Cloud core banking offers real-time accessibility, scalability, and enhanced data security by leveraging cloud infrastructure, enabling banks to rapidly adapt to market demands. Hosted core banking, while also using remote servers, typically involves dedicated environments with fixed resources, often resulting in limited flexibility and higher maintenance compared to cloud-native solutions. Discover the key differences and benefits to determine the best fit for modern banking institutions.
Why it is important
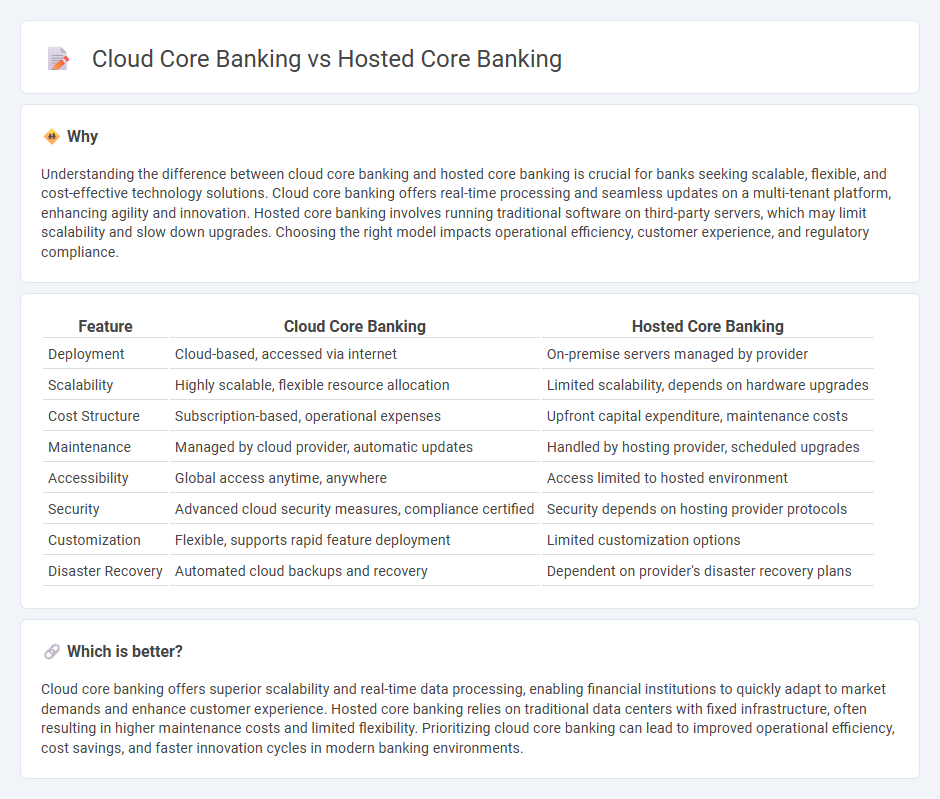
Understanding the difference between cloud core banking and hosted core banking is crucial for banks seeking scalable, flexible, and cost-effective technology solutions. Cloud core banking offers real-time processing and seamless updates on a multi-tenant platform, enhancing agility and innovation. Hosted core banking involves running traditional software on third-party servers, which may limit scalability and slow down upgrades. Choosing the right model impacts operational efficiency, customer experience, and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Core Banking | Hosted Core Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Cloud-based, accessed via internet | On-premise servers managed by provider |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, flexible resource allocation | Limited scalability, depends on hardware upgrades |
| Cost Structure | Subscription-based, operational expenses | Upfront capital expenditure, maintenance costs |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud provider, automatic updates | Handled by hosting provider, scheduled upgrades |
| Accessibility | Global access anytime, anywhere | Access limited to hosted environment |
| Security | Advanced cloud security measures, compliance certified | Security depends on hosting provider protocols |
| Customization | Flexible, supports rapid feature deployment | Limited customization options |
| Disaster Recovery | Automated cloud backups and recovery | Dependent on provider's disaster recovery plans |
Which is better?
Cloud core banking offers superior scalability and real-time data processing, enabling financial institutions to quickly adapt to market demands and enhance customer experience. Hosted core banking relies on traditional data centers with fixed infrastructure, often resulting in higher maintenance costs and limited flexibility. Prioritizing cloud core banking can lead to improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and faster innovation cycles in modern banking environments.
Connection
Cloud core banking and hosted core banking are interconnected through their reliance on cloud infrastructure to deliver banking services efficiently and securely. Cloud core banking leverages scalable, remotely managed platforms that enable real-time processing and seamless integration with digital channels. Hosted core banking operates within this ecosystem by providing dedicated environments on cloud servers, ensuring optimized performance and compliance with regulatory standards.
Key Terms
On-premises infrastructure
On-premises core banking relies on dedicated physical infrastructure within a financial institution's own data centers, providing direct control over hardware, security configurations, and data management. This setup typically offers lower latency and compliance advantages but requires significant capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance resources. Discover how choosing on-premises infrastructure can influence your bank's operational efficiency and data sovereignty.
Multi-tenant architecture
Hosted core banking systems typically use a single-tenant architecture, where each bank operates on dedicated servers, ensuring more control but higher maintenance costs. Cloud core banking platforms employ a multi-tenant architecture, allowing multiple banks to share the same infrastructure, optimizing resource utilization and scalability while enhancing cost efficiency. Explore the advantages of multi-tenant cloud core banking to understand how it transforms banking operations.
Scalability
Hosted core banking relies on on-premises infrastructure that may limit rapid scalability due to physical hardware constraints, often necessitating significant investment and time for capacity expansion. Cloud core banking platforms offer highly elastic scalability supported by cloud service providers, enabling banks to dynamically adjust resources in real-time in response to fluctuating demand. Explore the benefits of scalability in cloud core banking solutions to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
What is Core Banking? - IBM - Core banking refers to a centralized online real-time system that serves as the back-end hub for multiple bank branches, allowing seamless customer transactions from any location; it can be hosted on-premises or cloud-based, with hosted systems managed by third parties to provide secure, stable banking operations.
Hosted Core Processing Solution - Finovifi - Hosted core banking solutions relocate a bank's servers and equipment to a secure, managed data center, offering benefits like automated backups, continuous security monitoring, disaster recovery, and full network administration to simplify bank operations and improve reliability.
Core Banking Solutions | CSI - CSI provides a cloud-based hosted core banking platform that automates and integrates essential banking functions such as onboarding, loan servicing, deposits, and withdrawals, focusing on compliance, security, and customer support to enable banks to focus on business growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com