Account aggregation consolidates financial data from multiple sources into a single interface, enabling users to view and manage all accounts seamlessly. API banking facilitates real-time data exchange between banks and third-party applications, enhancing transactional efficiency and personalized services. Discover how these technologies reshape financial management and customer experience.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between account aggregation and API banking is crucial for leveraging secure, real-time financial data access versus consolidated data presentation. Account aggregation collects user financial data from multiple sources into one interface, enhancing personal money management apps. API banking enables direct, secure interactions with banks' core systems for services like payments and account management. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose the right technology for improved customer experience and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
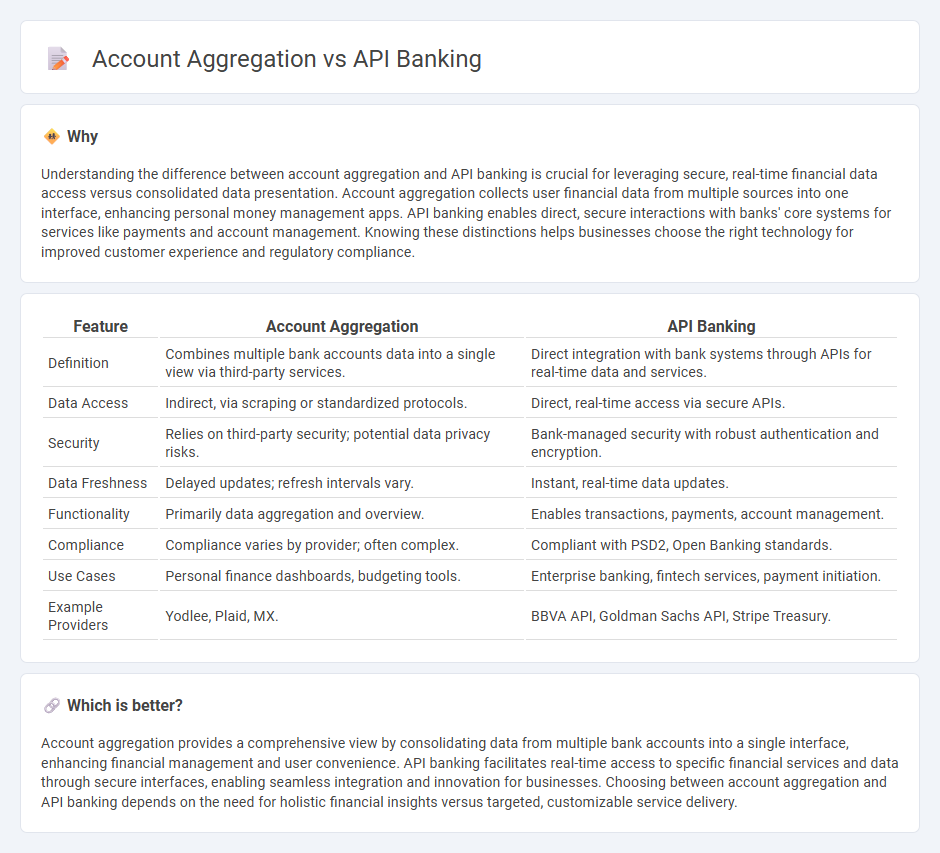
| Feature | Account Aggregation | API Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines multiple bank accounts data into a single view via third-party services. | Direct integration with bank systems through APIs for real-time data and services. |
| Data Access | Indirect, via scraping or standardized protocols. | Direct, real-time access via secure APIs. |
| Security | Relies on third-party security; potential data privacy risks. | Bank-managed security with robust authentication and encryption. |
| Data Freshness | Delayed updates; refresh intervals vary. | Instant, real-time data updates. |
| Functionality | Primarily data aggregation and overview. | Enables transactions, payments, account management. |
| Compliance | Compliance varies by provider; often complex. | Compliant with PSD2, Open Banking standards. |
| Use Cases | Personal finance dashboards, budgeting tools. | Enterprise banking, fintech services, payment initiation. |
| Example Providers | Yodlee, Plaid, MX. | BBVA API, Goldman Sachs API, Stripe Treasury. |
Which is better?
Account aggregation provides a comprehensive view by consolidating data from multiple bank accounts into a single interface, enhancing financial management and user convenience. API banking facilitates real-time access to specific financial services and data through secure interfaces, enabling seamless integration and innovation for businesses. Choosing between account aggregation and API banking depends on the need for holistic financial insights versus targeted, customizable service delivery.
Connection
Account aggregation and API banking are interconnected through the use of APIs that enable secure data sharing across multiple financial institutions, allowing users to view and manage their accounts in a single platform. APIs facilitate real-time data exchange between banks and third-party providers, enhancing transparency and financial management. This integration supports open banking initiatives, improving customer experience and fostering innovation in digital financial services.
Key Terms
**API Banking:**
API banking enables seamless integration of financial services directly into third-party applications, providing real-time transaction data and payment initiation capabilities. It offers enhanced security, improved customer experience, and greater personalization compared to traditional account aggregation. Discover how API banking transforms digital finance with advanced connectivity and control.
Open Banking
API banking enables direct, secure access to banking services through standardized application programming interfaces, enhancing real-time financial transactions and data exchange. Account aggregation consolidates financial information from multiple accounts into a single interface, providing a comprehensive overview without directly facilitating transactions. Explore how Open Banking leverages these technologies to transform financial ecosystems and empower smarter money management.
Real-time Transactions
API banking enables real-time transactions by providing direct, secure access to banking systems for immediate payment processing and balance updates. Account aggregation collects and consolidates financial data from multiple sources but typically lacks instantaneous transaction capabilities. Explore the key differences and benefits of each to optimize your financial services.
Source and External Links
Banking application programming interfaces (APIs) - API banking uses open protocols to let banks and third parties (like fintechs) securely connect, share data, and offer modular financial services--transforming how customers and businesses interact with money by enabling faster innovation and interoperability.
API Banking and Banking as a Service - API banking allows external systems to access bank account information, initiate transactions, and receive real-time alerts, while Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) lets non-banks offer banking features by integrating with licensed institutions via APIs, speeding up the launch of new financial products.
Banking APIs: Definition, Examples and Benefits - Banking APIs enable companies to integrate core financial services--like payments, data management, and risk assessment--directly into their platforms, streamlining operations and enhancing customer experiences without building complex banking infrastructure from scratch.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com