Open banking enables third-party developers to build applications and services around financial institutions through secure APIs, promoting transparency and customer empowerment. Banking as a service (BaaS) provides companies with the infrastructure and regulated banking capabilities to integrate financial services directly into their platforms. Explore the detailed differences and benefits of open banking and BaaS to optimize your financial strategies.
Why it is important
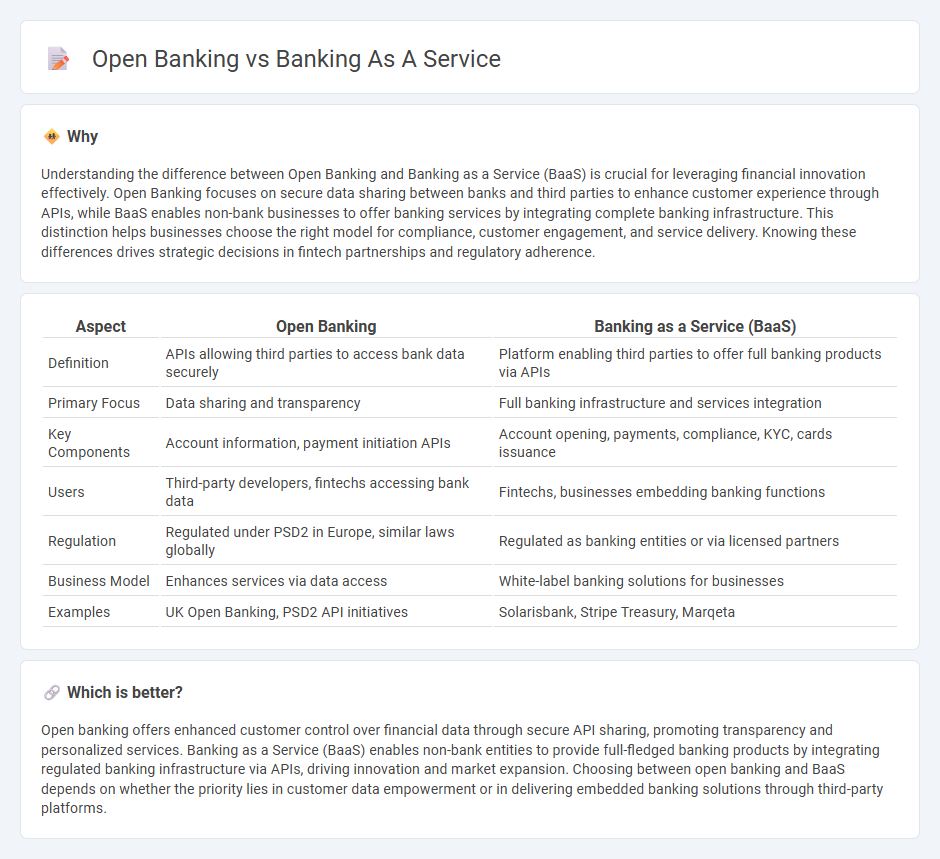
Understanding the difference between Open Banking and Banking as a Service (BaaS) is crucial for leveraging financial innovation effectively. Open Banking focuses on secure data sharing between banks and third parties to enhance customer experience through APIs, while BaaS enables non-bank businesses to offer banking services by integrating complete banking infrastructure. This distinction helps businesses choose the right model for compliance, customer engagement, and service delivery. Knowing these differences drives strategic decisions in fintech partnerships and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Open Banking | Banking as a Service (BaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | APIs allowing third parties to access bank data securely | Platform enabling third parties to offer full banking products via APIs |
| Primary Focus | Data sharing and transparency | Full banking infrastructure and services integration |
| Key Components | Account information, payment initiation APIs | Account opening, payments, compliance, KYC, cards issuance |
| Users | Third-party developers, fintechs accessing bank data | Fintechs, businesses embedding banking functions |
| Regulation | Regulated under PSD2 in Europe, similar laws globally | Regulated as banking entities or via licensed partners |
| Business Model | Enhances services via data access | White-label banking solutions for businesses |
| Examples | UK Open Banking, PSD2 API initiatives | Solarisbank, Stripe Treasury, Marqeta |
Which is better?
Open banking offers enhanced customer control over financial data through secure API sharing, promoting transparency and personalized services. Banking as a Service (BaaS) enables non-bank entities to provide full-fledged banking products by integrating regulated banking infrastructure via APIs, driving innovation and market expansion. Choosing between open banking and BaaS depends on whether the priority lies in customer data empowerment or in delivering embedded banking solutions through third-party platforms.
Connection
Open banking enables third-party providers to access bank data through APIs, enhancing customer experience and fostering innovation. Banking as a Service (BaaS) leverages open banking infrastructure to offer modular financial services via APIs, allowing non-bank entities to embed banking capabilities. Both concepts drive digital transformation by promoting seamless integration, greater financial inclusion, and personalized banking solutions.
Key Terms
API (Application Programming Interface)
Banking as a Service (BaaS) and Open Banking both leverage APIs to enable integration between financial institutions and third-party developers, but BaaS offers a comprehensive platform providing end-to-end banking services through APIs, including account management, payments, and compliance. Open Banking primarily focuses on secure data sharing and customer consent, allowing third parties to access bank data to develop innovative financial applications. Explore deeper insights on how APIs transform financial service ecosystems by examining the nuances of BaaS and Open Banking.
Third-party Providers (TPPs)
Banking as a Service (BaaS) enables Third-party Providers (TPPs) to offer financial products by integrating with a bank's infrastructure, providing seamless access to banking capabilities through APIs. Open Banking mandates banks to share customer data with authorized TPPs, fostering transparency and competition but requiring strict compliance with regulatory standards like PSD2 in Europe. Explore how these models empower TPPs to innovate financial services and enhance customer experiences.
White-label Banking
White-label banking enables companies to offer fully branded financial services by leveraging third-party banking infrastructure without building their own licenses or systems. This approach differs from open banking, which primarily permits secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers via APIs to foster innovation and competition. Explore how white-label banking can empower your brand with tailored financial solutions and seamless integration.
Source and External Links
Banking as a Service (BaaS): What It Is + Examples - This article explains Banking as a Service as a framework allowing non-banking businesses to offer tailored financial products through partnerships with licensed financial institutions.
Top Banking as a Service Companies in 2025 - This resource lists top BaaS companies and discusses how Banking as a Service enables non-banks to leverage traditional banking infrastructure for financial services.
What does Banking as a Service (BaaS) mean for business? - This article discusses BaaS as a business model where licensed banks and fintech companies provide banking infrastructure, products, and services to other businesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com