Composable banking offers modular financial services by integrating APIs, enabling banks to customize and rapidly innovate their offerings. Cloud banking leverages cloud infrastructure to provide scalable, secure, and flexible banking solutions with reduced operational costs. Explore the differences and benefits of composable and cloud banking to transform your financial services strategy.
Why it is important
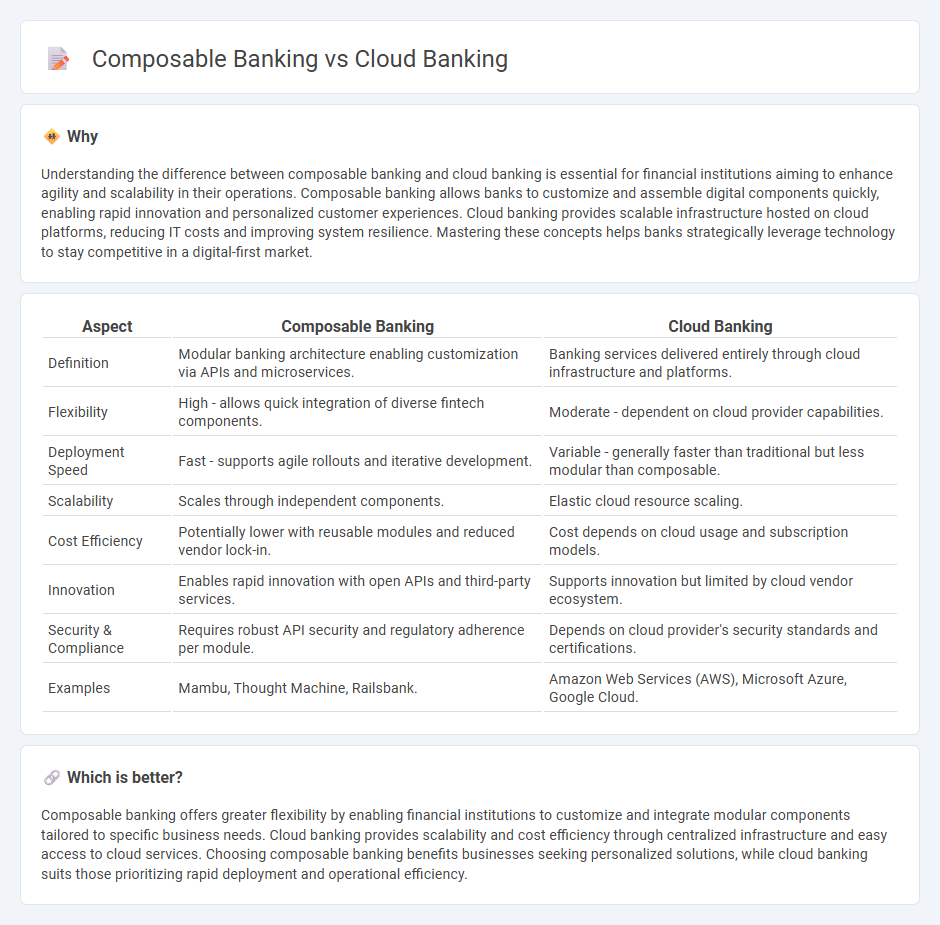
Understanding the difference between composable banking and cloud banking is essential for financial institutions aiming to enhance agility and scalability in their operations. Composable banking allows banks to customize and assemble digital components quickly, enabling rapid innovation and personalized customer experiences. Cloud banking provides scalable infrastructure hosted on cloud platforms, reducing IT costs and improving system resilience. Mastering these concepts helps banks strategically leverage technology to stay competitive in a digital-first market.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Composable Banking | Cloud Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modular banking architecture enabling customization via APIs and microservices. | Banking services delivered entirely through cloud infrastructure and platforms. |
| Flexibility | High - allows quick integration of diverse fintech components. | Moderate - dependent on cloud provider capabilities. |
| Deployment Speed | Fast - supports agile rollouts and iterative development. | Variable - generally faster than traditional but less modular than composable. |
| Scalability | Scales through independent components. | Elastic cloud resource scaling. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially lower with reusable modules and reduced vendor lock-in. | Cost depends on cloud usage and subscription models. |
| Innovation | Enables rapid innovation with open APIs and third-party services. | Supports innovation but limited by cloud vendor ecosystem. |
| Security & Compliance | Requires robust API security and regulatory adherence per module. | Depends on cloud provider's security standards and certifications. |
| Examples | Mambu, Thought Machine, Railsbank. | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud. |
Which is better?
Composable banking offers greater flexibility by enabling financial institutions to customize and integrate modular components tailored to specific business needs. Cloud banking provides scalability and cost efficiency through centralized infrastructure and easy access to cloud services. Choosing composable banking benefits businesses seeking personalized solutions, while cloud banking suits those prioritizing rapid deployment and operational efficiency.
Connection
Composable banking leverages modular APIs to enable seamless integration of cloud-native services, enhancing scalability and flexibility. Cloud banking provides the infrastructure and storage solutions that support real-time data processing and deployment of composable banking components. Together, they drive innovation by allowing financial institutions to rapidly develop and customize banking products in a secure, agile cloud environment.
Key Terms
Scalability
Cloud banking offers scalability by leveraging virtualized resources and elastic infrastructure to dynamically adjust computing power and storage. Composable banking enhances scalability through modular, API-driven components that enable rapid customization and flexible integration of services. Discover how each approach impacts your banking technology strategy for optimal growth.
Modular Architecture
Cloud banking leverages scalable cloud infrastructure to deliver flexible financial services with rapid deployment and reduced operational costs. Composable banking emphasizes modular architecture, allowing financial institutions to assemble and customize banking capabilities from interchangeable components that enhance agility and innovation. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of modular architecture in modern banking to transform your financial technology framework.
Integration
Cloud banking leverages cloud computing to deliver scalable financial services with flexible infrastructure and rapid deployment, emphasizing native cloud integration for seamless data flow and real-time analytics. Composable banking, on the other hand, uses modular, API-driven components to enable highly customizable and adaptable financial platforms, focusing on integrating best-of-breed services through open APIs to create tailored banking experiences. Explore how these integration strategies transform modern banking by enhancing agility, innovation, and customer-centric solutions.
Source and External Links
What is cloud banking? | IBM - Cloud banking refers to the on-demand delivery of banking services by financial institutions over the internet, leveraging cloud computing technology for remote data storage, application hosting, and management of banking functions.
Cloud Banking: A Comprehensive Guide to Selection, Pros & Cons ... - Cloud banking enables banks to access flexible, scalable computing resources on demand, improving operational efficiency, customer experience, and reducing costs by migrating core banking services, payments, analytics, and compliance to cloud platforms using AI, machine learning, and automation.
A Complete Guide to Cloud Banking - Crassula.io - Cloud banking platforms operate via major cloud providers (e.g., Microsoft Azure), offering models such as SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and BPaaS that support banking services remotely, allowing rapid scalability, flexibility, and eliminating the need for banks to maintain their own IT infrastructure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com