Stablecoin rails offer a decentralized, blockchain-based infrastructure enabling near-instantaneous cross-border payments with reduced transaction costs compared to traditional banking systems. Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems provide high-value transfer settlements on a centralized platform, ensuring finality and liquidity by processing transactions individually in real time. Explore the nuances between these financial technologies to understand their impact on modern banking ecosystems.
Why it is important
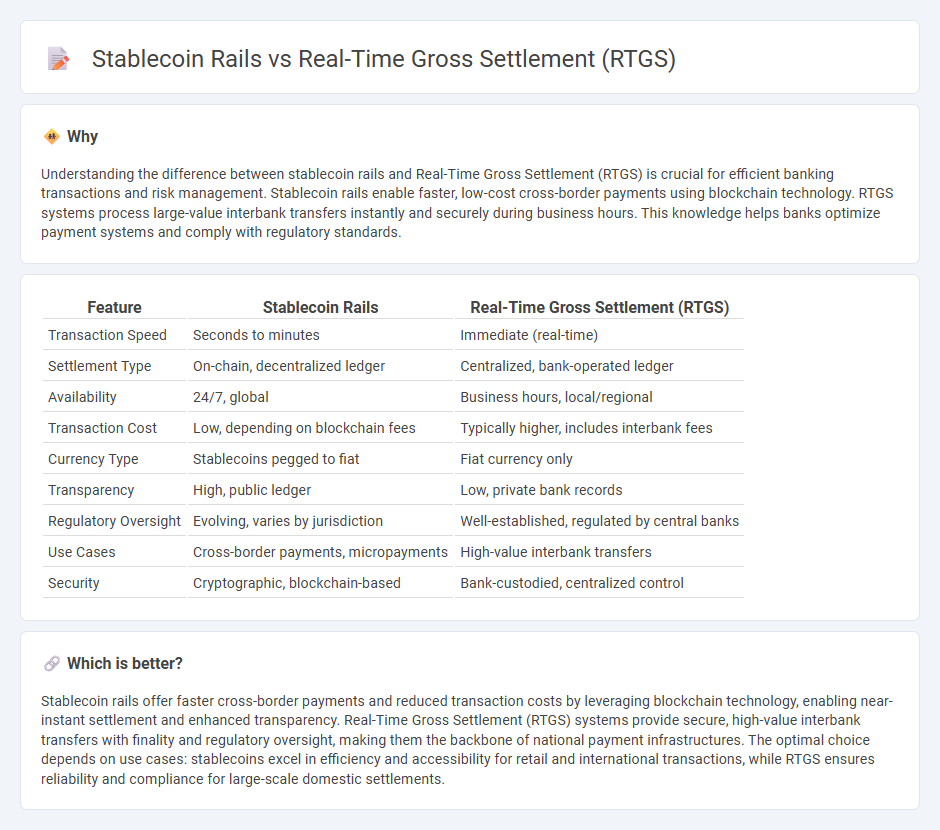
Understanding the difference between stablecoin rails and Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) is crucial for efficient banking transactions and risk management. Stablecoin rails enable faster, low-cost cross-border payments using blockchain technology. RTGS systems process large-value interbank transfers instantly and securely during business hours. This knowledge helps banks optimize payment systems and comply with regulatory standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Stablecoin Rails | Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Seconds to minutes | Immediate (real-time) |
| Settlement Type | On-chain, decentralized ledger | Centralized, bank-operated ledger |
| Availability | 24/7, global | Business hours, local/regional |
| Transaction Cost | Low, depending on blockchain fees | Typically higher, includes interbank fees |
| Currency Type | Stablecoins pegged to fiat | Fiat currency only |
| Transparency | High, public ledger | Low, private bank records |
| Regulatory Oversight | Evolving, varies by jurisdiction | Well-established, regulated by central banks |
| Use Cases | Cross-border payments, micropayments | High-value interbank transfers |
| Security | Cryptographic, blockchain-based | Bank-custodied, centralized control |
Which is better?
Stablecoin rails offer faster cross-border payments and reduced transaction costs by leveraging blockchain technology, enabling near-instant settlement and enhanced transparency. Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems provide secure, high-value interbank transfers with finality and regulatory oversight, making them the backbone of national payment infrastructures. The optimal choice depends on use cases: stablecoins excel in efficiency and accessibility for retail and international transactions, while RTGS ensures reliability and compliance for large-scale domestic settlements.
Connection
Stablecoin rails enhance Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) by providing a blockchain-based infrastructure that enables instantaneous and secure digital asset transfers, eliminating intermediaries. RTGS systems rely on stablecoins to facilitate liquidity and ensure settlement finality, reducing counterparty risk in high-value transactions. Integration of stablecoin technology with RTGS promotes interoperability between traditional banking systems and decentralized finance networks.
Key Terms
Settlement Finality
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems provide absolute settlement finality by instantly transferring funds on a gross basis, minimizing counterparty risk through irrevocable and unconditional transactions. In contrast, stablecoin payment rails, while enabling faster and more accessible cross-border transactions, may face challenges related to regulatory compliance and potential delays in on-chain settlement finality depending on blockchain consensus mechanisms. Explore the nuances between RTGS and stablecoin rails to understand their impact on global payment efficiency and risk management.
Source and External Links
RTGS for High Value Payments - Your Guide To Minimizing Risk - RTGS enables instant, final, and irrevocable electronic settlement of large-value interbank payments, processed individually in real time by central banks to minimize settlement risk.
What is Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)? - Modern Treasury - RTGS systems process and settle electronic payments between banks in real time, without batching, making them ideal for rapid, secure, high-value transactions managed by national central banks.
Real-time gross settlement - Wikipedia - RTGS systems transfer money or securities between banks in real time on a transaction-by-transaction ("gross") basis to avoid settlement risk, with payments being final and irrevocable once processed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com