Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledger technology to enable faster, transparent, and low-cost cross-border payments, unlike RTGS, which provides high-value domestic transfers with guaranteed real-time settlement through centralized banking systems. While RTGS excels in security and immediacy for large-scale transactions cleared individually, blockchain remittance reduces intermediaries, lowering fees and enhancing traceability across international corridors. Explore how these payment systems revolutionize banking infrastructure and financial inclusion worldwide.
Why it is important
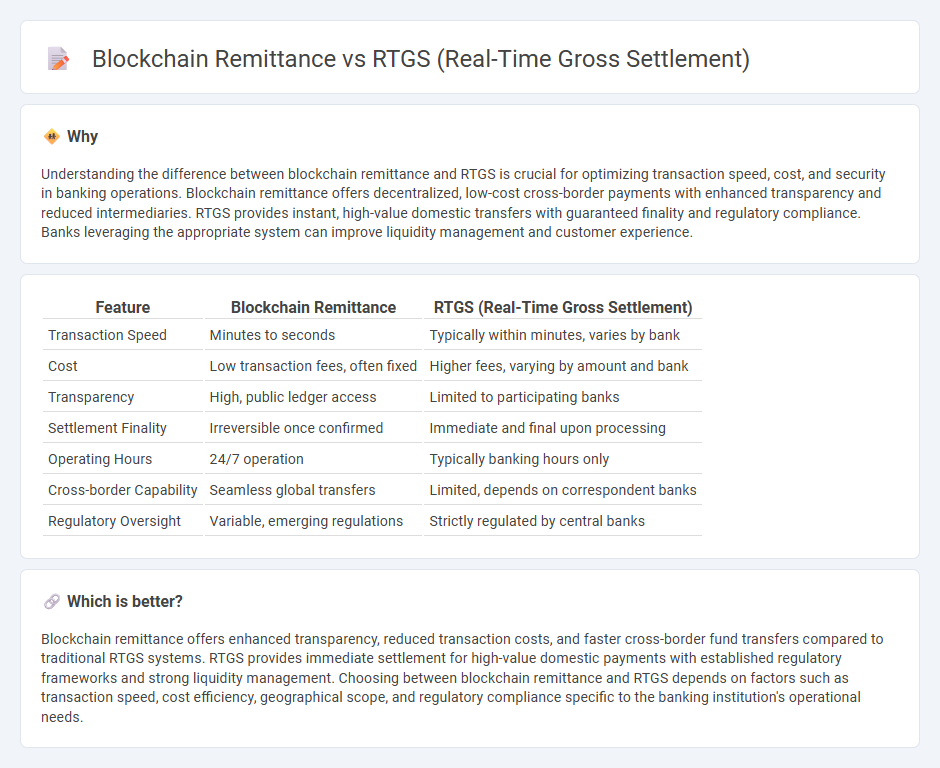
Understanding the difference between blockchain remittance and RTGS is crucial for optimizing transaction speed, cost, and security in banking operations. Blockchain remittance offers decentralized, low-cost cross-border payments with enhanced transparency and reduced intermediaries. RTGS provides instant, high-value domestic transfers with guaranteed finality and regulatory compliance. Banks leveraging the appropriate system can improve liquidity management and customer experience.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Remittance | RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement) |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to seconds | Typically within minutes, varies by bank |
| Cost | Low transaction fees, often fixed | Higher fees, varying by amount and bank |
| Transparency | High, public ledger access | Limited to participating banks |
| Settlement Finality | Irreversible once confirmed | Immediate and final upon processing |
| Operating Hours | 24/7 operation | Typically banking hours only |
| Cross-border Capability | Seamless global transfers | Limited, depends on correspondent banks |
| Regulatory Oversight | Variable, emerging regulations | Strictly regulated by central banks |
Which is better?
Blockchain remittance offers enhanced transparency, reduced transaction costs, and faster cross-border fund transfers compared to traditional RTGS systems. RTGS provides immediate settlement for high-value domestic payments with established regulatory frameworks and strong liquidity management. Choosing between blockchain remittance and RTGS depends on factors such as transaction speed, cost efficiency, geographical scope, and regulatory compliance specific to the banking institution's operational needs.
Connection
Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledger technology to enable secure, transparent, and instant cross-border fund transfers, reducing reliance on intermediaries. RTGS systems facilitate high-value interbank payments in real-time, ensuring finality and settlement certainty. The integration of blockchain with RTGS enhances transaction speed, reduces operational costs, and increases transparency in large-value payment settlements within the banking sector.
Key Terms
Settlement Finality
RTGS systems ensure settlement finality by processing transactions individually and instantly, eliminating settlement risk through irrevocable and unconditional transfer of funds. Blockchain remittance utilizes decentralized ledgers where finality depends on consensus algorithms, which may introduce probabilistic finality and potential delays. Explore the nuances of these settlement mechanisms to understand their impact on transaction security and speed.
Decentralization
RTGS operates through centralized banking systems ensuring immediate fund transfers between banks with final settlement, emphasizing reliability and regulatory oversight. Blockchain remittance utilizes decentralized ledgers, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing transparency. Explore deeper insights into how decentralization reshapes global remittance by discovering the latest technological trends.
Transaction Speed
RTGS systems process high-value interbank payments individually and instantly, ensuring finality without settlement risk within seconds to minutes. In contrast, blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledgers, where transaction speed depends heavily on network throughput and consensus mechanisms, often resulting in longer confirmation times ranging from seconds to hours. Explore deeper insights into how each method impacts financial operations and remittance efficiency.
Source and External Links
RTGS for High Value Payments - Your Guide To Minimizing Risk - Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) is an instantaneous electronic payment system for high-value payments, where transactions are settled individually and irrevocably in real time, usually managed by a country's central bank to minimize settlement risk.
What is Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)? - Modern Treasury - RTGS is a nationwide central bank-operated system enabling immediate processing and final settlement of fund transfers between banks without batching, suitable for large-value transactions requiring quick and secure transfers.
Real-time gross settlement - Wikipedia - RTGS systems settle transactions individually in real time to avoid settlement risk, ensuring payments are final and irrevocable immediately upon processing, and have been adopted globally since the 1980s as a critical financial market infrastructure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com