Cloud migration in banking offers enhanced scalability, cost efficiency, and real-time data processing compared to legacy system integration, which often involves high maintenance costs and limited flexibility. Migrating to cloud platforms supports advanced analytics, improved customer experiences, and robust security measures essential for modern financial services. Explore the advantages and challenges of cloud migration versus legacy integration to optimize your bank's technology strategy.
Why it is important
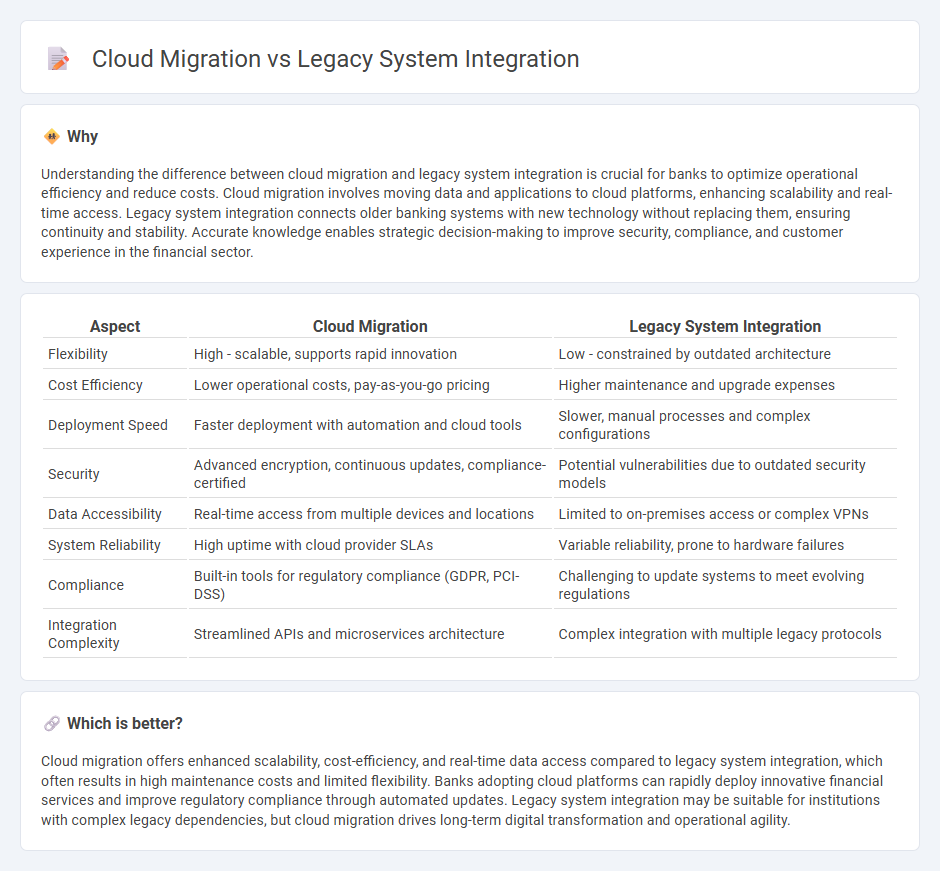
Understanding the difference between cloud migration and legacy system integration is crucial for banks to optimize operational efficiency and reduce costs. Cloud migration involves moving data and applications to cloud platforms, enhancing scalability and real-time access. Legacy system integration connects older banking systems with new technology without replacing them, ensuring continuity and stability. Accurate knowledge enables strategic decision-making to improve security, compliance, and customer experience in the financial sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cloud Migration | Legacy System Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High - scalable, supports rapid innovation | Low - constrained by outdated architecture |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs, pay-as-you-go pricing | Higher maintenance and upgrade expenses |
| Deployment Speed | Faster deployment with automation and cloud tools | Slower, manual processes and complex configurations |
| Security | Advanced encryption, continuous updates, compliance-certified | Potential vulnerabilities due to outdated security models |
| Data Accessibility | Real-time access from multiple devices and locations | Limited to on-premises access or complex VPNs |
| System Reliability | High uptime with cloud provider SLAs | Variable reliability, prone to hardware failures |
| Compliance | Built-in tools for regulatory compliance (GDPR, PCI-DSS) | Challenging to update systems to meet evolving regulations |
| Integration Complexity | Streamlined APIs and microservices architecture | Complex integration with multiple legacy protocols |
Which is better?
Cloud migration offers enhanced scalability, cost-efficiency, and real-time data access compared to legacy system integration, which often results in high maintenance costs and limited flexibility. Banks adopting cloud platforms can rapidly deploy innovative financial services and improve regulatory compliance through automated updates. Legacy system integration may be suitable for institutions with complex legacy dependencies, but cloud migration drives long-term digital transformation and operational agility.
Connection
Cloud migration enhances banking efficiency by enabling seamless integration with legacy systems, ensuring data consistency and operational continuity. Integrating legacy systems during cloud migration minimizes downtime and preserves critical transactional data, facilitating scalable and secure banking environments. This connection allows financial institutions to leverage advanced cloud capabilities while maintaining compliance and service reliability.
Key Terms
Middleware
Middleware plays a crucial role in legacy system integration by enabling communication and data exchange between disparate on-premises applications, ensuring seamless interoperability without extensive system overhaul. In cloud migration, middleware facilitates the transition by acting as a bridge between existing legacy systems and new cloud-native services, supporting hybrid environments and gradual modernization. Explore the latest middleware strategies to optimize both legacy integration and cloud migration efforts.
API Gateway
Legacy system integration often relies on API Gateways to facilitate communication between outdated software and modern applications, ensuring secure and scalable data exchange. Cloud migration leverages API Gateways to manage microservices and enable seamless access to cloud-native resources, optimizing performance and reliability. Explore further to understand how API Gateway strategies differ in these contexts and drive digital transformation.
Data Synchronization
Data synchronization in legacy system integration ensures consistent and accurate data flow between on-premises applications and newer platforms, minimizing disruption and maintaining operational integrity. Cloud migration often requires redesigning data synchronization processes to accommodate cloud-native architectures, supporting real-time updates, scalability, and enhanced data accessibility. Explore detailed strategies and best practices for achieving seamless data synchronization across legacy and cloud environments.
Source and External Links
Integrating Legacy Systems: How to Do It and What to Watch Out for - Legacy system integration connects older, established systems--such as mainframes, traditional databases, and message queues--with modern applications and platforms to preserve core functionality and enable gradual modernization without disrupting critical business operations.
What is Legacy System Integration? - SnapLogic - Legacy system integration involves using tools like APIs, middleware (ESB), and data integration platforms to enable communication and data exchange between outdated legacy systems and newer technologies, often without modifying the original system code.
How to Integrate Legacy Systems: Top Challenges and Strategies - Successful integration requires clearly defining objectives, assessing the legacy system's capabilities, and engaging all relevant teams to ensure requirements are met before proceeding with connecting legacy and modern systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com