Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns while supporting ethical and eco-friendly business practices. Positive screening focuses on selecting companies with strong ESG performance, actively avoiding those with negative social or environmental impacts. Explore the differences and benefits of these strategies to enhance your banking portfolio with responsible investment options.
Why it is important
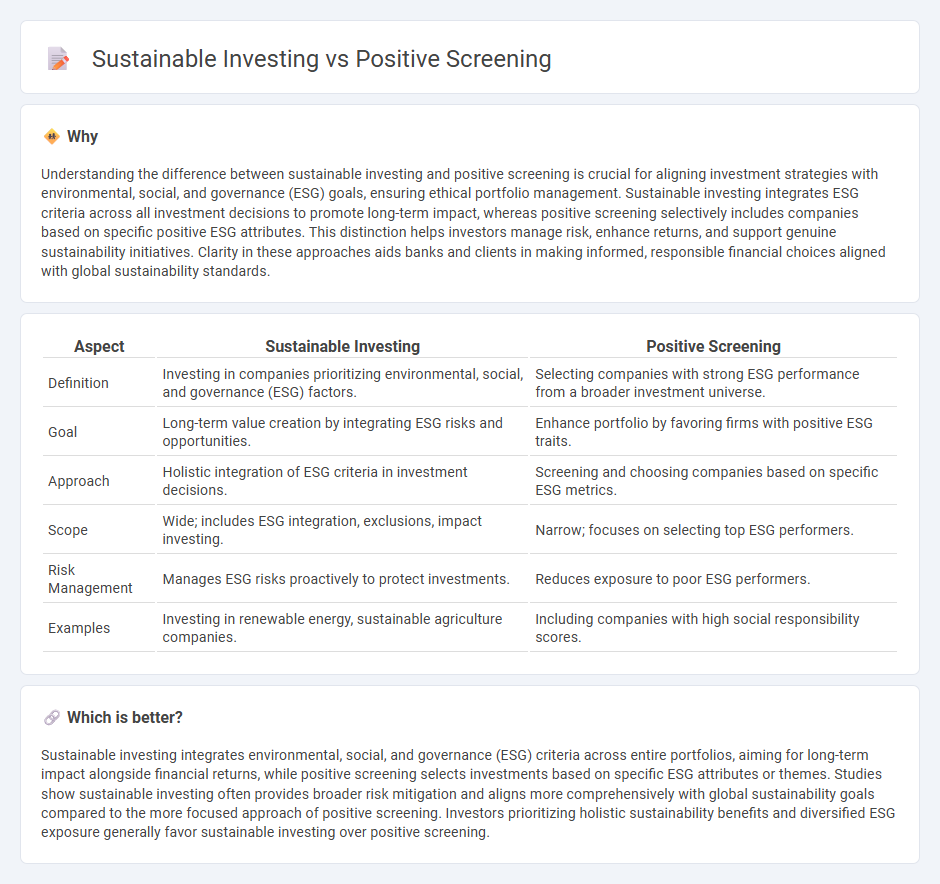
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and positive screening is crucial for aligning investment strategies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals, ensuring ethical portfolio management. Sustainable investing integrates ESG criteria across all investment decisions to promote long-term impact, whereas positive screening selectively includes companies based on specific positive ESG attributes. This distinction helps investors manage risk, enhance returns, and support genuine sustainability initiatives. Clarity in these approaches aids banks and clients in making informed, responsible financial choices aligned with global sustainability standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Positive Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing in companies prioritizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. | Selecting companies with strong ESG performance from a broader investment universe. |
| Goal | Long-term value creation by integrating ESG risks and opportunities. | Enhance portfolio by favoring firms with positive ESG traits. |
| Approach | Holistic integration of ESG criteria in investment decisions. | Screening and choosing companies based on specific ESG metrics. |
| Scope | Wide; includes ESG integration, exclusions, impact investing. | Narrow; focuses on selecting top ESG performers. |
| Risk Management | Manages ESG risks proactively to protect investments. | Reduces exposure to poor ESG performers. |
| Examples | Investing in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture companies. | Including companies with high social responsibility scores. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria across entire portfolios, aiming for long-term impact alongside financial returns, while positive screening selects investments based on specific ESG attributes or themes. Studies show sustainable investing often provides broader risk mitigation and aligns more comprehensively with global sustainability goals compared to the more focused approach of positive screening. Investors prioritizing holistic sustainability benefits and diversified ESG exposure generally favor sustainable investing over positive screening.
Connection
Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to guide investment decisions that support long-term ecological balance. Positive screening enhances this approach by deliberately selecting companies with strong ESG performance, fostering responsible corporate behavior. Both strategies drive capital towards businesses that contribute to sustainable development and financial resilience.
Key Terms
ESG Criteria
Positive screening involves selecting investments based on specific ESG criteria such as carbon footprint reduction or gender diversity, aiming to identify companies with strong environmental, social, and governance practices. Sustainable investing integrates ESG factors into the overall investment process to promote long-term value creation and mitigate risks associated with sustainability issues. Explore further to understand how these strategies shape responsible investment portfolios.
Portfolio Selection
Positive screening in portfolio selection involves choosing assets that meet specific environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, effectively filtering companies with desirable sustainability practices. Sustainable investing goes beyond screening by integrating ESG factors into the overall investment strategy to drive long-term impact and financial returns. Explore how these approaches can optimize portfolio performance while advancing responsible investment goals.
Impact Assessment
Positive screening selects investments based on specific ESG criteria, targeting companies with strong environmental, social, and governance performance. Sustainable investing incorporates impact assessment to evaluate the actual social and environmental outcomes of investments, ensuring alignment with broader sustainability goals. Explore how integrating impact assessment can enhance the effectiveness of sustainable investing strategies.
Source and External Links
Screening tests: a review with examples - PMC - Positive screening in medical testing refers to a result indicating that a person is at increased risk for a particular disease, warranting further diagnostic evaluation, but does not confirm the presence of the disease itself.
A Screen Positive Result: What does it mean and what do I do now? - Perinatal Services BC - In prenatal screening, a positive result (screen positive) means the chance of having a condition like Down syndrome is higher than a certain cut-off, leading to an offer of more definitive diagnostic testing, even though most people with this result do not actually have the condition.
Disease Screening - Statistics Teaching Tools - Positive predictive value measures the probability that someone with a positive screening test truly has the disease, and it is influenced by the test's sensitivity, specificity, and the prevalence of the disease in the population being screened.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com