy in banking. Income streaming involves a predictable flow of earnings from ongoing operations, while securitization income derives from pooled asset-backed securities, which carry different risk profiles. This distinction helps banks manage liquidity, ensure regulatory compliance, and optimize portfolio diversification. Properly identifying these income types enhances transparency and decision-making in financial reporting and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Income Streaming | Securitization Income |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistent inflow of income from diversified banking services or investments | Income generated by pooling and selling financial assets as securities |
| Revenue Source | Interest, fees, and service charges | Sale of asset-backed securities (ABS), mortgage-backed securities (MBS) |
| Risk Profile | Lower risk due to diversified and recurring income | Higher risk from asset performance and market fluctuations |
| Liquidity | Steady but limited liquidity based on income timing | High liquidity through marketable securities |
| Income Predictability | Highly predictable and stable | Variable, dependent on underlying asset performance |
| Complexity | Simple to moderate financial structuring | Complex legal and financial structuring |
| Typical Users | Retail banks, credit unions, service providers | Investment banks, asset managers, institutional investors |
| Regulatory Considerations | Subject to standard banking regulations | Subject to securitization-specific rules and disclosures |
Which is better?
Income streaming offers consistent cash flow by directly receiving payments from underlying assets, providing predictable revenue for banks. Securitization income derives from pooling and selling assets as securities, potentially yielding higher returns but involving greater risk and complexity. Banks prioritize income streaming for stability, while securitization suits institutions seeking diversification and enhanced capital efficiency.
Connection
Income streaming and securitization income are connected through their role in transforming future cash flows into immediate revenue for banks. Income streaming involves allocating predictable payment streams from loans or leases, which are then pooled and structured into securities during securitization. This process enables banks to generate upfront income by selling these asset-backed securities to investors while managing risk and improving liquidity.
Key Terms
Asset-backed securities (ABS)
Securitization income from Asset-Backed Securities (ABS) derives from pooling financial assets like loans or receivables and issuing new securities backed by these assets' cash flows. Income streaming, in contrast, refers to the structured distribution of payment streams to investors, prioritizing specific tranches with varying risk and return profiles. Explore our detailed guide to understand how ABS structures optimize income generation and risk allocation.
Interest income
Securitization income primarily derives from the interest payments on pooled financial assets, such as loans or mortgages, which are transformed into tradable securities. Income streaming, on the other hand, refers to the systematic distribution of interest income from these assets to investors based on predefined schedules or structures. Explore the detailed differences to optimize your investment strategy in fixed-income markets.
Cash flow tranche
Securitization income is derived from pooling financial assets and issuing tranches backed by cash flows, while income streaming focuses on directing those cash flows directly to investors based on predefined priorities. The cash flow tranche structure segments payments to prioritize return and risk exposure, ensuring predictable income streams aligned with investor risk appetite. Explore the intricacies of cash flow tranches to optimize your investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Back to basics: What Is Securitization? - Securitization income is generated from the cash flows of pooled assets (like loans), and the return (principal and interest) is distributed to investors according to the risk level of their tranches, with junior tranches bearing most of the risk but also offering higher potential returns.
Securitization - Through securitization, investors can potentially earn higher income by investing in specifically structured asset pools--such as mortgages or auto loans--that may offer favorable risk-adjusted returns and diversify their fixed income sources.
Understanding Securitized Products - Securitization income comes from the trust that holds the pooled loans, which issues bonds to investors; this system allows originators to offload loan exposure and investors to access new income streams from diversified loan pools.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com