Banking as a Service (BaaS) enables third-party providers to offer banking products by integrating with licensed banks through APIs, streamlining financial service delivery. Open Banking mandates banks to share customer data securely with authorized providers, fostering transparency and innovation in financial ecosystems. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both models to enhance your financial technology strategy.
Why it is important
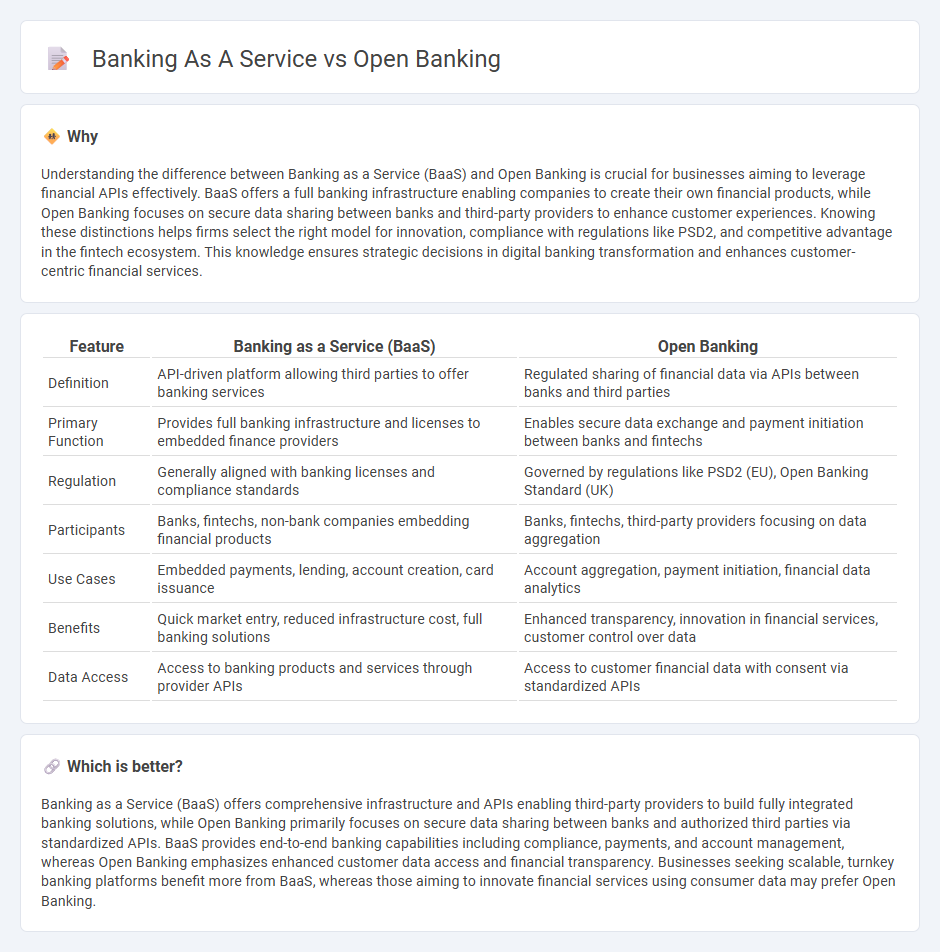
Understanding the difference between Banking as a Service (BaaS) and Open Banking is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage financial APIs effectively. BaaS offers a full banking infrastructure enabling companies to create their own financial products, while Open Banking focuses on secure data sharing between banks and third-party providers to enhance customer experiences. Knowing these distinctions helps firms select the right model for innovation, compliance with regulations like PSD2, and competitive advantage in the fintech ecosystem. This knowledge ensures strategic decisions in digital banking transformation and enhances customer-centric financial services.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Banking as a Service (BaaS) | Open Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | API-driven platform allowing third parties to offer banking services | Regulated sharing of financial data via APIs between banks and third parties |
| Primary Function | Provides full banking infrastructure and licenses to embedded finance providers | Enables secure data exchange and payment initiation between banks and fintechs |
| Regulation | Generally aligned with banking licenses and compliance standards | Governed by regulations like PSD2 (EU), Open Banking Standard (UK) |
| Participants | Banks, fintechs, non-bank companies embedding financial products | Banks, fintechs, third-party providers focusing on data aggregation |
| Use Cases | Embedded payments, lending, account creation, card issuance | Account aggregation, payment initiation, financial data analytics |
| Benefits | Quick market entry, reduced infrastructure cost, full banking solutions | Enhanced transparency, innovation in financial services, customer control over data |
| Data Access | Access to banking products and services through provider APIs | Access to customer financial data with consent via standardized APIs |
Which is better?
Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers comprehensive infrastructure and APIs enabling third-party providers to build fully integrated banking solutions, while Open Banking primarily focuses on secure data sharing between banks and authorized third parties via standardized APIs. BaaS provides end-to-end banking capabilities including compliance, payments, and account management, whereas Open Banking emphasizes enhanced customer data access and financial transparency. Businesses seeking scalable, turnkey banking platforms benefit more from BaaS, whereas those aiming to innovate financial services using consumer data may prefer Open Banking.
Connection
Banking as a Service (BaaS) leverages Open Banking APIs to enable third-party providers to access banking infrastructure and offer innovative financial products. Open Banking facilitates secure data sharing between banks and fintech companies, forming the foundation for BaaS platforms. This integration drives enhanced customer experiences and accelerates the digital transformation of financial services.
Key Terms
API (Application Programming Interface)
Open banking exposes APIs to third-party developers, enabling secure access to customer banking data and facilitating services like payment initiation and account information sharing. Banking as a Service (BaaS) provides comprehensive banking infrastructure via APIs, allowing non-bank companies to offer full-fledged banking products such as accounts, cards, and loans without traditional banking licenses. Explore our detailed comparison to understand the benefits and implementation strategies of open banking and BaaS APIs.
Third-Party Providers
Third-Party Providers (TPPs) play a crucial role in both open banking and Banking as a Service (BaaS) ecosystems by enabling access to customer data and banking infrastructure through APIs. In open banking, TPPs primarily focus on delivering innovative financial services by retrieving account information and initiating payments with customer consent. Banking as a Service expands this model by allowing TPPs to embed full-fledged banking products into their platforms, offering a broader range of financial solutions. Discover how TPPs transform the financial landscape with open banking and BaaS innovations.
Embedded Finance
Open banking enables third-party providers to access bank customer data via APIs, fostering innovative financial services through data sharing. Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers the infrastructure that allows non-bank companies to embed full banking capabilities like payments, loans, and accounts directly into their platforms. Explore how embedded finance is transforming customer experiences by blending the strengths of open banking and BaaS for seamless financial integration.
Source and External Links
Open Banking - Open banking allows customers to securely share their financial information with other banks or authorized financial organizations.
What is Open Banking? A Guide to the Future of Finance - This guide explains how open banking enables secure sharing of financial data between consumers and third-party providers through standardized APIs.
Open Banking Explained - Open banking is a model that allows third-party service providers to access consumer data from traditional banking systems, enhancing data-driven decision-making and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com