Invisible payments streamline transactions by eliminating the need for physical cards or cash, using technologies like biometric authentication and proximity sensors for seamless checkout experiences. Digital tokens enhance security by replacing sensitive payment information with encrypted unique identifiers, reducing fraud risks in online and mobile payments. Explore the impact of invisible payments and digital tokens on the future of banking security and convenience.
Why it is important
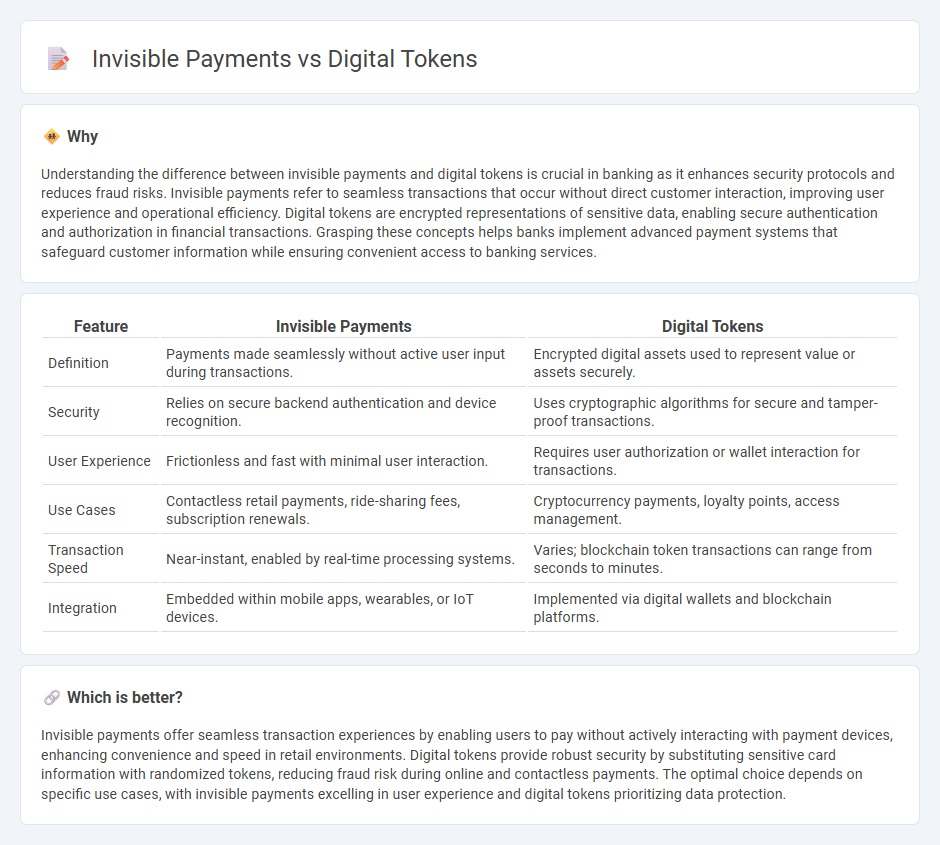
Understanding the difference between invisible payments and digital tokens is crucial in banking as it enhances security protocols and reduces fraud risks. Invisible payments refer to seamless transactions that occur without direct customer interaction, improving user experience and operational efficiency. Digital tokens are encrypted representations of sensitive data, enabling secure authentication and authorization in financial transactions. Grasping these concepts helps banks implement advanced payment systems that safeguard customer information while ensuring convenient access to banking services.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Invisible Payments | Digital Tokens |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Payments made seamlessly without active user input during transactions. | Encrypted digital assets used to represent value or assets securely. |
| Security | Relies on secure backend authentication and device recognition. | Uses cryptographic algorithms for secure and tamper-proof transactions. |
| User Experience | Frictionless and fast with minimal user interaction. | Requires user authorization or wallet interaction for transactions. |
| Use Cases | Contactless retail payments, ride-sharing fees, subscription renewals. | Cryptocurrency payments, loyalty points, access management. |
| Transaction Speed | Near-instant, enabled by real-time processing systems. | Varies; blockchain token transactions can range from seconds to minutes. |
| Integration | Embedded within mobile apps, wearables, or IoT devices. | Implemented via digital wallets and blockchain platforms. |
Which is better?
Invisible payments offer seamless transaction experiences by enabling users to pay without actively interacting with payment devices, enhancing convenience and speed in retail environments. Digital tokens provide robust security by substituting sensitive card information with randomized tokens, reducing fraud risk during online and contactless payments. The optimal choice depends on specific use cases, with invisible payments excelling in user experience and digital tokens prioritizing data protection.
Connection
Invisible payments utilize digital tokens to securely authenticate and authorize transactions without physical cards or cash, enhancing convenience and speed. Digital tokens replace sensitive payment information with encrypted identifiers, reducing fraud risks and enabling seamless contactless payments across various platforms. This integration drives the evolution of banking by supporting secure, frictionless financial interactions in both online and offline environments.
Key Terms
**Digital tokens:**
Digital tokens represent secured, blockchain-based assets that facilitate transparent and traceable transactions, enhancing digital contract and asset management. These tokens can embody various values, including cryptocurrencies, utility tokens, or security tokens, providing versatility across financial services and digital ecosystems. Explore the benefits and applications of digital tokens in transforming payment systems and asset transfers.
Blockchain
Digital tokens represent ownership or access rights on a blockchain, enabling secure, transparent transactions without intermediaries. Invisible payments leverage blockchain technology to automate and streamline financial exchanges, reducing friction and enhancing user convenience through seamless, often contactless, transactions. Explore how blockchain innovations are reshaping payment systems and digital asset management.
Cryptography
Digital tokens utilize advanced cryptographic techniques such as public-key encryption and zero-knowledge proofs to secure transactions and authenticate user identities, ensuring data integrity and privacy. Invisible payments leverage cryptography to enable seamless, contactless transactions by encrypting payment details and minimizing user interaction, enhancing both security and user experience. Explore how cutting-edge cryptographic methods differentiate these payment technologies and drive innovation in secure digital commerce.
Source and External Links
What is a token? Understanding crypto tokens: Types and functionality - A digital token is a crypto asset representing ownership or value on a blockchain, with types including utility tokens, security tokens, governance tokens, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) serving various purposes.
8. What is a (digital) token? - ICMA - A digital token is any digital representation of an interest, value, or rights to benefits, stored on a blockchain or distributed ledger technology (DLT), often described as a digital envelope containing codified information.
What is a token? - Coinbase - Tokens are a form of cryptoasset or cryptocurrency that can include DeFi tokens, governance tokens, NFTs, and security tokens which can represent voting rights, ownership, or unique digital assets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com