Real-time payments enable instant fund transfers between accounts, offering seamless and continuous transaction processing at any time, unlike RTGS which processes high-value transactions in batches during specific hours. RTGS, primarily used for large-value interbank transfers, ensures finality and irreversibility of payments with settlement occurring on a gross basis. Explore the key differences and benefits of real-time payments and RTGS to understand their impact on modern banking systems.
Why it is important
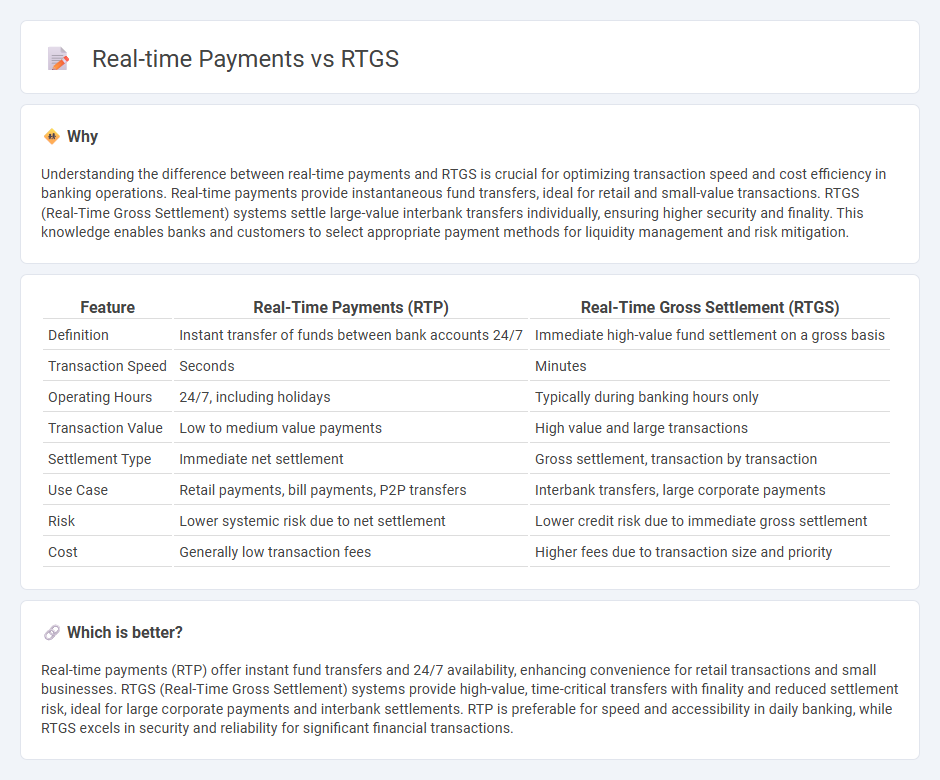
Understanding the difference between real-time payments and RTGS is crucial for optimizing transaction speed and cost efficiency in banking operations. Real-time payments provide instantaneous fund transfers, ideal for retail and small-value transactions. RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement) systems settle large-value interbank transfers individually, ensuring higher security and finality. This knowledge enables banks and customers to select appropriate payment methods for liquidity management and risk mitigation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Real-Time Payments (RTP) | Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant transfer of funds between bank accounts 24/7 | Immediate high-value fund settlement on a gross basis |
| Transaction Speed | Seconds | Minutes |
| Operating Hours | 24/7, including holidays | Typically during banking hours only |
| Transaction Value | Low to medium value payments | High value and large transactions |
| Settlement Type | Immediate net settlement | Gross settlement, transaction by transaction |
| Use Case | Retail payments, bill payments, P2P transfers | Interbank transfers, large corporate payments |
| Risk | Lower systemic risk due to net settlement | Lower credit risk due to immediate gross settlement |
| Cost | Generally low transaction fees | Higher fees due to transaction size and priority |
Which is better?
Real-time payments (RTP) offer instant fund transfers and 24/7 availability, enhancing convenience for retail transactions and small businesses. RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement) systems provide high-value, time-critical transfers with finality and reduced settlement risk, ideal for large corporate payments and interbank settlements. RTP is preferable for speed and accessibility in daily banking, while RTGS excels in security and reliability for significant financial transactions.
Connection
Real-time payments (RTP) and Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems both aim to facilitate immediate fund transfers between banks, enhancing liquidity and operational efficiency. RTP allows instant transfer of funds on a retail level throughout the day, while RTGS processes high-value interbank transactions individually in real time. The integration of RTP with RTGS infrastructure ensures secure, irrevocable settlements that support cash flow management in the banking sector.
Key Terms
Settlement
RTGS (Real-Time Gross Settlement) processes large-value interbank payments individually on a real-time basis, ensuring immediate and final settlement without netting. Real-time payments, also known as instant payments, facilitate consumer and business transactions with near-instant fund transfers typically available 24/7, enhancing liquidity and cash flow. Explore the distinct settlement mechanisms and benefits of RTGS and real-time payments to optimize your payment strategy.
Clearing
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems process high-value interbank transfers individually and immediately, ensuring finality and reducing settlement risk. Real-time payments, on the other hand, typically handle lower-value transactions with near-instantaneous clearing and settlement for retail payments. Explore the critical distinctions in clearing mechanisms to optimize your payment strategy.
Funds Transfer
Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) systems facilitate high-value, irrevocable funds transfers between banks, ensuring immediate settlement on a transaction-by-transaction basis. Real-time payments (RTP) enable instant, low-value consumer and business transactions with continuous availability and immediate confirmation. Explore the differences and applications of RTGS and RTP to optimize your funds transfer strategy.
Source and External Links
Real-time gross settlement - Wikipedia - RTGS systems are specialist funds transfer systems where money or securities move between banks in real time on a one-to-one basis, with each transaction settled immediately and irrevocably--no batch processing or netting occurs.
What is Real-Time Gross Settlement (RTGS)? - Modern Treasury - RTGS enables electronic payments between banks to process and settle instantly (not in batches), is managed by a country's central bank, and is typically used for large, high-value transactions where speed and security are critical.
RTGS for High Value Payments - Your Guide To Minimizing Risk - RTGS allows instant, final, and irrevocable electronic transfer of funds from one bank to another, is operated by central banks, and is primarily used for high-value interbank transactions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com