Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible home loan debt into tax-deductible investment loan debt, enhancing wealth-building potential while maintaining the mortgage. Refinancing replaces an existing loan with a new one, often to secure lower interest rates, better terms, or access additional funds, improving overall financial efficiency. Discover how these strategies can optimize your banking and financial goals.
Why it is important
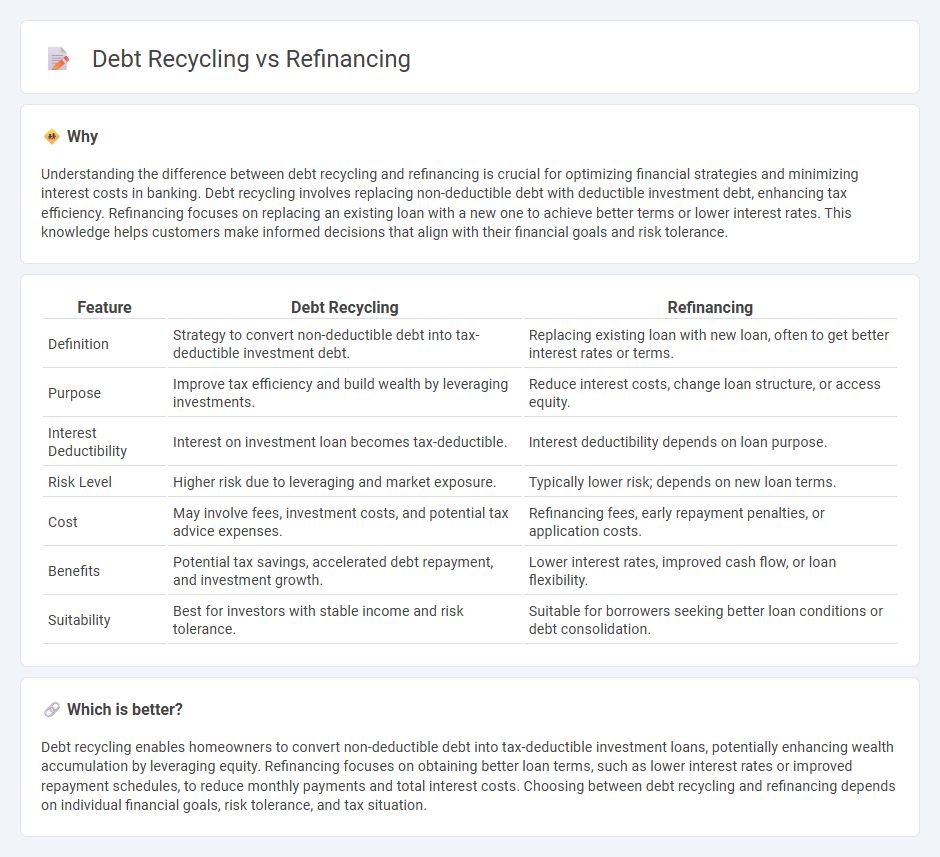
Understanding the difference between debt recycling and refinancing is crucial for optimizing financial strategies and minimizing interest costs in banking. Debt recycling involves replacing non-deductible debt with deductible investment debt, enhancing tax efficiency. Refinancing focuses on replacing an existing loan with a new one to achieve better terms or lower interest rates. This knowledge helps customers make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Debt Recycling | Refinancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy to convert non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt. | Replacing existing loan with new loan, often to get better interest rates or terms. |
| Purpose | Improve tax efficiency and build wealth by leveraging investments. | Reduce interest costs, change loan structure, or access equity. |
| Interest Deductibility | Interest on investment loan becomes tax-deductible. | Interest deductibility depends on loan purpose. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to leveraging and market exposure. | Typically lower risk; depends on new loan terms. |
| Cost | May involve fees, investment costs, and potential tax advice expenses. | Refinancing fees, early repayment penalties, or application costs. |
| Benefits | Potential tax savings, accelerated debt repayment, and investment growth. | Lower interest rates, improved cash flow, or loan flexibility. |
| Suitability | Best for investors with stable income and risk tolerance. | Suitable for borrowers seeking better loan conditions or debt consolidation. |
Which is better?
Debt recycling enables homeowners to convert non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment loans, potentially enhancing wealth accumulation by leveraging equity. Refinancing focuses on obtaining better loan terms, such as lower interest rates or improved repayment schedules, to reduce monthly payments and total interest costs. Choosing between debt recycling and refinancing depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax situation.
Connection
Debt recycling and refinancing are connected through their shared goal of optimizing financial management by leveraging existing debt to invest or reduce interest expenses. Debt recycling involves converting non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt, while refinancing replaces an existing loan with a new one to achieve better interest rates or terms. Effective refinancing enhances debt recycling strategies by lowering borrowing costs and improving cash flow for investment opportunities.
Key Terms
Interest Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in both refinancing and debt recycling strategies, directly impacting the cost of borrowing and potential savings. Refinancing aims to secure lower interest rates to reduce monthly payments or total interest paid over the loan term, whereas debt recycling leverages existing equity with the intent to convert non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt, often influenced by prevailing interest rates. Explore how varying interest rate environments affect these strategies to optimize your financial decisions effectively.
Loan Structure
Refinancing restructures existing loans to secure better interest rates or terms, often replacing one loan with another to improve cash flow or reduce monthly payments. Debt recycling strategically converts non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt by using equity release or refinancing to invest and accelerate wealth building. Explore the intricacies of loan structures in refinancing and debt recycling to optimize your financial strategy.
Equity
Refinancing leverages home equity by replacing an existing mortgage with a new loan, often to secure a lower interest rate or access additional funds, while debt recycling converts non-deductible debt into tax-deductible investment debt using equity release strategies. Both strategies utilize home equity for financial optimization but differ in approach and tax implications, with debt recycling specifically designed to enhance wealth accumulation. Explore how maximizing home equity through these methods can improve your financial strategy.
Source and External Links
Refinancing - Refinancing is the process of replacing an existing debt obligation with a new one, typically to secure better interest rates, alter loan terms, or consolidate multiple debts.
Current Refinance Rates - Compare Rates Today - Bankrate - Compare current refinance rates from multiple lenders to determine potential savings and follow a step-by-step process to evaluate your credit, equity, and paperwork before applying.
How Does Refinancing a Mortgage Work? - Refinancing a mortgage involves taking out a new loan to pay off your original mortgage, often to obtain a lower interest rate, change the loan term, or access home equity through cash-out options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com