Digital identity verification uses biometric data, government-issued IDs, and AI-driven analytics to ensure precise customer authentication in banking. Federated identity management allows users to access multiple financial services through a single set of credentials, enhancing user convenience and security. Explore how these technologies transform banking security and customer experience.
Why it is important
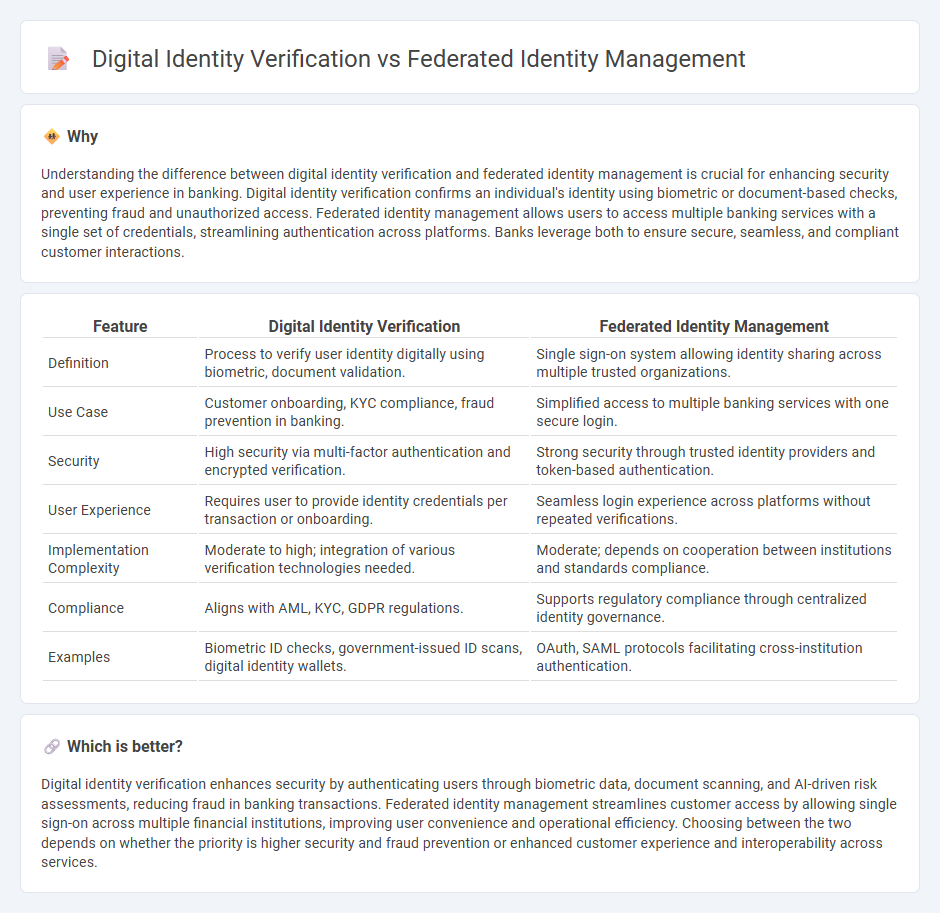
Understanding the difference between digital identity verification and federated identity management is crucial for enhancing security and user experience in banking. Digital identity verification confirms an individual's identity using biometric or document-based checks, preventing fraud and unauthorized access. Federated identity management allows users to access multiple banking services with a single set of credentials, streamlining authentication across platforms. Banks leverage both to ensure secure, seamless, and compliant customer interactions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Federated Identity Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process to verify user identity digitally using biometric, document validation. | Single sign-on system allowing identity sharing across multiple trusted organizations. |
| Use Case | Customer onboarding, KYC compliance, fraud prevention in banking. | Simplified access to multiple banking services with one secure login. |
| Security | High security via multi-factor authentication and encrypted verification. | Strong security through trusted identity providers and token-based authentication. |
| User Experience | Requires user to provide identity credentials per transaction or onboarding. | Seamless login experience across platforms without repeated verifications. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate to high; integration of various verification technologies needed. | Moderate; depends on cooperation between institutions and standards compliance. |
| Compliance | Aligns with AML, KYC, GDPR regulations. | Supports regulatory compliance through centralized identity governance. |
| Examples | Biometric ID checks, government-issued ID scans, digital identity wallets. | OAuth, SAML protocols facilitating cross-institution authentication. |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification enhances security by authenticating users through biometric data, document scanning, and AI-driven risk assessments, reducing fraud in banking transactions. Federated identity management streamlines customer access by allowing single sign-on across multiple financial institutions, improving user convenience and operational efficiency. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority is higher security and fraud prevention or enhanced customer experience and interoperability across services.
Connection
Digital identity verification establishes the authenticity of users' credentials, enabling secure access to banking services. Federated identity management builds on this verification by allowing multiple banking platforms to share verified identity information seamlessly. This integration enhances customer experience and reduces fraud risks across interconnected financial institutions.
Key Terms
**Federated Identity Management:**
Federated Identity Management (FIM) enables multiple organizations to share and authenticate user identities across diverse systems using a centralized framework, enhancing security and user convenience through single sign-on (SSO) solutions. This approach reduces the need for multiple passwords while streamlining access control and compliance across partner domains. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of Federated Identity Management to strengthen your digital security ecosystem.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Federated identity management enables users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials through Single Sign-On (SSO), streamlining authentication processes across organizational boundaries without the need to create separate accounts. Digital identity verification, on the other hand, focuses on confirming a user's identity using biometric data, government-issued IDs, or other trustworthy credentials before granting access, enhancing security at the initial login stage. Explore the differences and benefits of these identity solutions to optimize your organization's access management strategy.
Identity Provider (IdP)
Federated identity management relies on an Identity Provider (IdP) to authenticate users across multiple trusted domains, enabling seamless single sign-on experiences without repeated logins. Digital identity verification involves the IdP validating user credentials and attributes against authoritative sources to confirm identity authenticity and prevent fraud. Explore how advanced IdP technologies streamline secure access and enhance user trust in various applications.
Source and External Links
What is Federated Identity: How It Works & Benefits | OneLogin - Federated identity management (FIM) enables users to access multiple applications and domains using a single set of credentials by establishing trust relationships between service providers and identity providers that authenticate users across systems without repeated logins.
What is Federated Identity Management (FIM)? How Does It Work? - FIM is an arrangement allowing users to use the same digital identity across multiple enterprises or trust domains, with identity providers managing access and authentication to improve user experience and security across affiliated organizations.
Federated identity - Wikipedia - Federated identity management involves shared policies and protocols across organizations to link electronic identities, enabling single sign-on across diverse IT systems while addressing cross-domain access challenges in decentralized environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com