Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible mortgage debt into tax-deductible investment debt, enhancing wealth-building strategies through efficient loan management. An offset account, linked to a home loan, reduces interest by offsetting the mortgage balance with savings but does not change the nature of the debt. Explore the nuances between debt recycling and offset accounts to optimize your financial planning.
Why it is important
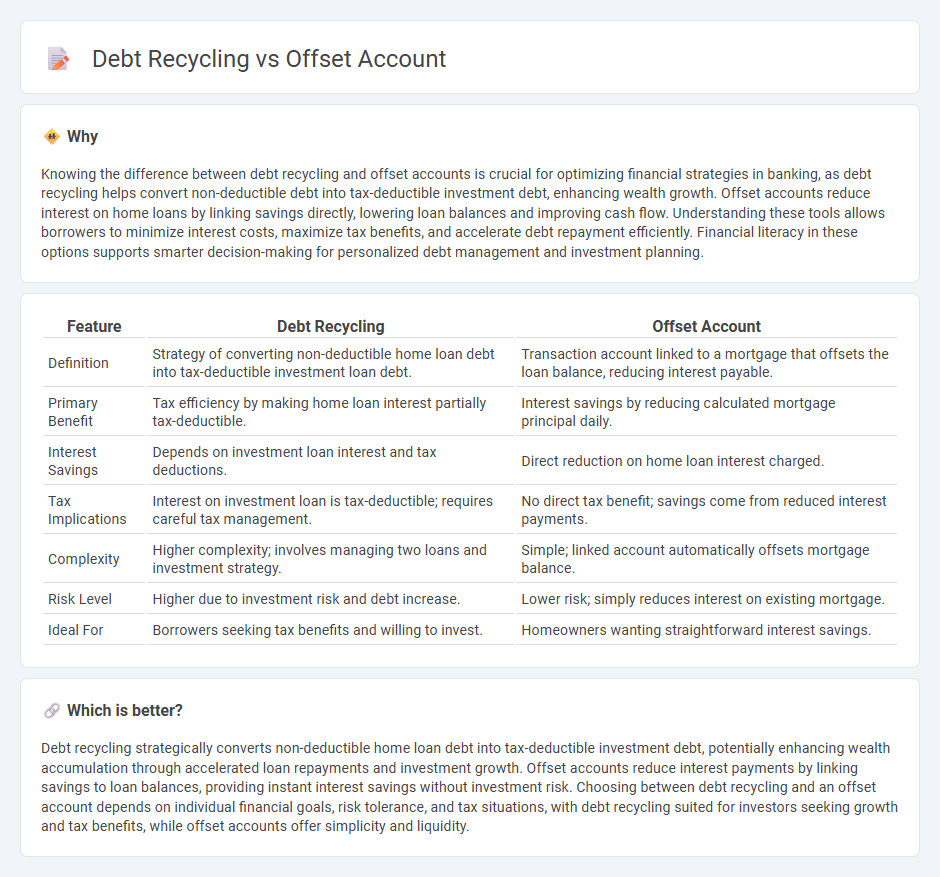
Knowing the difference between debt recycling and offset accounts is crucial for optimizing financial strategies in banking, as debt recycling helps convert non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt, enhancing wealth growth. Offset accounts reduce interest on home loans by linking savings directly, lowering loan balances and improving cash flow. Understanding these tools allows borrowers to minimize interest costs, maximize tax benefits, and accelerate debt repayment efficiently. Financial literacy in these options supports smarter decision-making for personalized debt management and investment planning.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Debt Recycling | Offset Account |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy of converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment loan debt. | Transaction account linked to a mortgage that offsets the loan balance, reducing interest payable. |
| Primary Benefit | Tax efficiency by making home loan interest partially tax-deductible. | Interest savings by reducing calculated mortgage principal daily. |
| Interest Savings | Depends on investment loan interest and tax deductions. | Direct reduction on home loan interest charged. |
| Tax Implications | Interest on investment loan is tax-deductible; requires careful tax management. | No direct tax benefit; savings come from reduced interest payments. |
| Complexity | Higher complexity; involves managing two loans and investment strategy. | Simple; linked account automatically offsets mortgage balance. |
| Risk Level | Higher due to investment risk and debt increase. | Lower risk; simply reduces interest on existing mortgage. |
| Ideal For | Borrowers seeking tax benefits and willing to invest. | Homeowners wanting straightforward interest savings. |
Which is better?
Debt recycling strategically converts non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt, potentially enhancing wealth accumulation through accelerated loan repayments and investment growth. Offset accounts reduce interest payments by linking savings to loan balances, providing instant interest savings without investment risk. Choosing between debt recycling and an offset account depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax situations, with debt recycling suited for investors seeking growth and tax benefits, while offset accounts offer simplicity and liquidity.
Connection
Debt recycling leverages an offset account by using savings held within the account to reduce interest on a home loan, effectively converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt. The offset account balance directly lowers the loan principal on which interest is calculated, enhancing cash flow efficiency. This strategy optimizes debt management by simultaneously minimizing interest expenses and enabling investment growth.
Key Terms
Loan Interest
Offset accounts reduce loan interest by linking savings to the mortgage, effectively lowering the principal amount on which interest is calculated. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment loan debt, enhancing interest efficiency through strategic borrowing. Explore detailed strategies to optimize loan interest management and boost financial benefits.
Investment Income
An offset account reduces interest on your mortgage by linking your savings directly to your home loan balance, effectively lowering the amount of interest charged and enhancing cash flow for potential investments. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt, leveraging your home equity to fund investments that generate passive income, thus optimizing your overall investment income. Explore how these strategies can maximize your wealth-building potential and investment returns.
Principal Reduction
Offset accounts reduce the principal balance by linking savings to the home loan, decreasing interest payable and accelerating principal repayment. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment debt while maintaining cash flow, boosting wealth and reducing principal over time. Discover how these strategies impact your financial goals and principal reduction in more detail.
Source and External Links
Offset accounts explained | ANZ - An offset account is a transaction account linked to your home loan, where the balance reduces the amount of interest charged on your loan while keeping your money accessible for everyday use.
What is an offset account - CommBank - An offset account lets you offset your home loan balance with the funds in the account, so you only pay interest on the difference, and the money remains available for withdrawals or deposits as needed.
What is an offset account? - NerdWallet Australia - An offset account is a transaction account that, when linked to your home loan, reduces the interest you pay by offsetting your mortgage balance with the account's balance, and the money can be accessed just like a regular bank account.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com