Credit builder cards are designed specifically to help individuals with limited or poor credit history improve their credit score through responsible usage and timely payments. Secured credit cards require a cash deposit as collateral, which serves as the credit limit and reduces lender risk, making them accessible to those with no or damaged credit. Explore the key differences, benefits, and application criteria to determine which card suits your financial goals best.
Why it is important
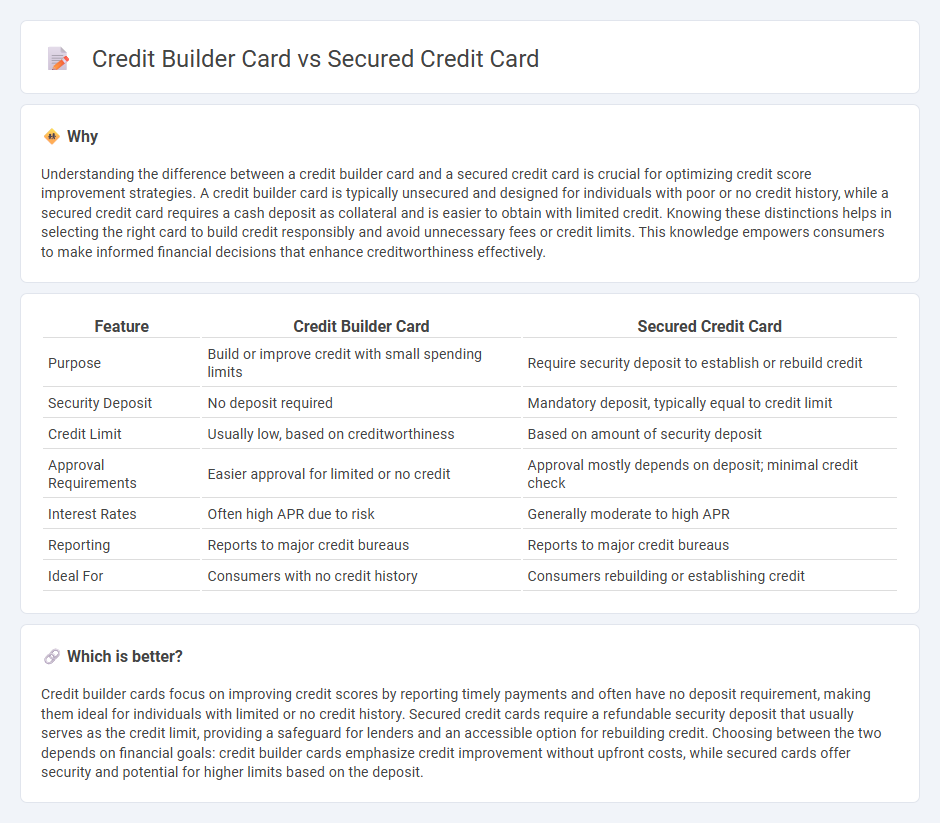
Understanding the difference between a credit builder card and a secured credit card is crucial for optimizing credit score improvement strategies. A credit builder card is typically unsecured and designed for individuals with poor or no credit history, while a secured credit card requires a cash deposit as collateral and is easier to obtain with limited credit. Knowing these distinctions helps in selecting the right card to build credit responsibly and avoid unnecessary fees or credit limits. This knowledge empowers consumers to make informed financial decisions that enhance creditworthiness effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Credit Builder Card | Secured Credit Card |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Build or improve credit with small spending limits | Require security deposit to establish or rebuild credit |
| Security Deposit | No deposit required | Mandatory deposit, typically equal to credit limit |
| Credit Limit | Usually low, based on creditworthiness | Based on amount of security deposit |
| Approval Requirements | Easier approval for limited or no credit | Approval mostly depends on deposit; minimal credit check |
| Interest Rates | Often high APR due to risk | Generally moderate to high APR |
| Reporting | Reports to major credit bureaus | Reports to major credit bureaus |
| Ideal For | Consumers with no credit history | Consumers rebuilding or establishing credit |
Which is better?
Credit builder cards focus on improving credit scores by reporting timely payments and often have no deposit requirement, making them ideal for individuals with limited or no credit history. Secured credit cards require a refundable security deposit that usually serves as the credit limit, providing a safeguard for lenders and an accessible option for rebuilding credit. Choosing between the two depends on financial goals: credit builder cards emphasize credit improvement without upfront costs, while secured cards offer security and potential for higher limits based on the deposit.
Connection
Both credit builder cards and secured credit cards aim to help individuals establish or improve their credit history by reporting payment activity to credit bureaus. Secured credit cards require a cash deposit as collateral, which often serves as the credit limit, while credit builder cards may not always require a deposit but focus on encouraging responsible credit use. Both products play a critical role in building credit scores, especially for those with limited or poor credit backgrounds.
Key Terms
Collateral
Secured credit cards require a cash deposit as collateral, which typically equals the credit limit, reducing risk for issuers and aiding users with poor or no credit history to build or rebuild credit. Credit builder cards may not always mandate collateral but often come with higher interest rates and lower limits, designed primarily to improve credit scores without upfront deposits. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which card best supports your financial growth and credit goals.
Credit Limit
Secured credit cards typically require a refundable security deposit equal to the credit limit, ensuring a fixed spending cap for users, while credit builder cards may offer higher or adjustable limits without large upfront deposits by relying on monthly payments and creditworthiness. The credit limit on secured cards directly correlates with the deposit amount, providing predictable credit availability, whereas credit builder cards look to nurture credit scores through responsible use and on-time payments. Explore detailed comparisons to find which card type best aligns with your credit-building goals.
Credit Reporting
Secured credit cards and credit builder cards both report to major credit bureaus, helping establish or improve credit scores by reflecting responsible payment behavior. Secured credit cards often require a cash deposit as collateral, directly influencing credit limits and reporting, while credit builder cards usually have no deposit but may have higher interest rates. Discover how each option can strategically impact your credit history and boost financial credibility.
Source and External Links
What Is a Secured Credit Card and Does It Build Credit? - A secured credit card requires a cash deposit equal to the credit limit, which acts as collateral, and helps build or improve credit history by reporting payment activity to credit bureaus, making it suitable for people with no or poor credit.
What Is a Secured Credit Card? - A secured credit card is opened with a refundable security deposit that typically equals or is less than the credit limit, functioning like a credit card while using the deposit as collateral and helping users build credit when payments are made on time.
Best Secured Credit Cards for July 2025 - Secured credit cards require a refundable security deposit to establish a credit line and are designed to help individuals build or rebuild credit, with options varying by deposit amounts, rewards, and credit limit potential.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com