Invisible payments leverage advanced sensor technologies and biometric authentication to enable seamless transactions without requiring physical interaction, enhancing user convenience and security. QR code payments rely on scanning a visible code via mobile devices, facilitating quick and easy transactions but often requiring user engagement and internet connectivity. Explore the advantages and applications of both payment methods to understand their impact on the future of banking.
Why it is important
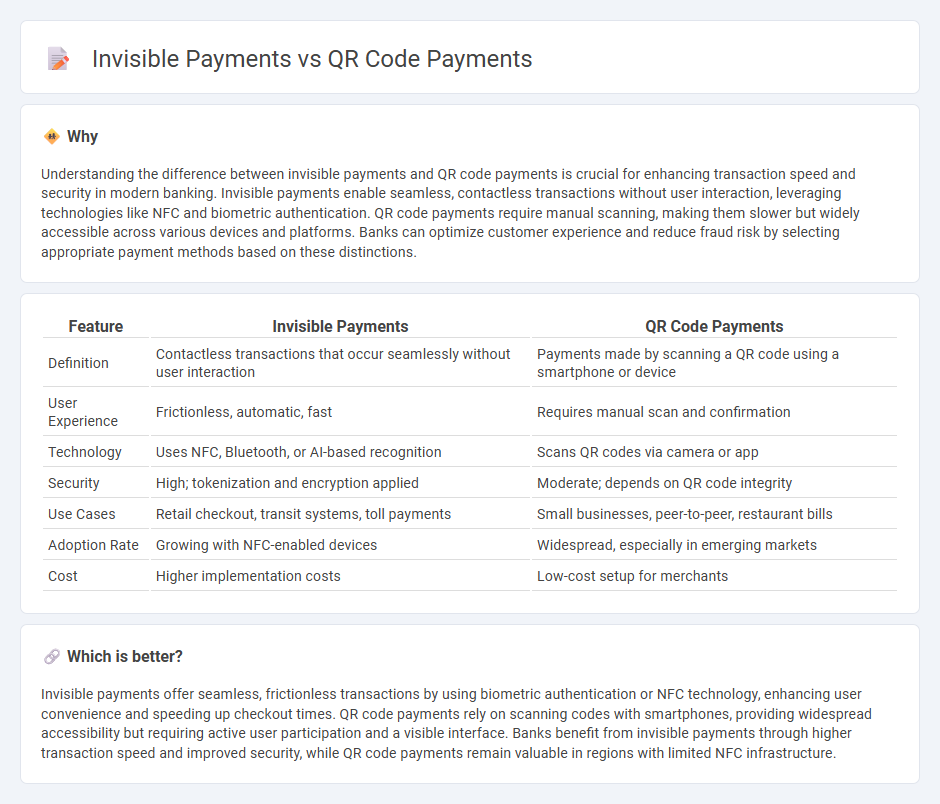
Understanding the difference between invisible payments and QR code payments is crucial for enhancing transaction speed and security in modern banking. Invisible payments enable seamless, contactless transactions without user interaction, leveraging technologies like NFC and biometric authentication. QR code payments require manual scanning, making them slower but widely accessible across various devices and platforms. Banks can optimize customer experience and reduce fraud risk by selecting appropriate payment methods based on these distinctions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Invisible Payments | QR Code Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contactless transactions that occur seamlessly without user interaction | Payments made by scanning a QR code using a smartphone or device |
| User Experience | Frictionless, automatic, fast | Requires manual scan and confirmation |
| Technology | Uses NFC, Bluetooth, or AI-based recognition | Scans QR codes via camera or app |
| Security | High; tokenization and encryption applied | Moderate; depends on QR code integrity |
| Use Cases | Retail checkout, transit systems, toll payments | Small businesses, peer-to-peer, restaurant bills |
| Adoption Rate | Growing with NFC-enabled devices | Widespread, especially in emerging markets |
| Cost | Higher implementation costs | Low-cost setup for merchants |
Which is better?
Invisible payments offer seamless, frictionless transactions by using biometric authentication or NFC technology, enhancing user convenience and speeding up checkout times. QR code payments rely on scanning codes with smartphones, providing widespread accessibility but requiring active user participation and a visible interface. Banks benefit from invisible payments through higher transaction speed and improved security, while QR code payments remain valuable in regions with limited NFC infrastructure.
Connection
Invisible payments leverage technologies such as NFC and biometric authentication to enable seamless transactions without physical cards, closely aligning with QR code payments that use user-scanned codes to initiate quick digital transfers. Both payment methods enhance security and convenience in banking by reducing cash handling and minimizing transaction time at retail points. The integration of these technologies supports the growing trend toward contactless, frictionless payment experiences in modern financial services.
Key Terms
Tokenization
Tokenization enhances security in both QR code payments and invisible payments by replacing sensitive card data with unique tokens, reducing fraud risks. QR code payments rely on tokenized information embedded in the code, facilitating secure and quick transactions, whereas invisible payments use tokenization behind the scenes for seamless, contactless processing without user interaction. Explore our in-depth analysis to understand how tokenization transforms payment security and user experience.
Authentication
QR code payments require user interaction for authentication, typically involving scanning the code and entering a PIN or biometric verification. Invisible payments leverage background authentication methods such as tokenization and behavioral biometrics to enable seamless, contactless transactions without explicit user input. Explore the evolving authentication technologies shaping the future of digital payments.
Merchant Identification
QR code payments rely on scanning a visible code linked directly to the merchant's unique identifier, ensuring clear and accurate merchant identification during transactions. Invisible payments utilize background technologies such as NFC or AI-driven recognition that authenticate the merchant seamlessly without requiring active user scanning. Explore how these technologies impact transaction security and customer experience by learning more about merchant identification in payment systems.
Source and External Links
A guide to QR code payments | Checkout.com - QR code payments, also called scan-to-pay, enable businesses to accept mobile payments by having customers scan a code that directs them to authorize a transfer, open a payment page, or send funds through a mobile app, making checkout easy and contactless.
QR code payment - Wikipedia - A QR code payment is a mobile payment method where the consumer scans a merchant's QR code with their smartphone, enters the payment amount, and submits, serving as a card-not-present alternative to traditional electronic payments without requiring specialized hardware like payment terminals.
The Rise of QR Code Payments: A Complete Guide for Businesses ... - QR code payments work by merchants generating static or dynamic QR codes which consumers scan with their mobile payment apps, authorize payments with PIN or biometric verification, and have the payment processed in real-time, offering a secure and seamless digital transaction experience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com