Virtual cards provide secure, single-use numbers linked to your primary account, reducing fraud risk during online transactions. Payment gateways act as intermediaries that authorize and process payments between merchants and customers, ensuring smooth and encrypted fund transfers. Explore in-depth insights to understand which solution best fits your business needs.
Why it is important
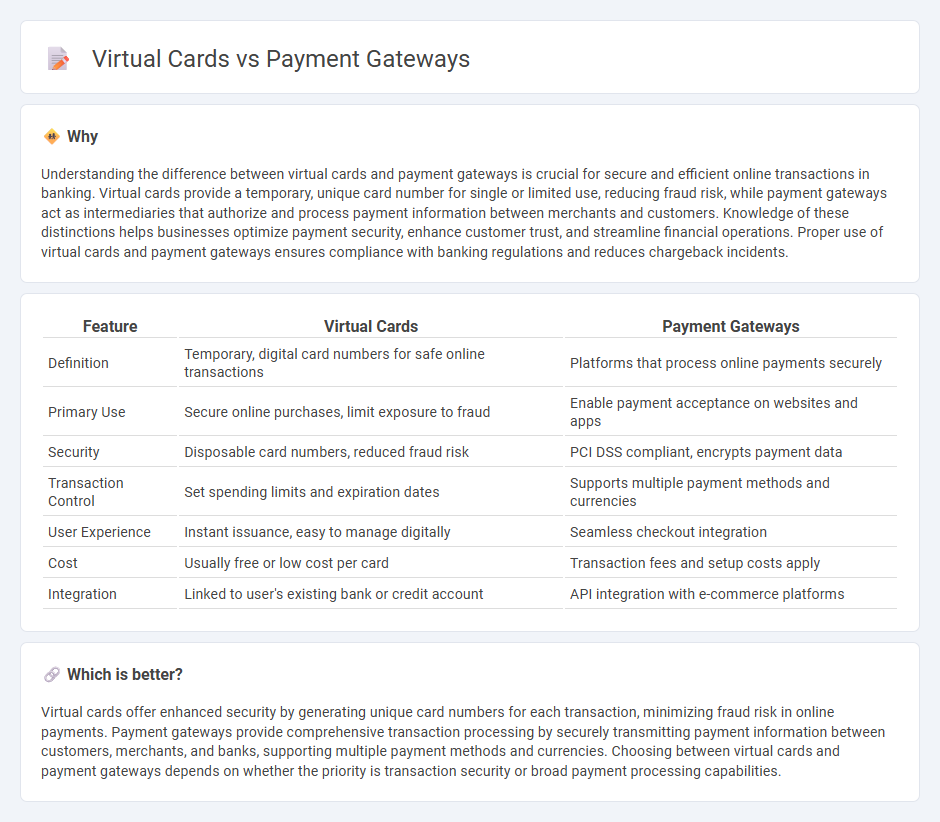
Understanding the difference between virtual cards and payment gateways is crucial for secure and efficient online transactions in banking. Virtual cards provide a temporary, unique card number for single or limited use, reducing fraud risk, while payment gateways act as intermediaries that authorize and process payment information between merchants and customers. Knowledge of these distinctions helps businesses optimize payment security, enhance customer trust, and streamline financial operations. Proper use of virtual cards and payment gateways ensures compliance with banking regulations and reduces chargeback incidents.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Virtual Cards | Payment Gateways |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary, digital card numbers for safe online transactions | Platforms that process online payments securely |
| Primary Use | Secure online purchases, limit exposure to fraud | Enable payment acceptance on websites and apps |
| Security | Disposable card numbers, reduced fraud risk | PCI DSS compliant, encrypts payment data |
| Transaction Control | Set spending limits and expiration dates | Supports multiple payment methods and currencies |
| User Experience | Instant issuance, easy to manage digitally | Seamless checkout integration |
| Cost | Usually free or low cost per card | Transaction fees and setup costs apply |
| Integration | Linked to user's existing bank or credit account | API integration with e-commerce platforms |
Which is better?
Virtual cards offer enhanced security by generating unique card numbers for each transaction, minimizing fraud risk in online payments. Payment gateways provide comprehensive transaction processing by securely transmitting payment information between customers, merchants, and banks, supporting multiple payment methods and currencies. Choosing between virtual cards and payment gateways depends on whether the priority is transaction security or broad payment processing capabilities.
Connection
Virtual cards function as digital payment instruments linked to a user's bank account or credit line, facilitating secure online transactions. Payment gateways act as intermediaries that authorize and process these virtual card payments by encrypting sensitive information and ensuring seamless communication between the merchant's platform and financial institutions. The integration of virtual cards with payment gateways enhances transaction security, reduces fraud risks, and streamlines the checkout experience in e-commerce and digital banking ecosystems.
Key Terms
Transaction Authentication
Transaction authentication in payment gateways relies on multi-factor authentication (MFA) protocols and secure encryption methods like 3D Secure and tokenization to verify cardholder identity, reducing fraud risk. Virtual cards enhance transaction security by generating unique, single-use card numbers tied to specific merchants or transaction limits, offering dynamic control and preventing unauthorized use. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how each solution amplifies transactional security and fraud prevention.
Tokenization
Payment gateways securely process transactions by encrypting card details, while virtual cards enhance security through tokenization, replacing sensitive data with unique tokens during each transaction. Tokenization reduces fraud risk by ensuring actual card information is never exposed or stored by merchants. Explore the benefits and implementation of tokenization in payment systems to boost transactional security.
Settlement Process
Payment gateways facilitate the authorization and processing of online transactions, transferring funds securely from customers to merchants, while settlement occurs through banks or acquiring institutions that finalize fund transfers to merchant accounts. Virtual cards, on the other hand, serve as secure payment instruments linked to specific accounts, enabling controlled spending and instant settlement on financial platforms or card issuers. Explore the detailed differences in settlement processes to optimize your payment strategy.
Source and External Links
Payment Gateways in 2025: Main Types + How They Work - Payment gateways are merchant services that process credit card payments for ecommerce and physical stores, with popular providers including PayPal, Square, Stripe, and Apple Pay, each offering specific features for online or in-person transactions and security.
Payment Gateways: What They Are And How To Choose One - A payment gateway acts as an intermediary that securely captures and transmits payment data between customers, merchants, and banks, supporting encryption and PCI DSS compliance to prevent fraud in online transactions.
Payment gateway - A payment gateway authorizes credit card or direct payment processing by connecting payment portals like websites or apps to acquiring banks or processors, enabling e-commerce, in-app, and point-of-sale payments across various payment methods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com