Cloud core banking leverages cloud computing to provide scalable, flexible, and cost-effective banking solutions, enabling real-time processing and enhanced customer experiences. Coreless banking eliminates the need for traditional core banking systems by integrating multiple agile, API-driven services, facilitating faster innovation and seamless digital transactions. Explore the differences to discover which modern banking infrastructure best suits your business needs.
Why it is important
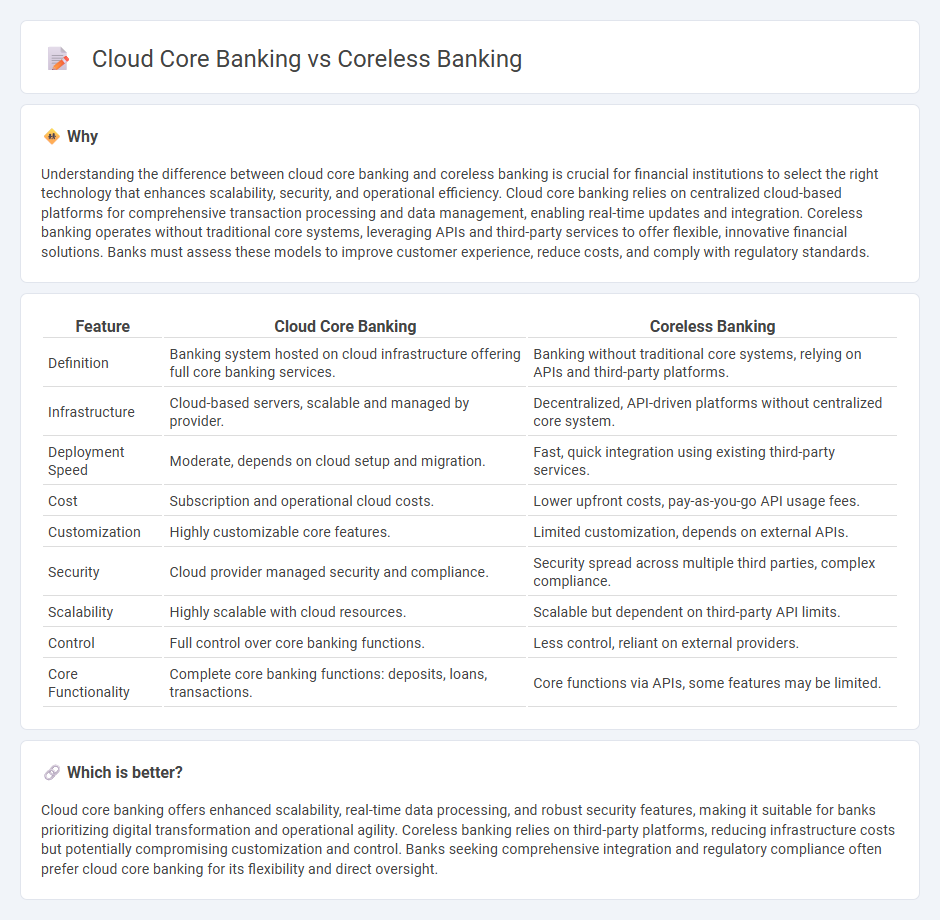
Understanding the difference between cloud core banking and coreless banking is crucial for financial institutions to select the right technology that enhances scalability, security, and operational efficiency. Cloud core banking relies on centralized cloud-based platforms for comprehensive transaction processing and data management, enabling real-time updates and integration. Coreless banking operates without traditional core systems, leveraging APIs and third-party services to offer flexible, innovative financial solutions. Banks must assess these models to improve customer experience, reduce costs, and comply with regulatory standards.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cloud Core Banking | Coreless Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Banking system hosted on cloud infrastructure offering full core banking services. | Banking without traditional core systems, relying on APIs and third-party platforms. |
| Infrastructure | Cloud-based servers, scalable and managed by provider. | Decentralized, API-driven platforms without centralized core system. |
| Deployment Speed | Moderate, depends on cloud setup and migration. | Fast, quick integration using existing third-party services. |
| Cost | Subscription and operational cloud costs. | Lower upfront costs, pay-as-you-go API usage fees. |
| Customization | Highly customizable core features. | Limited customization, depends on external APIs. |
| Security | Cloud provider managed security and compliance. | Security spread across multiple third parties, complex compliance. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with cloud resources. | Scalable but dependent on third-party API limits. |
| Control | Full control over core banking functions. | Less control, reliant on external providers. |
| Core Functionality | Complete core banking functions: deposits, loans, transactions. | Core functions via APIs, some features may be limited. |
Which is better?
Cloud core banking offers enhanced scalability, real-time data processing, and robust security features, making it suitable for banks prioritizing digital transformation and operational agility. Coreless banking relies on third-party platforms, reducing infrastructure costs but potentially compromising customization and control. Banks seeking comprehensive integration and regulatory compliance often prefer cloud core banking for its flexibility and direct oversight.
Connection
Cloud core banking leverages cloud technology to host banking systems on remote servers, enabling scalable, flexible, and cost-effective financial services. Coreless banking eliminates traditional core banking infrastructure by relying entirely on cloud-based platforms, APIs, and third-party services to deliver seamless digital banking experiences. Both models prioritize agility, real-time processing, and enhanced customer engagement by utilizing cloud-native architectures and innovative fintech integrations.
Key Terms
Decentralized Architecture
Coreless banking eliminates the dependency on traditional core systems by leveraging decentralized architecture, enabling real-time, distributed transaction processing across multiple nodes without a central database. Cloud core banking systems, while hosted on scalable cloud infrastructure, often retain a centralized core, which may limit flexibility and increase latency compared to fully decentralized models. Explore the advantages of decentralized architectures in coreless banking to understand their impact on agility, security, and innovation in financial services.
Scalability
Coreless banking leverages decentralized technologies enabling infinite scalability through distributed ledger systems, eliminating traditional core banking constraints. Cloud core banking utilizes cloud infrastructure to enhance scalability by dynamically allocating resources based on demand, facilitating rapid growth and operational efficiency. Explore deeper insights on how each platform transforms scalability in modern banking systems.
Real-time Data Processing
Coreless banking eliminates the dependency on traditional core banking systems by leveraging microservices and APIs for seamless, real-time data processing, enabling instant transaction updates and improved customer experiences. Cloud core banking offers scalable infrastructure with centralized data management, ensuring high availability and swift processing speeds across multiple channels. Explore how real-time data processing transforms banking efficiency and customer satisfaction in both coreless and cloud-based models.
Source and External Links
Advantages and disadvantages of coreless banking | Innowise - Coreless banking leverages decentralized, microservice-based architecture for enhanced resilience, global accessibility, and tailored compliance, though it also presents significant implementation challenges.
What Financial Institutions Need to Know About Coreless Banking - Coreless banking enables banks of all sizes to customize and innovate financial products using best-of-breed modules from multiple vendors, reducing costs and increasing flexibility compared to legacy systems.
Kill your core: The banking revolution you didn't see coming - Coreless banking decouples monolithic systems into agile, scalable microservices, allowing rapid innovation, cost reduction, and improved customer experiences through cloud-native, componentized solutions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com