Sustainable banking focuses on financing projects and businesses that prioritize environmental and social responsibility, integrating ethical standards into financial decisions to promote long-term ecological balance. Retail banking serves individuals with everyday financial services such as deposits, loans, and mortgages, emphasizing convenience and accessibility for personal financial management. Discover how these distinct banking approaches shape the future of finance and impact both society and individual customers.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable banking and retail banking is crucial for aligning financial decisions with environmental and social responsibility goals. Sustainable banking focuses on investments that promote ecological balance and ethical practices, while retail banking primarily serves individual consumers with everyday financial services like savings accounts and loans. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers and investors choose banking services that reflect their values and long-term financial strategies. This knowledge supports informed decision-making that can drive positive economic and social impact.
Comparison Table
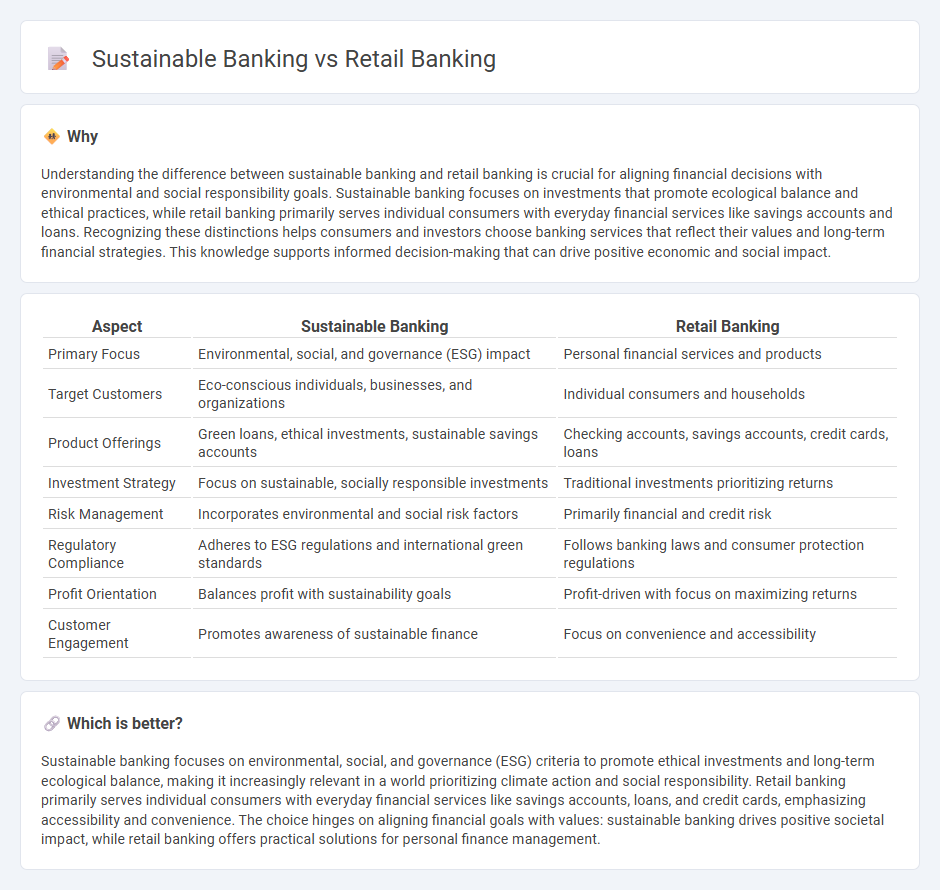
| Aspect | Sustainable Banking | Retail Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impact | Personal financial services and products |
| Target Customers | Eco-conscious individuals, businesses, and organizations | Individual consumers and households |
| Product Offerings | Green loans, ethical investments, sustainable savings accounts | Checking accounts, savings accounts, credit cards, loans |
| Investment Strategy | Focus on sustainable, socially responsible investments | Traditional investments prioritizing returns |
| Risk Management | Incorporates environmental and social risk factors | Primarily financial and credit risk |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to ESG regulations and international green standards | Follows banking laws and consumer protection regulations |
| Profit Orientation | Balances profit with sustainability goals | Profit-driven with focus on maximizing returns |
| Customer Engagement | Promotes awareness of sustainable finance | Focus on convenience and accessibility |
Which is better?
Sustainable banking focuses on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote ethical investments and long-term ecological balance, making it increasingly relevant in a world prioritizing climate action and social responsibility. Retail banking primarily serves individual consumers with everyday financial services like savings accounts, loans, and credit cards, emphasizing accessibility and convenience. The choice hinges on aligning financial goals with values: sustainable banking drives positive societal impact, while retail banking offers practical solutions for personal finance management.
Connection
Sustainable banking integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into retail banking products and services, promoting eco-friendly loans and green investment options. Retail banks play a critical role by offering sustainable financial solutions such as green mortgages, ethical savings accounts, and carbon footprint tracking tools that encourage responsible consumer behavior. This synergy supports the global transition to a low-carbon economy while enhancing long-term financial stability and customer trust.
Key Terms
Retail banking:
Retail banking centers on providing financial services such as savings accounts, mortgages, personal loans, and credit cards to individual consumers. It prioritizes accessibility, customer convenience, and everyday financial needs while ensuring regulatory compliance and risk management. Explore how retail banking continues to evolve in the digital age and its impact on customer experience.
Personal Loans
Retail banking personal loans primarily emphasize competitive interest rates, flexible repayment terms, and quick approval processes to meet diverse consumer needs. Sustainable banking personal loans prioritize funding eco-friendly projects, supporting renewable energy initiatives, and promoting responsible borrowing practices aligned with environmental and social governance standards. Explore how sustainable banking transforms personal lending by integrating ethics and environmental impact into financial decisions.
Savings Accounts
Retail banking savings accounts typically offer standard interest rates with a focus on liquidity and accessibility, catering to everyday consumer needs. Sustainable banking savings accounts prioritize investments in environmentally and socially responsible projects, often featuring competitive rates tied to green initiatives. Explore how sustainable savings options align your financial goals with positive social impact.
Source and External Links
Retail banking (Wikipedia) - Retail banking, also known as consumer or personal banking, provides financial services like savings and checking accounts, loans, mortgages, and cards to individual customers rather than businesses or corporations.
What Is Retail Banking? (The Forage) - Retail banks offer products such as checking and savings accounts, debit and credit cards, ATMs, mortgages, and personal loans to individuals, families, and small businesses.
Retail Banking (App State Finance Department) - Retail bankers assist customers with personal financial needs, including loans, deposits, and insurance, primarily through direct interaction in branches.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com