Behavioral biometrics analyze unique patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and touchscreen gestures to verify user identity beyond traditional passwords. Passwords remain vulnerable to theft, reuse, and phishing attacks, while behavioral biometrics provide continuous, dynamic authentication enhancing security in banking systems. Explore how integrating behavioral biometrics can transform password-based authentication for safer banking experiences.
Why it is important
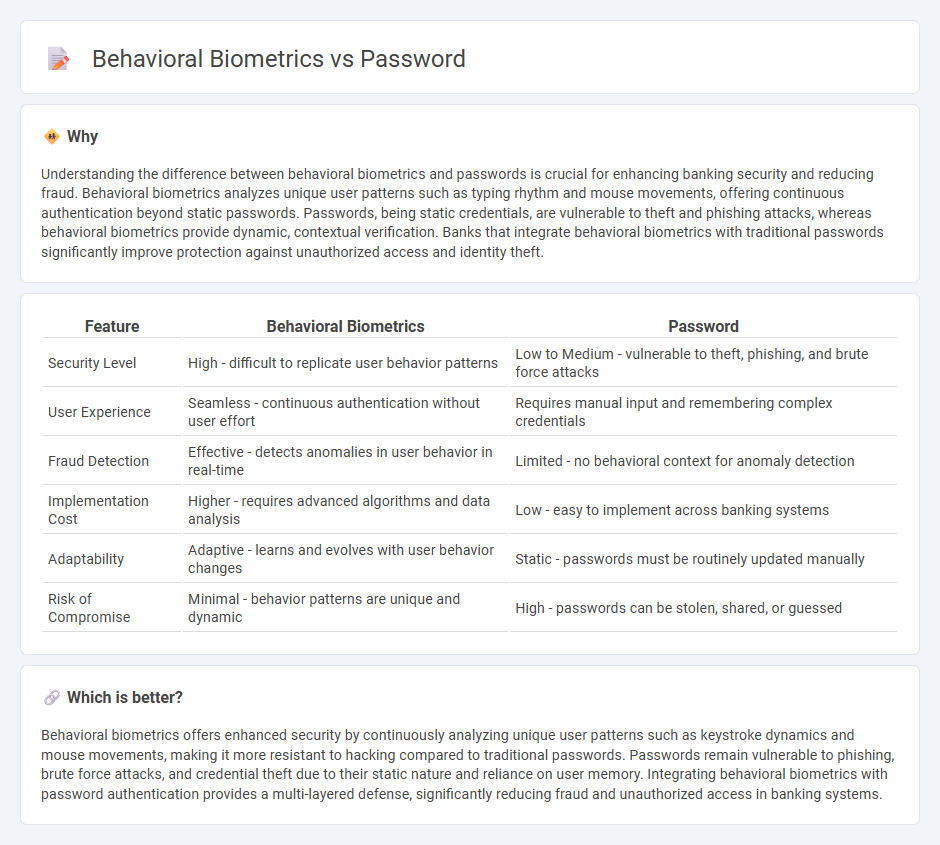
Understanding the difference between behavioral biometrics and passwords is crucial for enhancing banking security and reducing fraud. Behavioral biometrics analyzes unique user patterns such as typing rhythm and mouse movements, offering continuous authentication beyond static passwords. Passwords, being static credentials, are vulnerable to theft and phishing attacks, whereas behavioral biometrics provide dynamic, contextual verification. Banks that integrate behavioral biometrics with traditional passwords significantly improve protection against unauthorized access and identity theft.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Behavioral Biometrics | Password |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | High - difficult to replicate user behavior patterns | Low to Medium - vulnerable to theft, phishing, and brute force attacks |
| User Experience | Seamless - continuous authentication without user effort | Requires manual input and remembering complex credentials |
| Fraud Detection | Effective - detects anomalies in user behavior in real-time | Limited - no behavioral context for anomaly detection |
| Implementation Cost | Higher - requires advanced algorithms and data analysis | Low - easy to implement across banking systems |
| Adaptability | Adaptive - learns and evolves with user behavior changes | Static - passwords must be routinely updated manually |
| Risk of Compromise | Minimal - behavior patterns are unique and dynamic | High - passwords can be stolen, shared, or guessed |
Which is better?
Behavioral biometrics offers enhanced security by continuously analyzing unique user patterns such as keystroke dynamics and mouse movements, making it more resistant to hacking compared to traditional passwords. Passwords remain vulnerable to phishing, brute force attacks, and credential theft due to their static nature and reliance on user memory. Integrating behavioral biometrics with password authentication provides a multi-layered defense, significantly reducing fraud and unauthorized access in banking systems.
Connection
Behavioral biometrics enhances banking security by analyzing unique patterns such as keystroke dynamics, mouse movements, and touchscreen interactions to authenticate users beyond traditional password entry. Integrating behavioral biometrics with passwords creates a multi-factor authentication system, reducing the risk of unauthorized access due to stolen or compromised credentials. Financial institutions leverage this combination to detect anomalies in real-time, preventing fraud and ensuring secure online transactions.
Key Terms
Authentication
Passwords remain the most common authentication method despite vulnerabilities like phishing and credential theft. Behavioral biometrics analyze unique user patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, and touchscreen interactions to enhance security without requiring physical tokens. Explore how combining these methods can create robust, user-friendly authentication frameworks.
Security
Passwords remain a traditional security measure but are vulnerable to hacking, phishing, and brute-force attacks. Behavioral biometrics analyzes unique user patterns such as typing dynamics, mouse movements, and gait, providing enhanced fraud detection and continuous authentication. Explore the latest advancements in behavioral biometrics to strengthen your security framework.
User identification
Passwords rely on secret knowledge for user identification, often vulnerable to theft or guessing, while behavioral biometrics analyze unique user patterns such as typing rhythm, mouse movements, or gait for continuous authentication, offering enhanced security and reduced fraud risk. Behavioral biometrics leverage machine learning algorithms to create dynamic user profiles that adapt over time, increasing accuracy compared to static passwords. Discover more about how behavioral biometrics revolutionize secure user identification beyond traditional password systems.
Source and External Links
Password - Wikipedia - A password is secret data, typically a string of characters, used to confirm a user's identity.
Passwords on the App Store - This app lets you securely store and access passwords, passkeys, and other credentials across your Apple devices.
Manage Your Passwords Safely & Easily - Google Password Manager - Google Password Manager saves your passwords securely in your Google Account, allowing access from any device.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com