Instant payments offer real-time fund transfers that enhance cash flow and improve transaction efficiency in banking. Deferred payments, on the other hand, involve scheduled settlements that provide flexibility for managing liquidity and credit risk. Explore the benefits and use cases of both instant and deferred payments to optimize your financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between instant payments and deferred payments is crucial for managing cash flow and ensuring timely transactions. Instant payments provide immediate fund transfers, enhancing liquidity and reducing settlement risk. Deferred payments delay fund availability, which can impact budgeting and financial planning. Accurate knowledge supports better decision-making in personal and corporate banking.
Comparison Table
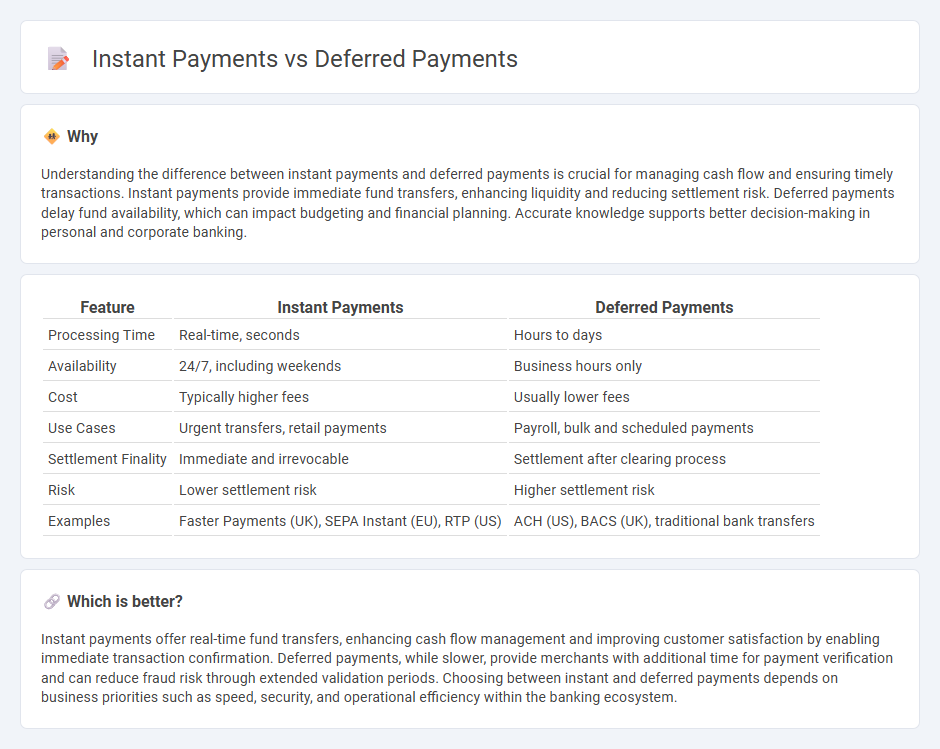
| Feature | Instant Payments | Deferred Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Time | Real-time, seconds | Hours to days |
| Availability | 24/7, including weekends | Business hours only |
| Cost | Typically higher fees | Usually lower fees |
| Use Cases | Urgent transfers, retail payments | Payroll, bulk and scheduled payments |
| Settlement Finality | Immediate and irrevocable | Settlement after clearing process |
| Risk | Lower settlement risk | Higher settlement risk |
| Examples | Faster Payments (UK), SEPA Instant (EU), RTP (US) | ACH (US), BACS (UK), traditional bank transfers |
Which is better?
Instant payments offer real-time fund transfers, enhancing cash flow management and improving customer satisfaction by enabling immediate transaction confirmation. Deferred payments, while slower, provide merchants with additional time for payment verification and can reduce fraud risk through extended validation periods. Choosing between instant and deferred payments depends on business priorities such as speed, security, and operational efficiency within the banking ecosystem.
Connection
Instant payments and deferred payments are interconnected components of modern banking that enhance transaction flexibility and cash flow management. Instant payments enable immediate fund transfers, promoting real-time financial settlements, while deferred payments allow transactions to be processed at a later date, supporting scheduled or installment-based financial obligations. Both methods optimize liquidity and risk management for banks and customers by balancing immediacy and planned payment structures.
Key Terms
Settlement Time
Deferred payments settle transactions at a later date, often taking several days to complete, which can impact cash flow and liquidity management. Instant payments, processed within seconds or minutes, provide immediate settlement, enhancing real-time fund availability and reducing credit risk for businesses and consumers. Explore more details on the advantages and applications of each payment type to optimize your transaction strategy.
Credit Risk
Deferred payments extend the credit exposure period, increasing the likelihood of default due to delayed funds transfer, which elevates credit risk for lenders. Instant payments reduce credit risk by enabling immediate settlement, ensuring funds are secured quickly and minimizing the chance of payment failure. Explore more to understand how businesses can optimize payment structures to manage credit risk effectively.
Liquidity
Deferred payments enable businesses to manage liquidity by delaying cash outflows, improving short-term financial flexibility and working capital. Instant payments enhance liquidity management by providing immediate fund availability, reducing settlement risk and enabling real-time cash flow monitoring. Explore how these payment methods impact liquidity strategies in various industries.
Source and External Links
How does a deferred payment agreement work? | WSCC Publication - A deferred payment is a loan secured by your home that covers care costs you can't afford, repaid usually after selling the home or from your estate after death, allowing you to keep contributing from your income meanwhile.
Does Deferring a Payment Hurt Your Credit? - Experian - Deferred payments delay payment obligations temporarily, with terms varying by loan type, typically not hurting credit if approved, and can involve adding postponed payments to the loan term or repaying later, such as after mortgage sale or refinancing.
What Is a Deferred Payment and How Does it Work? - altLINE - A deferred payment agreement allows delaying payment to a future date and often involves installments, enabling customers or businesses to spread out large purchases when upfront payment isn't feasible.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com