Pay by bank services enable direct payments from a consumer's bank account, offering enhanced security and reducing transaction fees compared to prepaid cards, which require pre-loading funds before use. Prepaid cards provide controlled spending limits and accessibility without a linked bank account, making them suitable for budgeting and unbanked users. Explore the differences in features and benefits between pay by bank and prepaid cards to determine the best option for your financial needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between pay by bank and prepaid card is crucial for managing transaction fees, security, and accessibility effectively. Pay by bank transactions typically offer direct access to funds with lower fees and stronger fraud protection through the banking system. Prepaid cards provide controlled spending limits and are ideal for budgeting but may have higher fees and limited recourse in disputes. Knowing these differences helps consumers choose the best payment method for their financial needs and security preferences.
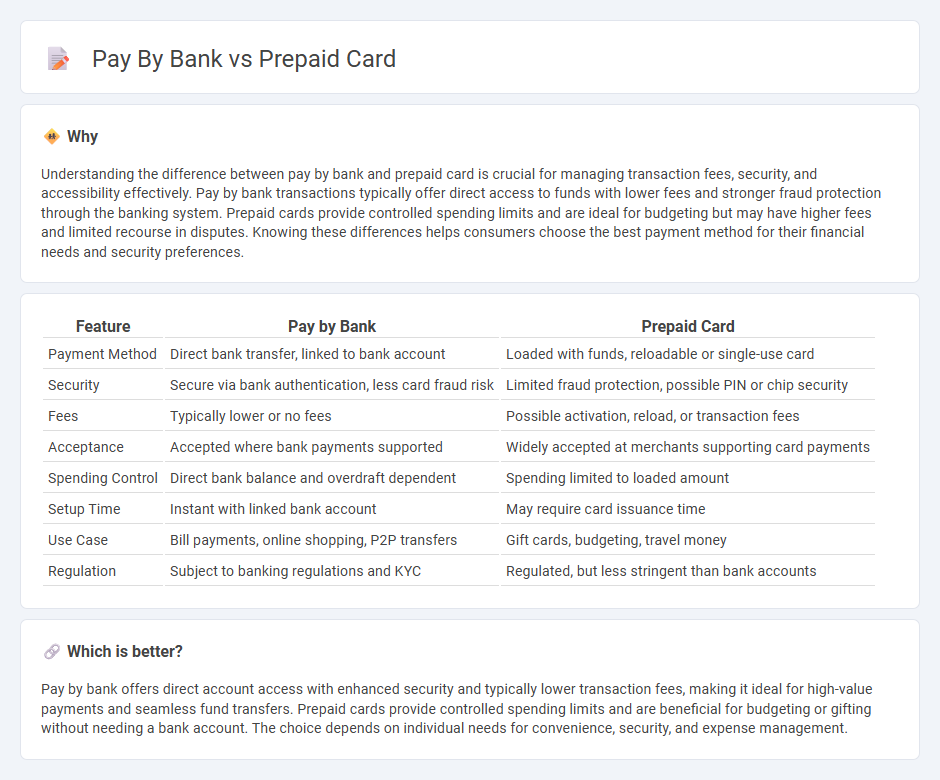
Comparison Table
| Feature | Pay by Bank | Prepaid Card |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Method | Direct bank transfer, linked to bank account | Loaded with funds, reloadable or single-use card |
| Security | Secure via bank authentication, less card fraud risk | Limited fraud protection, possible PIN or chip security |
| Fees | Typically lower or no fees | Possible activation, reload, or transaction fees |
| Acceptance | Accepted where bank payments supported | Widely accepted at merchants supporting card payments |
| Spending Control | Direct bank balance and overdraft dependent | Spending limited to loaded amount |
| Setup Time | Instant with linked bank account | May require card issuance time |
| Use Case | Bill payments, online shopping, P2P transfers | Gift cards, budgeting, travel money |
| Regulation | Subject to banking regulations and KYC | Regulated, but less stringent than bank accounts |
Which is better?
Pay by bank offers direct account access with enhanced security and typically lower transaction fees, making it ideal for high-value payments and seamless fund transfers. Prepaid cards provide controlled spending limits and are beneficial for budgeting or gifting without needing a bank account. The choice depends on individual needs for convenience, security, and expense management.
Connection
Pay by bank services enable direct payments from a consumer's bank account, offering a secure alternative to traditional card payments by reducing reliance on card networks. Prepaid cards, funded in advance with a set balance, often link to a bank account or digital wallet, facilitating controlled spending without overdraft risks. Both payment methods leverage electronic banking infrastructure to provide seamless, real-time transactions that enhance financial management and reduce fraud.
Key Terms
Stored Value
Prepaid cards store a fixed monetary value loaded in advance, allowing users to spend only the available balance without credit risk, while pay by bank services directly debit funds from the user's bank account, offering real-time transaction authorization and eliminating the need for preloading. Stored value on prepaid cards provides budgeting control and limits overspending, whereas pay by bank transactions reflect live account balances, ensuring seamless payment processing. Learn more about the advantages and operational differences between prepaid cards and pay by bank methods to choose the best payment solution.
Direct Account Debit
Direct Account Debit enables seamless payments directly from a bank account, offering real-time authorization and enhanced security compared to prepaid cards that rely on preloaded funds. This method reduces the risk of declined transactions and simplifies account reconciliation for businesses by ensuring funds are available at payment time. Explore how Direct Account Debit can streamline your payment processes and improve cash flow management.
Settlement
Settlement with prepaid cards involves immediate fund availability as payments draw directly from preloaded balances, minimizing credit risk and enabling real-time transaction processing. Pay by bank settlement relies on direct bank transfers, often involving slower clearing times through banking networks, which can affect transaction finality and settlement speed. Explore the differences in payment settlement mechanisms to optimize your transaction processing strategy.
Source and External Links
What Is a Prepaid Card and How Does It Work? - Prepaid cards allow purchases like credit and debit cards but require preloading funds, which act as a spending limit.
How do I shop for and buy a prepaid card? - This guide helps you purchase and register prepaid cards, which can be bought online or in retail stores, ensuring protection and eligibility for additional features.
Visa Prepaid Cards - Visa Prepaid cards offer a convenient reloadable option for making purchases and paying bills, accepted anywhere Visa Debit is accepted.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com