Behavioral biometrics analyze unique user patterns such as typing speed, mouse movements, and navigation habits to enhance security and fraud detection in banking. Device fingerprinting collects information about a user's device configuration, including browser settings, IP address, and hardware details, to identify and track devices accessing financial services. Explore deeper insights on how these technologies redefine secure banking experiences.
Why it is important
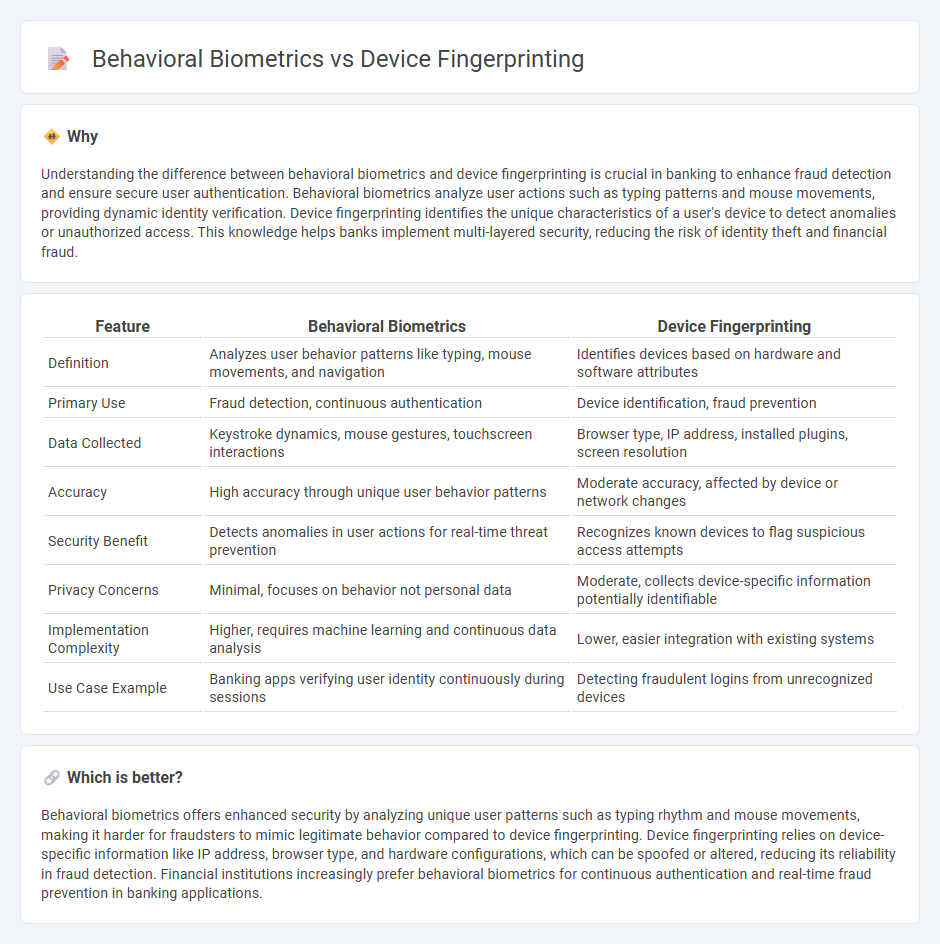
Understanding the difference between behavioral biometrics and device fingerprinting is crucial in banking to enhance fraud detection and ensure secure user authentication. Behavioral biometrics analyze user actions such as typing patterns and mouse movements, providing dynamic identity verification. Device fingerprinting identifies the unique characteristics of a user's device to detect anomalies or unauthorized access. This knowledge helps banks implement multi-layered security, reducing the risk of identity theft and financial fraud.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Behavioral Biometrics | Device Fingerprinting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes user behavior patterns like typing, mouse movements, and navigation | Identifies devices based on hardware and software attributes |
| Primary Use | Fraud detection, continuous authentication | Device identification, fraud prevention |
| Data Collected | Keystroke dynamics, mouse gestures, touchscreen interactions | Browser type, IP address, installed plugins, screen resolution |
| Accuracy | High accuracy through unique user behavior patterns | Moderate accuracy, affected by device or network changes |
| Security Benefit | Detects anomalies in user actions for real-time threat prevention | Recognizes known devices to flag suspicious access attempts |
| Privacy Concerns | Minimal, focuses on behavior not personal data | Moderate, collects device-specific information potentially identifiable |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher, requires machine learning and continuous data analysis | Lower, easier integration with existing systems |
| Use Case Example | Banking apps verifying user identity continuously during sessions | Detecting fraudulent logins from unrecognized devices |
Which is better?
Behavioral biometrics offers enhanced security by analyzing unique user patterns such as typing rhythm and mouse movements, making it harder for fraudsters to mimic legitimate behavior compared to device fingerprinting. Device fingerprinting relies on device-specific information like IP address, browser type, and hardware configurations, which can be spoofed or altered, reducing its reliability in fraud detection. Financial institutions increasingly prefer behavioral biometrics for continuous authentication and real-time fraud prevention in banking applications.
Connection
Behavioral biometrics analyze unique user patterns such as typing rhythm and navigation habits, while device fingerprinting collects hardware and software attributes to identify devices. Together, they create a layered security approach in banking by correlating user behavior with device data to detect fraud more accurately. This integration enhances authentication processes, reducing false positives and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive financial accounts.
Key Terms
Device identification
Device fingerprinting collects unique hardware and software characteristics such as browser type, OS version, IP address, and installed plugins to create a digital profile for device identification. Behavioral biometrics analyzes user interactions like typing patterns, mouse movements, and touchscreen gestures to verify identity based on behavioral traits rather than device specifics. Explore detailed comparisons and use cases to understand which method suits your security needs best.
User behavior analysis
Device fingerprinting collects unique device attributes such as browser version, IP address, and installed plugins to identify users across sessions, while behavioral biometrics analyzes patterns like typing rhythm, mouse movements, and navigation habits to verify identity based on user behavior. User behavior analysis in behavioral biometrics offers dynamic and continuous authentication by detecting deviations in an individual's habitual interactions, enhancing security beyond static device data. Explore in-depth comparisons and applications of these technologies to strengthen identity verification strategies.
Fraud detection
Device fingerprinting analyzes unique device attributes such as IP address, browser settings, and hardware configurations to identify and track users for fraud detection. Behavioral biometrics evaluates patterns like typing rhythm, mouse movements, and touch gestures to distinguish legitimate users from fraudulent actors with high accuracy. Explore how combining these technologies enhances fraud prevention strategies in your security framework.
Source and External Links
Comprehensive Device Fingerprinting Solutions for Fraud Defense - Device fingerprinting generates a unique identifier for each device by collecting hardware, OS, and software data to detect fraud, authenticate users, and personalize marketing with high accuracy, especially in industries requiring secure interactions like e-commerce and finance.
Device Fingerprinting: What It Is And How Does It Work? - Clearcode - Device fingerprinting uses JavaScript to collect detailed device and browser information, creating a unique hash to track users, which is stored server-side and difficult to block, often combined with cookies to improve tracking accuracy and identify users across devices.
How device fingerprinting improves fraud prevention - Plaid - Device fingerprinting combines software and hardware data into a unique ID to detect fraudsters by recognizing suspicious device behavior, even when fraudsters attempt to evade detection by clearing caches, switching browsers, or using spoofing tools.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com