Behavioral biometrics analyzes patterns in user activity such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and device handling to verify identity, offering continuous and passive authentication. Fingerprint recognition relies on unique physical patterns of a user's fingerprint, providing quick and direct access control but often requiring physical contact. Explore the differences between these two biometric methods to understand which technology best enhances banking security.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between behavioral biometrics and fingerprint recognition is vital in banking to enhance security measures by combining physiological and behavioral data for identity verification. Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns like typing rhythm and mouse movements, detecting anomalies that indicate fraud even if fingerprints are compromised. Fingerprint recognition relies on physical characteristics that are static but can be spoofed or stolen, emphasizing the need for multi-factor authentication. This knowledge helps banks deploy layered security frameworks, reducing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive financial information effectively.
Comparison Table
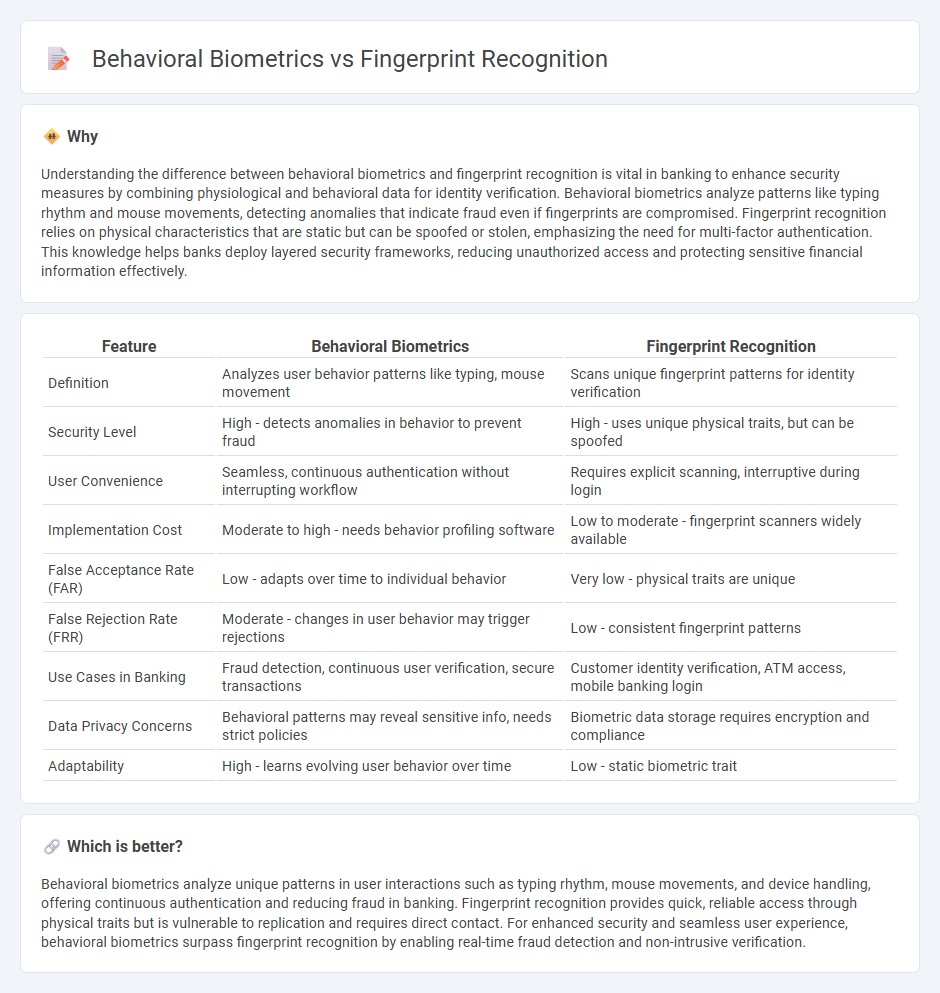
| Feature | Behavioral Biometrics | Fingerprint Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes user behavior patterns like typing, mouse movement | Scans unique fingerprint patterns for identity verification |
| Security Level | High - detects anomalies in behavior to prevent fraud | High - uses unique physical traits, but can be spoofed |
| User Convenience | Seamless, continuous authentication without interrupting workflow | Requires explicit scanning, interruptive during login |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate to high - needs behavior profiling software | Low to moderate - fingerprint scanners widely available |
| False Acceptance Rate (FAR) | Low - adapts over time to individual behavior | Very low - physical traits are unique |
| False Rejection Rate (FRR) | Moderate - changes in user behavior may trigger rejections | Low - consistent fingerprint patterns |
| Use Cases in Banking | Fraud detection, continuous user verification, secure transactions | Customer identity verification, ATM access, mobile banking login |
| Data Privacy Concerns | Behavioral patterns may reveal sensitive info, needs strict policies | Biometric data storage requires encryption and compliance |
| Adaptability | High - learns evolving user behavior over time | Low - static biometric trait |
Which is better?
Behavioral biometrics analyze unique patterns in user interactions such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and device handling, offering continuous authentication and reducing fraud in banking. Fingerprint recognition provides quick, reliable access through physical traits but is vulnerable to replication and requires direct contact. For enhanced security and seamless user experience, behavioral biometrics surpass fingerprint recognition by enabling real-time fraud detection and non-intrusive verification.
Connection
Behavioral biometrics analyze unique patterns in user interactions such as typing speed and mouse movements to enhance fraud detection in banking. Fingerprint recognition provides a physical biometric layer verifying user identity through unique fingerprint patterns. Integrating both methods strengthens multi-factor authentication, reducing unauthorized access and improving overall security in banking systems.
Key Terms
Authentication
Fingerprint recognition offers precise authentication by analyzing unique dermatoglyphic patterns, making it highly reliable for identity verification in security systems. Behavioral biometrics enhances authentication by monitoring dynamic user actions such as typing rhythm, gait, and mouse movements, providing continuous and passive verification to detect potential fraud. Explore in-depth comparisons and benefits to determine the best authentication method suited for your security needs.
Liveness detection
Fingerprint recognition relies on analyzing unique ridge patterns to verify identity, often enhanced by Liveness detection techniques such as pulse or sweat detection to prevent spoofing. Behavioral biometrics assess patterns like typing rhythm, gait, or touchscreen interactions, using continuous Liveness detection to ensure real-time authenticity. Explore further to understand how these technologies safeguard security through advanced Liveness detection.
User behavior analysis
Fingerprint recognition relies on unique physiological patterns, offering high accuracy for user identification but limited adaptability to changes in behavior. Behavioral biometrics analyze patterns like typing rhythm, mouse movement, and touchscreen interaction, providing continuous authentication and detecting anomalies in user behavior. Explore detailed insights into how behavioral biometrics enhance security beyond fingerprint recognition.
Source and External Links
Fingerprint Technology - Innovatrics - How it Works - Fingerprint recognition verifies identity by comparing captured fingerprint images with stored biometric templates using pattern-matching algorithms based on unique ridge patterns and minutiae points.
Fingerprint Biometrics: Definition & How Secure It Is - Fingerprint biometrics uses scanners like optical, capacitive, ultrasound, or thermal types to capture fingerprint images and stores mathematical representations for secure authentication without saving the actual fingerprint image.
Fingerprint technology - Exploring the advancements - The technology centers on analyzing ridge patterns and minutiae points to create biometric templates that are classified, stored, and matched with captured fingerprints via algorithmic pattern matching for identification or verification.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com