Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using fabricated personal information to open fraudulent bank accounts, while credential stuffing exploits stolen username and password combinations to gain unauthorized access to existing accounts. Both pose significant risks to banking security by enabling financial theft and increasing fraud losses. Discover strategies to safeguard your financial assets from these sophisticated cyber threats.
Why it is important
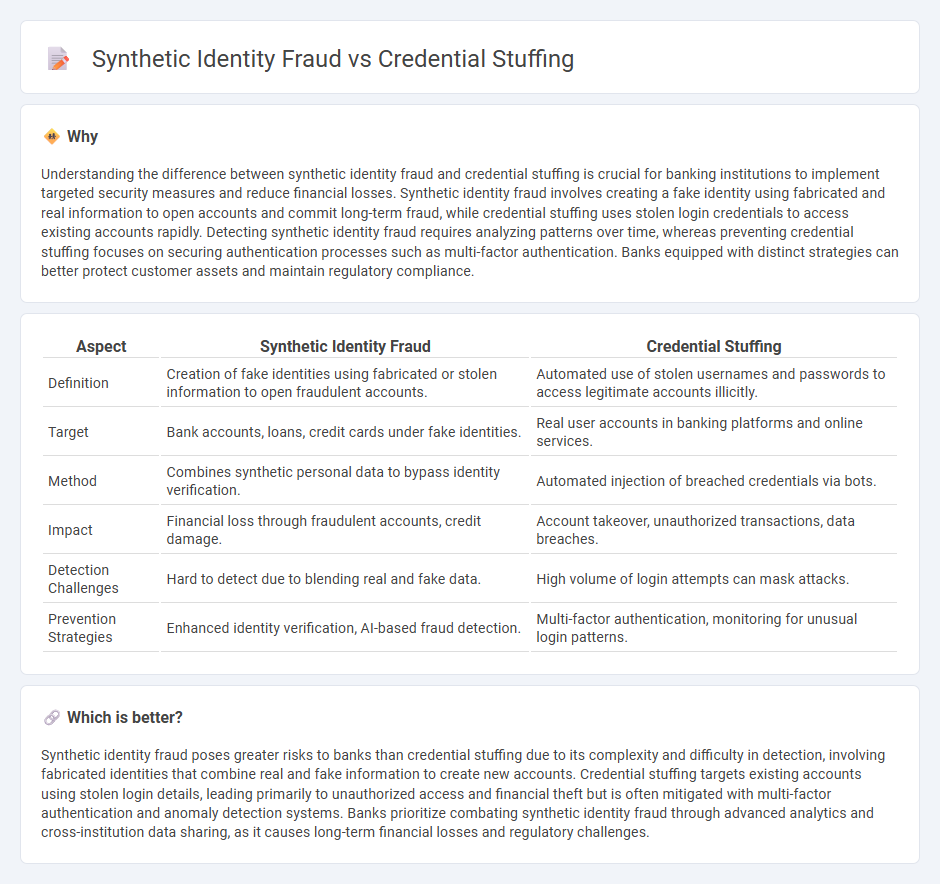
Understanding the difference between synthetic identity fraud and credential stuffing is crucial for banking institutions to implement targeted security measures and reduce financial losses. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating a fake identity using fabricated and real information to open accounts and commit long-term fraud, while credential stuffing uses stolen login credentials to access existing accounts rapidly. Detecting synthetic identity fraud requires analyzing patterns over time, whereas preventing credential stuffing focuses on securing authentication processes such as multi-factor authentication. Banks equipped with distinct strategies can better protect customer assets and maintain regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Identity Fraud | Credential Stuffing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of fake identities using fabricated or stolen information to open fraudulent accounts. | Automated use of stolen usernames and passwords to access legitimate accounts illicitly. |
| Target | Bank accounts, loans, credit cards under fake identities. | Real user accounts in banking platforms and online services. |
| Method | Combines synthetic personal data to bypass identity verification. | Automated injection of breached credentials via bots. |
| Impact | Financial loss through fraudulent accounts, credit damage. | Account takeover, unauthorized transactions, data breaches. |
| Detection Challenges | Hard to detect due to blending real and fake data. | High volume of login attempts can mask attacks. |
| Prevention Strategies | Enhanced identity verification, AI-based fraud detection. | Multi-factor authentication, monitoring for unusual login patterns. |
Which is better?
Synthetic identity fraud poses greater risks to banks than credential stuffing due to its complexity and difficulty in detection, involving fabricated identities that combine real and fake information to create new accounts. Credential stuffing targets existing accounts using stolen login details, leading primarily to unauthorized access and financial theft but is often mitigated with multi-factor authentication and anomaly detection systems. Banks prioritize combating synthetic identity fraud through advanced analytics and cross-institution data sharing, as it causes long-term financial losses and regulatory challenges.
Connection
Synthetic identity fraud and credential stuffing are interconnected through their exploitation of stolen or fabricated digital identities to gain unauthorized access to banking systems. Cybercriminals use credential stuffing to test large volumes of compromised login credentials against multiple banking platforms, facilitating the creation or activation of synthetic identities that blend real and fake information. This combination enables fraudsters to bypass security measures, access accounts, and execute unauthorized transactions, increasing financial institutions' vulnerability to losses and compliance risks.
Key Terms
Authentication
Credential stuffing exploits stolen username and password combinations to bypass authentication systems, often through automated login attempts, posing significant risks to digital security. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fabricated identities by combining real and fictitious information to manipulate authentication processes and gain unauthorized access or financial benefits. Explore how advanced authentication technologies combat these threats to enhance security protocols.
Identity Verification
Credential stuffing exploits stolen username and password pairs to gain unauthorized access, often bypassing weak identity verification methods. Synthetic identity fraud creates fake identities combining fabricated and stolen information, challenging traditional verification systems that rely on static data points. Explore advanced identity verification solutions to effectively detect and prevent these evolving cyber threats.
Fraud Detection
Credential stuffing exploits stolen usernames and passwords from data breaches to gain unauthorized access, often detected through anomalous login patterns and rapid-fire attempts. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fictitious identities by combining real and fabricated information, challenging fraud detection systems with subtle inconsistencies in application data and behavior. Explore advanced fraud detection techniques to effectively combat both credential stuffing and synthetic identity fraud.
Source and External Links
Credential stuffing - Wikipedia - Credential stuffing is a cyberattack where attackers use stolen username and password pairs from one breach to gain unauthorized access to accounts on other websites through automated login attempts.
Credential stuffing - OWASP Foundation - This attack involves automatically injecting stolen credentials into website login forms to fraudulently access user accounts, taking advantage of widespread password reuse across different services.
What Is Credential Stuffing? - Akamai - Attackers use bots to repeatedly try logging into websites with credentials bought from the dark web, targeting popular sites where users often reuse passwords, and may sell or misuse successfully accessed accounts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com