Instant settlement enables real-time transaction processing, ensuring funds are transferred and available immediately, which enhances liquidity and reduces counterparty risk. Periodic settlement consolidates transactions over a set timeframe, often resulting in batch processing that may delay fund availability but can reduce operational costs. Explore the advantages and use cases of both settlement methods to optimize your banking operations.
Why it is important
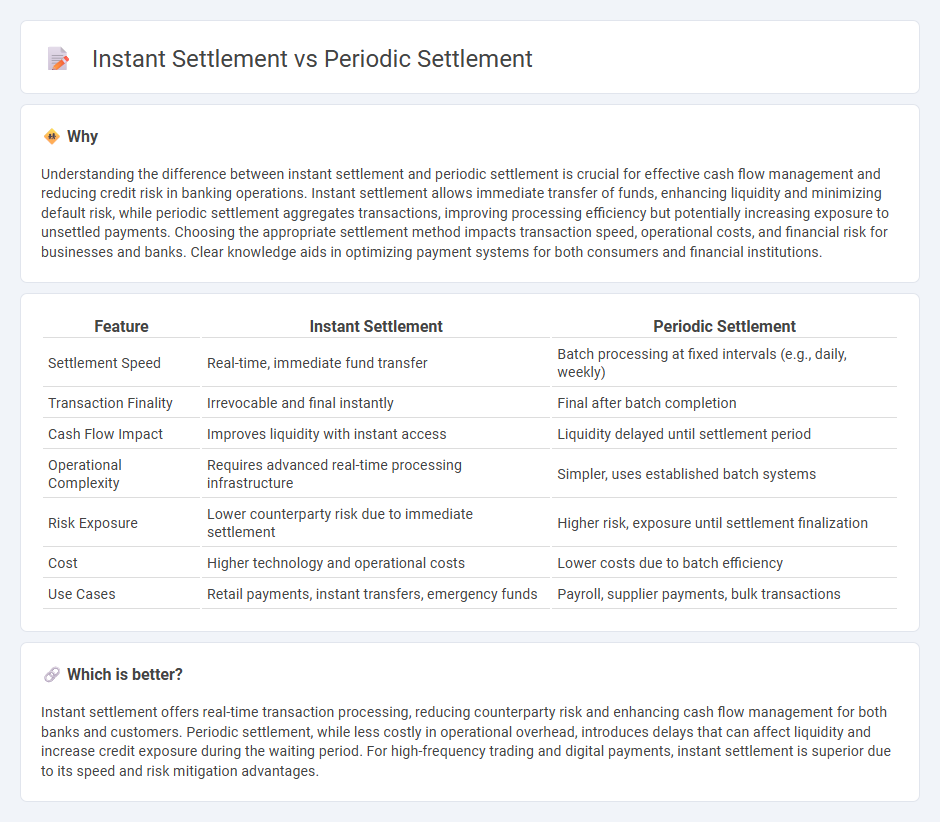
Understanding the difference between instant settlement and periodic settlement is crucial for effective cash flow management and reducing credit risk in banking operations. Instant settlement allows immediate transfer of funds, enhancing liquidity and minimizing default risk, while periodic settlement aggregates transactions, improving processing efficiency but potentially increasing exposure to unsettled payments. Choosing the appropriate settlement method impacts transaction speed, operational costs, and financial risk for businesses and banks. Clear knowledge aids in optimizing payment systems for both consumers and financial institutions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Instant Settlement | Periodic Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Settlement Speed | Real-time, immediate fund transfer | Batch processing at fixed intervals (e.g., daily, weekly) |
| Transaction Finality | Irrevocable and final instantly | Final after batch completion |
| Cash Flow Impact | Improves liquidity with instant access | Liquidity delayed until settlement period |
| Operational Complexity | Requires advanced real-time processing infrastructure | Simpler, uses established batch systems |
| Risk Exposure | Lower counterparty risk due to immediate settlement | Higher risk, exposure until settlement finalization |
| Cost | Higher technology and operational costs | Lower costs due to batch efficiency |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, instant transfers, emergency funds | Payroll, supplier payments, bulk transactions |
Which is better?
Instant settlement offers real-time transaction processing, reducing counterparty risk and enhancing cash flow management for both banks and customers. Periodic settlement, while less costly in operational overhead, introduces delays that can affect liquidity and increase credit exposure during the waiting period. For high-frequency trading and digital payments, instant settlement is superior due to its speed and risk mitigation advantages.
Connection
Instant settlement enables immediate transfer of funds between bank accounts, enhancing liquidity and real-time transaction processing. Periodic settlement aggregates multiple transactions over a defined interval, settling these collectively at scheduled times. Both mechanisms are interconnected as instant settlement improves individual transaction speed while periodic settlement optimizes operational efficiency by consolidating transactions for bulk processing.
Key Terms
Clearing
Periodic settlement in clearing involves aggregating transactions over a specific period before finalizing payments and transfers, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing liquidity demands. Instant settlement processes transactions in real time, minimizing counterparty risk and providing immediate finality of funds and securities. Explore detailed mechanisms and benefits of each settlement method to optimize clearing operations in financial markets.
Settlement Time
Periodic settlement processes transactions in batches at predefined intervals, such as daily or weekly, which can result in delays in fund availability and reconciliation. Instant settlement enables real-time transaction processing, providing immediate fund transfer and reducing counterparty risk, critical for high-frequency trading and time-sensitive payments. Explore more to understand how settlement time impacts liquidity and operational efficiency in financial systems.
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)
Periodic settlement processes accumulate transactions over a set interval before netting and settling, reducing liquidity requirements but increasing settlement risk due to delays. Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems execute each payment individually and immediately upon initiation, ensuring finality and reducing credit risk by eliminating batch processing delays. Explore the advantages and operational mechanisms of RTGS to understand its impact on modern payment infrastructures.
Source and External Links
What Is a Periodic Payment Settlement? Do I Need One? - A periodic payment settlement is a claim settlement arrangement to compensate for personal injury through a series of guaranteed, tax-free payments made at scheduled intervals, offering financial security and flexibility over a lump sum settlement.
Periodic Payment Settlement Act - Annuity.org - The Periodic Payment Settlement Act of 1982 authorized long-term periodic payment settlements for lawsuits, allowing injured parties to receive ongoing, tax-exempt payments instead of lump sums, enhancing financial stability and tax benefits.
What is periodic settlement, and why is it important? - Bitstamp - Periodic settlement in financial contexts refers to reconciling profits and losses on open positions at regular intervals, highlighting the importance of periodic settlements in transactional clearing processes, distinct from the legal structured settlement meaning.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com