Sustainable banking focuses on integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial decisions to promote long-term ecological balance and social well-being. Development banking targets economic growth by providing financial resources and support to underdeveloped sectors, infrastructure projects, and small enterprises. Explore how these two banking models drive financial inclusion and responsible investment.
Why it is important
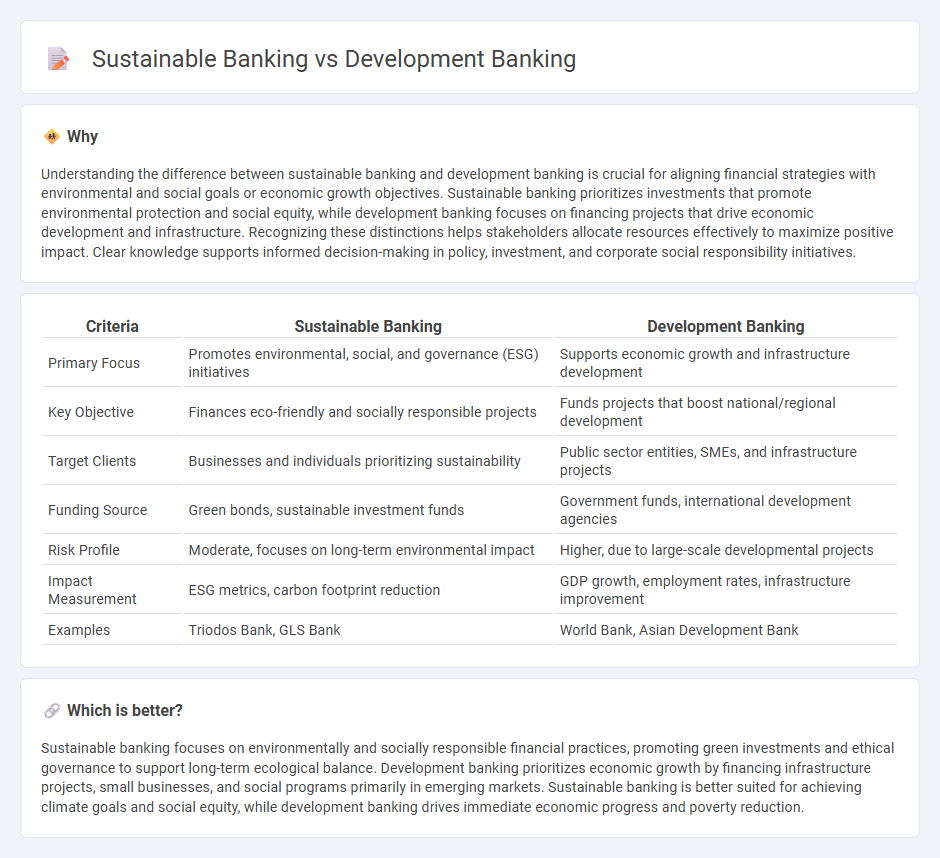
Understanding the difference between sustainable banking and development banking is crucial for aligning financial strategies with environmental and social goals or economic growth objectives. Sustainable banking prioritizes investments that promote environmental protection and social equity, while development banking focuses on financing projects that drive economic development and infrastructure. Recognizing these distinctions helps stakeholders allocate resources effectively to maximize positive impact. Clear knowledge supports informed decision-making in policy, investment, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Sustainable Banking | Development Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Promotes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives | Supports economic growth and infrastructure development |
| Key Objective | Finances eco-friendly and socially responsible projects | Funds projects that boost national/regional development |
| Target Clients | Businesses and individuals prioritizing sustainability | Public sector entities, SMEs, and infrastructure projects |
| Funding Source | Green bonds, sustainable investment funds | Government funds, international development agencies |
| Risk Profile | Moderate, focuses on long-term environmental impact | Higher, due to large-scale developmental projects |
| Impact Measurement | ESG metrics, carbon footprint reduction | GDP growth, employment rates, infrastructure improvement |
| Examples | Triodos Bank, GLS Bank | World Bank, Asian Development Bank |
Which is better?
Sustainable banking focuses on environmentally and socially responsible financial practices, promoting green investments and ethical governance to support long-term ecological balance. Development banking prioritizes economic growth by financing infrastructure projects, small businesses, and social programs primarily in emerging markets. Sustainable banking is better suited for achieving climate goals and social equity, while development banking drives immediate economic progress and poverty reduction.
Connection
Sustainable banking integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into financial services, promoting long-term economic growth while minimizing ecological impact. Development banking focuses on funding infrastructure and social projects that stimulate economic development, often addressing underserved communities. Both banking types align by channeling investments into projects that foster sustainable development goals, combining financial returns with socio-environmental benefits.
Key Terms
Project Financing
Development banking emphasizes long-term project financing aimed at infrastructure, industrial growth, and social development, often supporting government or large-scale public projects. Sustainable banking prioritizes funding projects that promote environmental stewardship, social equity, and economic viability, aligning investments with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Explore how these banking models uniquely drive project financing and impact global development goals.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Development banking prioritizes financing projects that stimulate economic growth and infrastructure in emerging markets, often supporting public sector initiatives with long-term social benefits. Sustainable banking centers on integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into financing decisions to promote responsible investments that minimize environmental impact and encourage social equity. Explore the distinct approaches of development and sustainable banking to understand their roles in fostering inclusive and eco-friendly financial ecosystems.
Impact Assessment
Development banking prioritizes funding projects that drive economic growth and social infrastructure, measuring success through metrics like job creation and regional development impact. Sustainable banking emphasizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, integrating impact assessments that evaluate carbon footprint, resource efficiency, and community well-being. Explore how tailored impact assessments in both banking models shape financial strategies and long-term value creation.
Source and External Links
Development finance institution - Wikipedia - Development finance institutions, also known as development banks, provide risk capital for economic development projects on a non-commercial basis, often established by governments to fund initiatives that would not attract commercial lending.
Development Banking in the Global Economy (PDF) - National development banks play a significant role globally, with over 450 institutions managing more than $8 trillion in assets and providing essential financing when private capital is unavailable or unwilling to invest.
Inter-American Development Bank - The Inter-American Development Bank Group is a leading multilateral development bank, providing financing, knowledge, and innovative financial tools to promote sustainable development and resilience in Latin America and the Caribbean.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com