Instant payments enable real-time transfer of funds between bank accounts within seconds, supporting retail and consumer transactions 24/7 with immediate confirmation. RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement) processes high-value interbank transfers individually and irrevocably, settling transactions in real time but primarily during business hours to manage liquidity and reduce settlement risk. Discover the key differences and benefits of instant payments and RTGS to optimize your banking operations and financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between instant payments and RTGS is crucial for optimizing transaction speed and cost efficiency in banking. Instant payments provide immediate fund transfers 24/7, ideal for low-value transactions and consumer convenience. RTGS processes high-value, time-critical payments individually with final settlement, ensuring security and liquidity management. Knowing these distinctions helps banks and customers choose the appropriate payment method to meet specific transactional needs and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
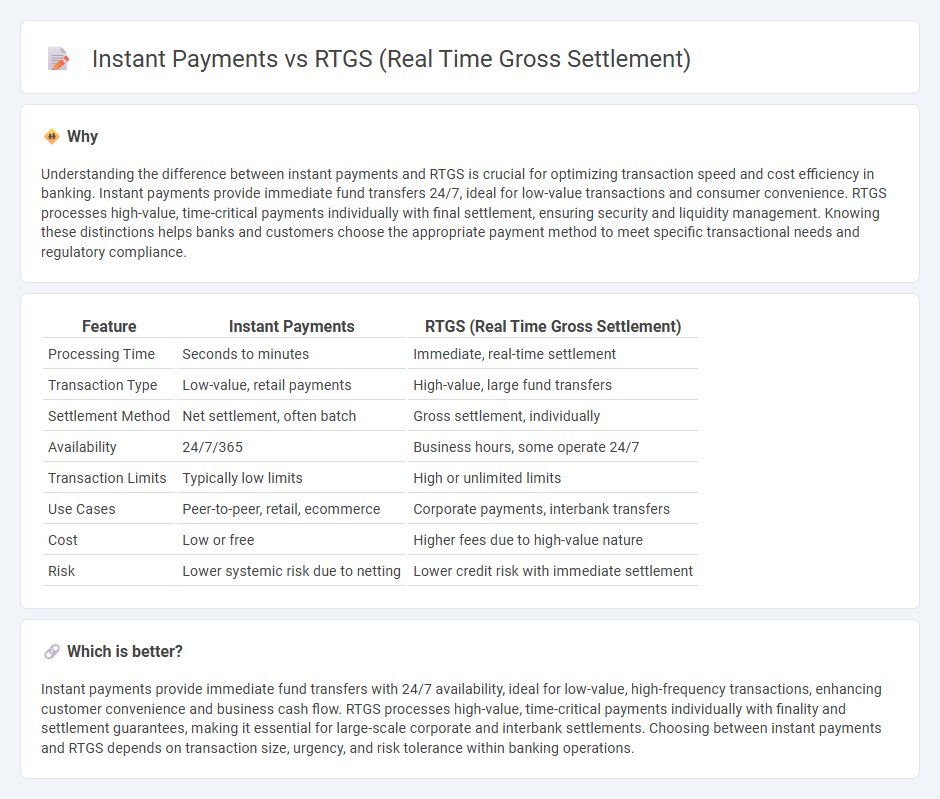
| Feature | Instant Payments | RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement) |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Seconds to minutes | Immediate, real-time settlement |
| Transaction Type | Low-value, retail payments | High-value, large fund transfers |
| Settlement Method | Net settlement, often batch | Gross settlement, individually |
| Availability | 24/7/365 | Business hours, some operate 24/7 |
| Transaction Limits | Typically low limits | High or unlimited limits |
| Use Cases | Peer-to-peer, retail, ecommerce | Corporate payments, interbank transfers |
| Cost | Low or free | Higher fees due to high-value nature |
| Risk | Lower systemic risk due to netting | Lower credit risk with immediate settlement |
Which is better?
Instant payments provide immediate fund transfers with 24/7 availability, ideal for low-value, high-frequency transactions, enhancing customer convenience and business cash flow. RTGS processes high-value, time-critical payments individually with finality and settlement guarantees, making it essential for large-scale corporate and interbank settlements. Choosing between instant payments and RTGS depends on transaction size, urgency, and risk tolerance within banking operations.
Connection
Instant payments and Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems are interconnected through their shared goal of facilitating immediate fund transfers between banks and financial institutions. RTGS processes high-value transactions individually and settles them in real time, ensuring finality and reducing settlement risk, which forms the backbone infrastructure for many instant payment systems. The seamless integration of RTGS allows instant payments to achieve rapid settlement, enhancing liquidity management and improving overall efficiency in the banking sector.
Key Terms
Settlement Time
RTGS processes high-value interbank transfers individually in real time, ensuring immediate settlement without netting, typically within minutes during operating hours. Instant payments enable round-the-clock, immediate settlement of retail transactions, often completed in seconds for low to medium-value transfers. Discover more about how settlement times impact financial liquidity and transaction efficiency.
Finality of Payment
RTGS ensures payment finality by settling transactions individually and irrevocably in real-time through central bank funds, minimizing settlement risk. Instant payments confirm immediate fund availability and beneficiary credit but may involve deferred settlement, impacting legal finality. Explore the detailed distinctions between RTGS and instant payments to understand their impact on liquidity and risk management.
Credit Risk
RTGS (Real Time Gross Settlement) systems settle high-value interbank payments individually and immediately, eliminating settlement risk by ensuring final and irrevocable transactions during business hours. Instant payments, processed 24/7, enable rapid fund transfers but may expose banks to higher credit risk due to deferred liquidity management and potential settlement delays in underlying clearing mechanisms. Explore the detailed comparison of credit risk implications and operational frameworks for RTGS versus instant payment systems to optimize your financial strategies.
Source and External Links
RTGS for High Value Payments - Your Guide To Minimizing Risk - RTGS is a bank-operated payment system enabling instant, individual, irrevocable, and final settlement of high-value funds transfers in real time, usually run by a country's central bank to minimize settlement risk.
What is Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)? - Modern Treasury - RTGS is a nationwide electronic payment system processing and settling transactions instantly and individually without batching, mainly for large-value transfers, managed by a country's central bank to enhance security and speed.
Real-time gross settlement - Wikipedia - RTGS systems perform real-time and one-to-one settlement of payments between banks to avoid settlement risk, with finality and irrevocability, historically developed since the 1970s and widely adopted by central banks globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com