Digital identity verification leverages advanced technologies such as biometrics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain to authenticate users quickly and securely, reducing fraud and enhancing customer experience. Manual document verification relies on physical inspection of identification papers by human agents, often resulting in slower processing times and higher error rates. Explore how digital solutions are transforming banking security and efficiency compared to traditional methods.
Why it is important
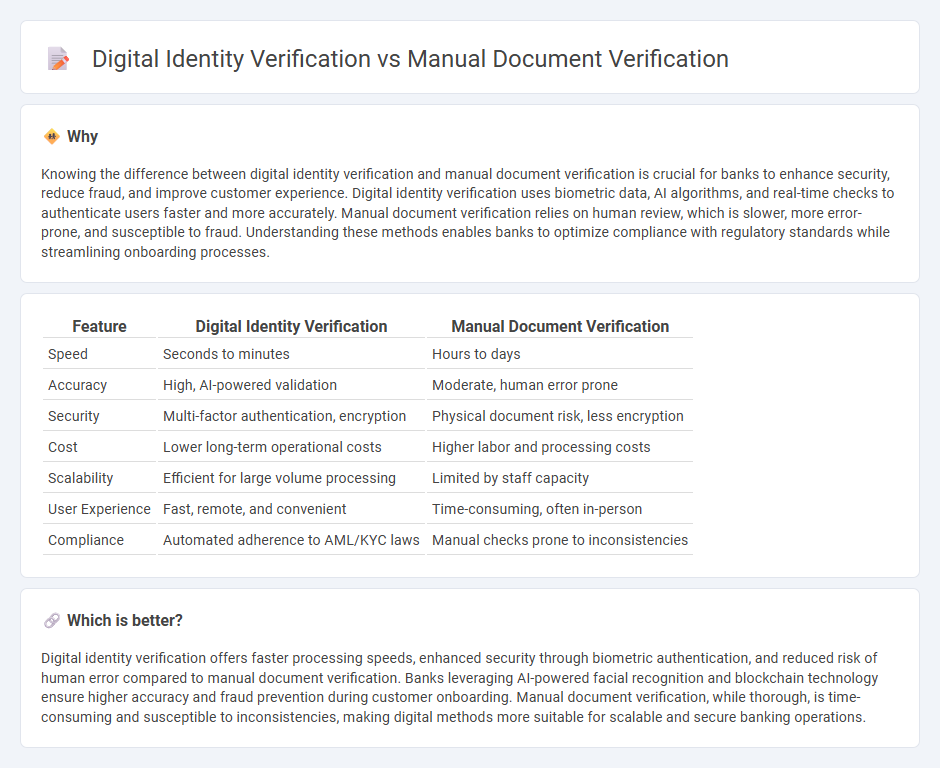
Knowing the difference between digital identity verification and manual document verification is crucial for banks to enhance security, reduce fraud, and improve customer experience. Digital identity verification uses biometric data, AI algorithms, and real-time checks to authenticate users faster and more accurately. Manual document verification relies on human review, which is slower, more error-prone, and susceptible to fraud. Understanding these methods enables banks to optimize compliance with regulatory standards while streamlining onboarding processes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Identity Verification | Manual Document Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Seconds to minutes | Hours to days |
| Accuracy | High, AI-powered validation | Moderate, human error prone |
| Security | Multi-factor authentication, encryption | Physical document risk, less encryption |
| Cost | Lower long-term operational costs | Higher labor and processing costs |
| Scalability | Efficient for large volume processing | Limited by staff capacity |
| User Experience | Fast, remote, and convenient | Time-consuming, often in-person |
| Compliance | Automated adherence to AML/KYC laws | Manual checks prone to inconsistencies |
Which is better?
Digital identity verification offers faster processing speeds, enhanced security through biometric authentication, and reduced risk of human error compared to manual document verification. Banks leveraging AI-powered facial recognition and blockchain technology ensure higher accuracy and fraud prevention during customer onboarding. Manual document verification, while thorough, is time-consuming and susceptible to inconsistencies, making digital methods more suitable for scalable and secure banking operations.
Connection
Digital identity verification and manual document verification are interconnected processes that enhance banking security and customer onboarding. Digital identity verification uses biometric data and AI-powered tools to validate identities instantly, while manual document verification involves human experts examining physical or scanned documents for authenticity. Combining these methods reduces fraud risk, accelerates transaction approvals, and ensures regulatory compliance in banking operations.
Key Terms
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Manual document verification in KYC involves physical inspection of identity proofs, resulting in slower processing times and higher risk of human error, whereas digital identity verification leverages biometric data, AI algorithms, and real-time database checks to enhance accuracy and speed. Digital KYC solutions reduce fraud, improve customer onboarding, and ensure compliance with global regulations such as AML and GDPR more efficiently than traditional methods. Explore advanced digital identity verification to optimize your KYC processes and strengthen security protocols.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
Manual document verification in AML processes involves physical inspection and human validation of identity documents, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Digital identity verification leverages biometric data, AI, and database cross-referencing to quickly and accurately authenticate identities, enhancing compliance with AML regulations and reducing fraud risk. Explore advanced digital verification solutions to streamline AML compliance and improve security.
Biometric Authentication
Manual document verification relies heavily on physical inspection and human judgment, often leading to delays and increased risk of errors or fraud. Digital identity verification utilizing biometric authentication--such as facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and iris detection--ensures higher accuracy, speed, and security by leveraging automated algorithms and AI-driven analysis. Explore how integrating biometric technologies can revolutionize identity verification processes and enhance compliance.
Source and External Links
Document Verification: Meaning & Importance - Incode - Manual document verification involves human reviewers checking physical or digital copies of customer documents and comparing them with company records to confirm authenticity and accuracy.
What is Manual Identity Verification? - Caf.io - Manual identity verification is conducted by trained experts who inspect document security features, personal information, and photo likeness, either in person or remotely, to ensure the submitted ID belongs to the actual user.
Manual vs. Automated Document Verification: What to Choose? - Manual verification is slower and less scalable than automated solutions, relying on employees to personally assess document authenticity, which can be prone to human error and inefficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com