Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using a mix of real and fabricated information to deceive banking systems and obtain credit or services. Phishing attacks target individuals by tricking them into revealing personal banking credentials through fraudulent emails or websites. Explore the differences between these banking threats to better protect your financial assets.
Why it is important
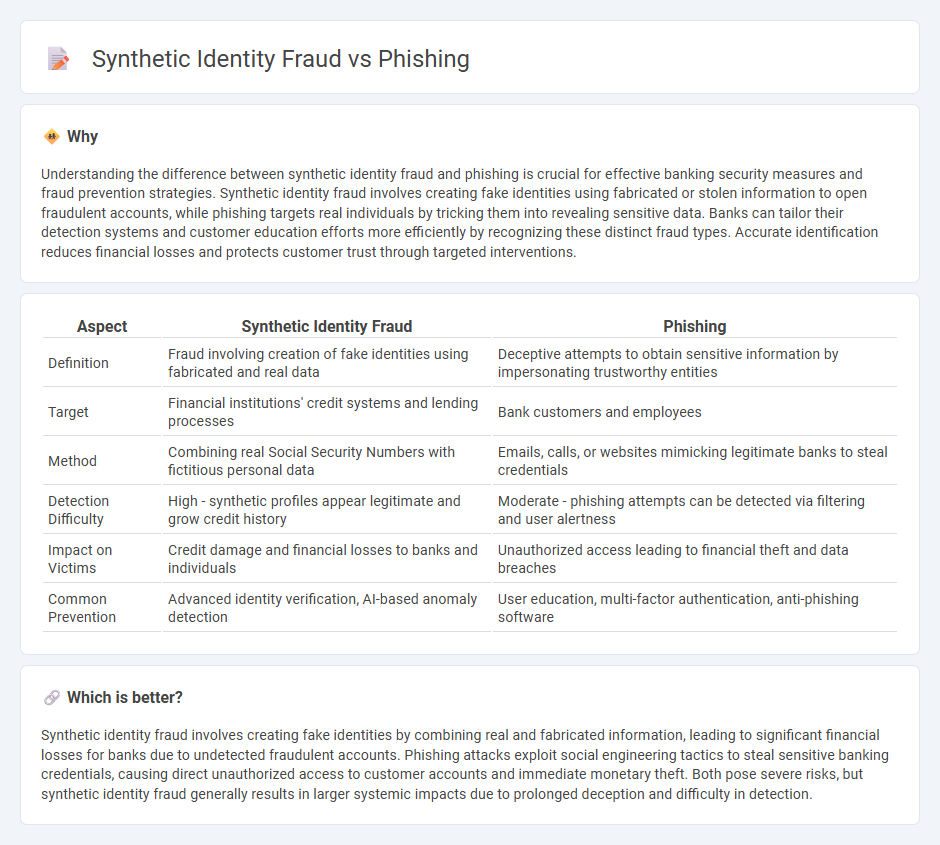
Understanding the difference between synthetic identity fraud and phishing is crucial for effective banking security measures and fraud prevention strategies. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using fabricated or stolen information to open fraudulent accounts, while phishing targets real individuals by tricking them into revealing sensitive data. Banks can tailor their detection systems and customer education efforts more efficiently by recognizing these distinct fraud types. Accurate identification reduces financial losses and protects customer trust through targeted interventions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Synthetic Identity Fraud | Phishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fraud involving creation of fake identities using fabricated and real data | Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information by impersonating trustworthy entities |
| Target | Financial institutions' credit systems and lending processes | Bank customers and employees |
| Method | Combining real Social Security Numbers with fictitious personal data | Emails, calls, or websites mimicking legitimate banks to steal credentials |
| Detection Difficulty | High - synthetic profiles appear legitimate and grow credit history | Moderate - phishing attempts can be detected via filtering and user alertness |
| Impact on Victims | Credit damage and financial losses to banks and individuals | Unauthorized access leading to financial theft and data breaches |
| Common Prevention | Advanced identity verification, AI-based anomaly detection | User education, multi-factor authentication, anti-phishing software |
Which is better?
Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities by combining real and fabricated information, leading to significant financial losses for banks due to undetected fraudulent accounts. Phishing attacks exploit social engineering tactics to steal sensitive banking credentials, causing direct unauthorized access to customer accounts and immediate monetary theft. Both pose severe risks, but synthetic identity fraud generally results in larger systemic impacts due to prolonged deception and difficulty in detection.
Connection
Synthetic identity fraud often relies on phishing attacks to gather personal information by deceiving individuals into revealing sensitive data. Cybercriminals use phishing schemes to obtain fragments of identity details, which they then combine to create synthetic identities for fraudulent banking activities. This interconnected process increases vulnerability within financial institutions, leading to significant financial losses and regulatory challenges.
Key Terms
Authentication
Phishing attacks exploit weak authentication by tricking users into revealing credentials, while synthetic identity fraud circumvents authentication by creating fabricated identities that pass verification checks. Effective authentication strategies, including multi-factor authentication and biometric verification, can mitigate risks from both phishing and synthetic identity fraud. Discover advanced authentication techniques to protect against these evolving threats.
Social Engineering
Phishing attacks exploit social engineering by deceiving individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords or financial details through fake emails or websites. Synthetic identity fraud combines real and fabricated data to create new identities, often manipulated via social engineering tactics to gain trust and access financial services. Explore the distinct methods and defense strategies against these social engineering threats to protect your digital identity.
Identity Fabrication
Phishing involves tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information, while synthetic identity fraud centers on creating entirely fabricated identities by combining real and fake data to exploit financial systems. Identity fabrication in synthetic fraud allows criminals to bypass traditional verification methods and establish credit histories that appear legitimate. Explore the nuances of identity fabrication techniques to better understand and prevent evolving fraud tactics.
Source and External Links
What Is Phishing? - Meaning, Attack Types & More - Phishing is a cyber-attack using deceptive communication such as emails or texts to trick victims into revealing sensitive information like login credentials or financial data, leveraging psychological manipulation rather than technical flaws.
What is phishing? | Phishing attack prevention - Phishing involves tricking users into divulging sensitive information by impersonating reputable sources, often leading to stolen data like passwords or credit card numbers used for malicious purposes.
Protect yourself from phishing - Phishing attacks attempt to steal money or identity by masquerading as legitimate entities and prompting urgent actions from victims, such as revealing passwords or bank details on fake websites.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com