Income streaming provides consistent cash flow through regular payments such as dividends, interest, or rental income, offering stability for financial planning. Investment gains focus on capital appreciation by buying low and selling high, potentially generating higher returns but with increased risk and market volatility. Explore the key differences and benefits of income streaming versus investment gains to optimize your banking strategy.
Why it is important
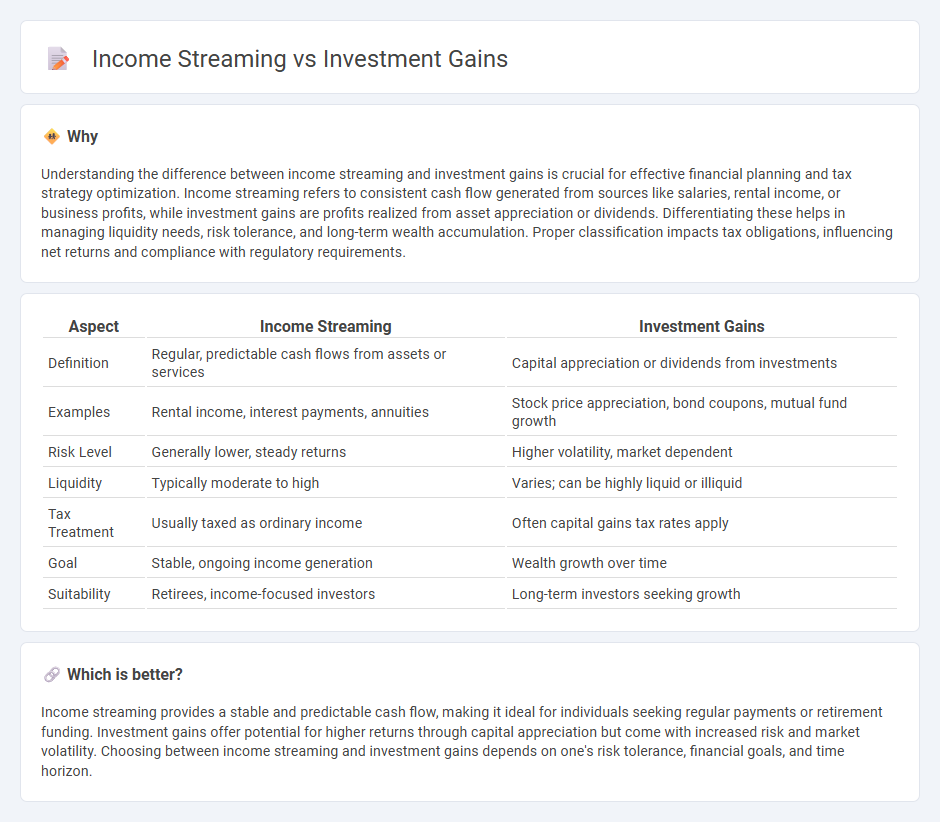
Understanding the difference between income streaming and investment gains is crucial for effective financial planning and tax strategy optimization. Income streaming refers to consistent cash flow generated from sources like salaries, rental income, or business profits, while investment gains are profits realized from asset appreciation or dividends. Differentiating these helps in managing liquidity needs, risk tolerance, and long-term wealth accumulation. Proper classification impacts tax obligations, influencing net returns and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Income Streaming | Investment Gains |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regular, predictable cash flows from assets or services | Capital appreciation or dividends from investments |
| Examples | Rental income, interest payments, annuities | Stock price appreciation, bond coupons, mutual fund growth |
| Risk Level | Generally lower, steady returns | Higher volatility, market dependent |
| Liquidity | Typically moderate to high | Varies; can be highly liquid or illiquid |
| Tax Treatment | Usually taxed as ordinary income | Often capital gains tax rates apply |
| Goal | Stable, ongoing income generation | Wealth growth over time |
| Suitability | Retirees, income-focused investors | Long-term investors seeking growth |
Which is better?
Income streaming provides a stable and predictable cash flow, making it ideal for individuals seeking regular payments or retirement funding. Investment gains offer potential for higher returns through capital appreciation but come with increased risk and market volatility. Choosing between income streaming and investment gains depends on one's risk tolerance, financial goals, and time horizon.
Connection
Income streaming and investment gains are interconnected through portfolio diversification and cash flow optimization strategies that maximize returns while minimizing risks. Continuous income streams from dividends, interest payments, and rental income contribute to reinvestment opportunities, enhancing overall investment growth. Effective management of these income streams boosts liquidity, enabling investors to capitalize on market opportunities and compound gains over time.
Key Terms
Capital Appreciation
Capital appreciation focuses on increasing the value of assets over time, which can result in significant investment gains through the growth of stock prices, real estate, or other holdings. Unlike income streaming, which prioritizes regular cash flow such as dividends or rental income, capital appreciation emphasizes long-term wealth accumulation by reinvesting profits and holding assets. Discover how prioritizing capital appreciation can enhance your portfolio's performance and secure your financial future.
Dividend Yield
Dividend yield represents the percentage of a company's share price paid out annually in dividends, serving as a key metric for income streaming strategies. Investment gains focus on capital appreciation, where the value of the asset increases over time, often resulting in higher total returns despite lower immediate cash flow. Explore detailed comparisons of dividend yield and investment gains to optimize your portfolio's balance between income and growth.
Interest Income
Interest income from investment gains primarily derives from fixed-income securities such as bonds, certificates of deposit, and treasury bills, offering a predictable cash flow and relatively lower risk compared to equity investments. This income streaming strategy emphasizes consistent returns and capital preservation, making it suitable for conservative investors seeking steady portfolio growth. Explore detailed insights on leveraging interest income for optimized long-term financial planning.
Source and External Links
What is capital gains tax? | Vanguard - Investment gains are called capital gains, which are profits made when you sell investments for more than you paid, and these gains become taxable when realized through the sale of the investment.
Capital Gains Explained | FINRA.org - Capital gains reflect the money made from selling an investment at a profit, and their tax rate depends on whether the investment was held short-term (one year or less) or long-term (more than one year), with long-term gains typically taxed at a lower rate.
Investing 101: Understanding types of investment income - Capital gains are one type of investment income earned from selling assets at a profit; they can be short-term or long-term, with tax rates varying accordingly, and they differ from other investment income like dividends and interest.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com