Neobanking leverages digital-first platforms to provide seamless, user-centric financial services without physical branches, contrasting with traditional core banking systems that manage essential banking operations through centralized infrastructures. These modern neobanks utilize advanced APIs and cloud technologies to offer real-time transactions and personalized experiences, while core banking focuses on maintaining robust data integrity and compliance across legacy systems. Explore the evolving dynamics between neobanking innovation and core banking stability to understand their impact on the financial industry.
Why it is important
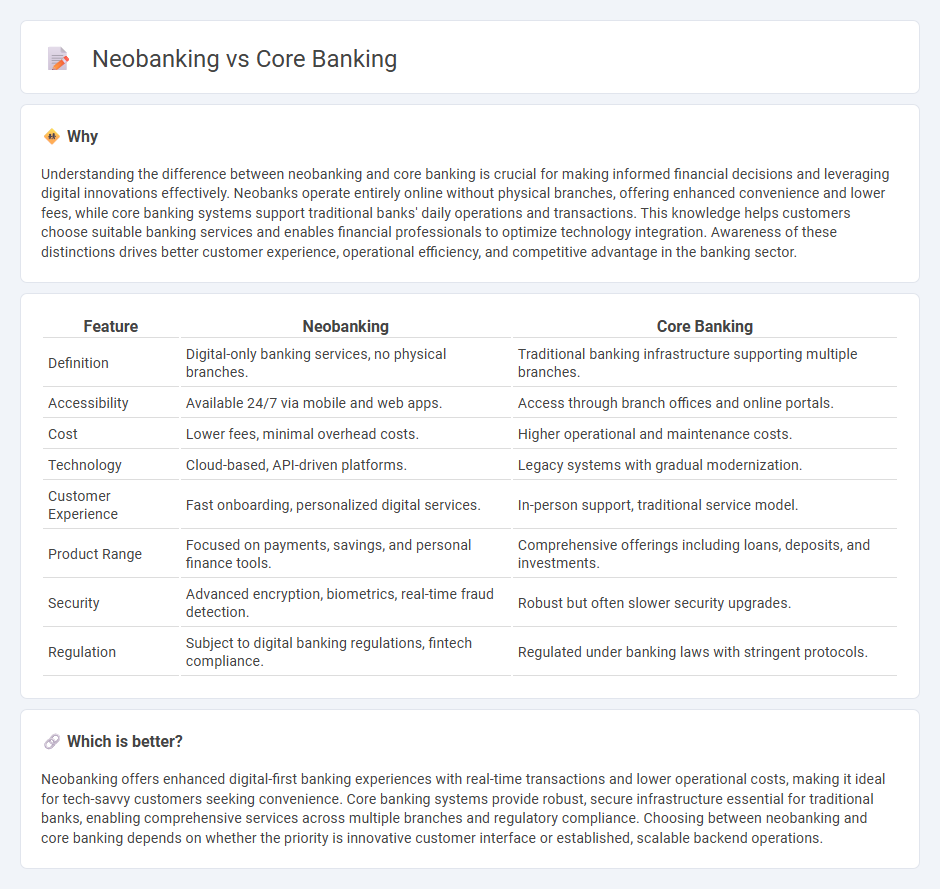
Understanding the difference between neobanking and core banking is crucial for making informed financial decisions and leveraging digital innovations effectively. Neobanks operate entirely online without physical branches, offering enhanced convenience and lower fees, while core banking systems support traditional banks' daily operations and transactions. This knowledge helps customers choose suitable banking services and enables financial professionals to optimize technology integration. Awareness of these distinctions drives better customer experience, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage in the banking sector.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Neobanking | Core Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital-only banking services, no physical branches. | Traditional banking infrastructure supporting multiple branches. |
| Accessibility | Available 24/7 via mobile and web apps. | Access through branch offices and online portals. |
| Cost | Lower fees, minimal overhead costs. | Higher operational and maintenance costs. |
| Technology | Cloud-based, API-driven platforms. | Legacy systems with gradual modernization. |
| Customer Experience | Fast onboarding, personalized digital services. | In-person support, traditional service model. |
| Product Range | Focused on payments, savings, and personal finance tools. | Comprehensive offerings including loans, deposits, and investments. |
| Security | Advanced encryption, biometrics, real-time fraud detection. | Robust but often slower security upgrades. |
| Regulation | Subject to digital banking regulations, fintech compliance. | Regulated under banking laws with stringent protocols. |
Which is better?
Neobanking offers enhanced digital-first banking experiences with real-time transactions and lower operational costs, making it ideal for tech-savvy customers seeking convenience. Core banking systems provide robust, secure infrastructure essential for traditional banks, enabling comprehensive services across multiple branches and regulatory compliance. Choosing between neobanking and core banking depends on whether the priority is innovative customer interface or established, scalable backend operations.
Connection
Neobanking relies heavily on advanced core banking systems that provide the essential infrastructure for account management, transaction processing, and regulatory compliance. Core banking platforms enable neobanks to operate digitally without traditional branch networks, ensuring real-time data synchronization and seamless customer experiences. Integration between neobanks and core banking technology drives innovation in financial services through API-based connectivity and cloud-native architectures.
Key Terms
Centralized Processing
Core banking systems rely on centralized processing units to manage all financial transactions, customer data, and account activities within a unified infrastructure. Neobanks leverage cloud-based platforms that also centralize processing but often emphasize real-time data analytics and seamless API integrations for enhanced agility. Explore how centralized processing shapes the future of banking efficiency and customer experience by learning more.
Digital-Only Services
Core banking systems enable traditional banks to manage customer accounts and transactions across multiple branches in real time, supporting a wide range of financial services. Neobanking offers exclusively digital-only services with no physical branches, leveraging mobile apps and cloud platforms to provide streamlined banking experiences and lower operational costs. Explore the key differences and benefits of each to understand how digital-only services are reshaping banking today.
API Integration
Core banking systems provide centralized management of banking operations, featuring robust API integration capabilities that enable seamless connectivity with external applications and third-party services. Neobanks rely heavily on API-driven architecture to deliver agile, customer-centric digital banking experiences, leveraging APIs to integrate with fintech platforms, payment gateways, and data analytics tools. Explore further to understand how API integration shapes the future of digital banking infrastructure.
Source and External Links
What is Core Banking? - Core banking is a centralized, online real-time system that connects multiple branches of the same bank, allowing customers to access and perform transactions seamlessly from any branch, supported by a back-end ecosystem of servers and software for secure and efficient banking operations.
Core banking - Wikipedia - Core banking refers to banking services provided by a network of bank branches where customers can perform basic transactions like deposits, loans, and payments across any branch, enabled by software that centralizes record keeping and allows real-time data sharing.
What Is Core Banking: Definition, Features, Benefits - Core banking systems streamline banking operations through automation, enabling faster transactions, enhancing customer experience via online services, increasing revenue through new products, and reducing risks using secure technologies like encryption and two-factor authentication.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com