Instant settlement enables real-time transaction completion, enhancing liquidity and reducing credit risk between parties. Net settlement aggregates multiple transactions over a period, settling the net balance to improve processing efficiency and lower operational costs. Explore the advantages and applications of these settlement methods to optimize your banking operations.
Why it is important
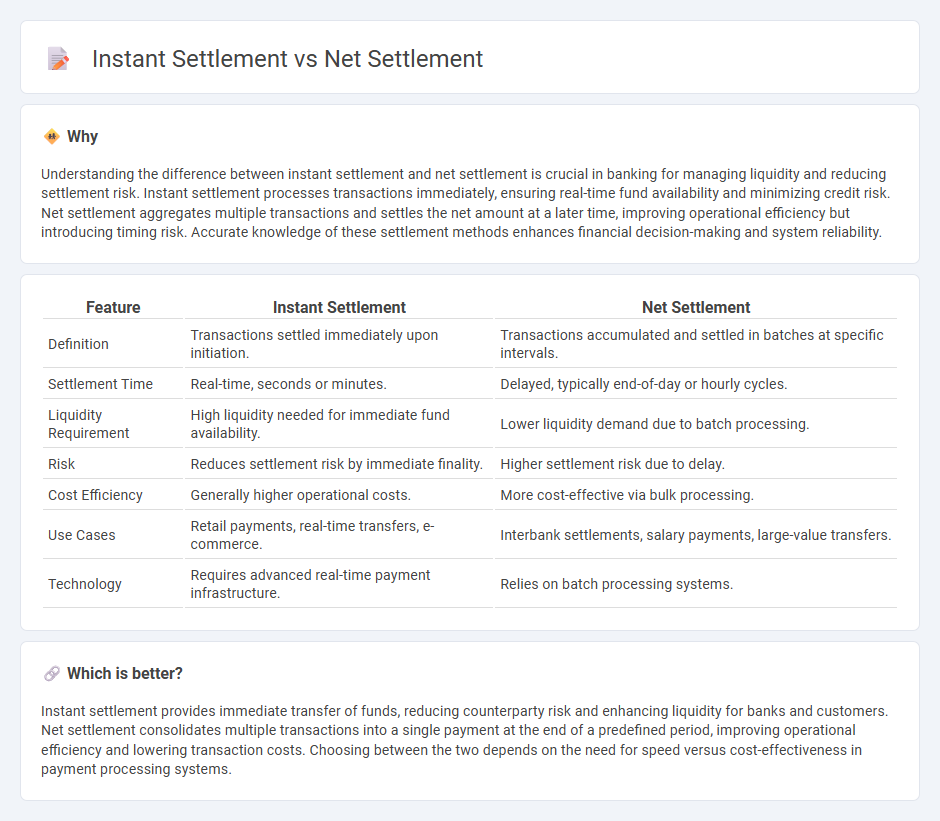
Understanding the difference between instant settlement and net settlement is crucial in banking for managing liquidity and reducing settlement risk. Instant settlement processes transactions immediately, ensuring real-time fund availability and minimizing credit risk. Net settlement aggregates multiple transactions and settles the net amount at a later time, improving operational efficiency but introducing timing risk. Accurate knowledge of these settlement methods enhances financial decision-making and system reliability.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Instant Settlement | Net Settlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transactions settled immediately upon initiation. | Transactions accumulated and settled in batches at specific intervals. |
| Settlement Time | Real-time, seconds or minutes. | Delayed, typically end-of-day or hourly cycles. |
| Liquidity Requirement | High liquidity needed for immediate fund availability. | Lower liquidity demand due to batch processing. |
| Risk | Reduces settlement risk by immediate finality. | Higher settlement risk due to delay. |
| Cost Efficiency | Generally higher operational costs. | More cost-effective via bulk processing. |
| Use Cases | Retail payments, real-time transfers, e-commerce. | Interbank settlements, salary payments, large-value transfers. |
| Technology | Requires advanced real-time payment infrastructure. | Relies on batch processing systems. |
Which is better?
Instant settlement provides immediate transfer of funds, reducing counterparty risk and enhancing liquidity for banks and customers. Net settlement consolidates multiple transactions into a single payment at the end of a predefined period, improving operational efficiency and lowering transaction costs. Choosing between the two depends on the need for speed versus cost-effectiveness in payment processing systems.
Connection
Instant settlement enables immediate transfer of funds between parties, enhancing liquidity and reducing credit risk. Net settlement aggregates multiple transactions into a single batch, optimizing processing efficiency and minimizing operational costs. Together, these methods streamline banking operations by balancing real-time fund availability with settlement efficiency.
Key Terms
Clearing
Net settlement consolidates multiple transactions over a period, allowing clearinghouses to offset payments and reduce the number of funds exchanged, thus enhancing liquidity efficiency. Instant settlement completes transactions in real-time, minimizing counterparty risk but increasing the demand for immediate liquidity and operational resources within the clearing process. Explore more to understand how these clearing mechanisms impact financial system stability and transactional throughput.
Settlement Time
Net settlement aggregates multiple transactions to settle at predetermined intervals, often end-of-day, reducing transaction processing load but delaying final fund availability. Instant settlement processes each transaction individually in real-time, ensuring immediate fund transfer and enhanced liquidity for users. Explore the differences further to determine which settlement method aligns best with your financial needs.
Liquidity
Net settlement consolidates multiple transactions into a single payment, reducing liquidity demands by allowing participants to fund only the net amount owed at the end of a settlement cycle. Instant settlement requires immediate fund transfer for each transaction, increasing liquidity requirements as participants must have sufficient balances ready at all times. Explore how these settlement mechanisms impact liquidity management and operational efficiency in payment systems.
Source and External Links
Settlement (Net vs. Gross) - Modern Treasury - Net settlement aggregates transaction data over a period, settling the net balance between banks at the end of the day through a clearinghouse, reducing the number and size of transactions to improve liquidity management.
What Is Net Settlement and How Does It Work? - SmartAsset - Net settlement consolidates multiple transactions into a single net payment between financial institutions, typically processed in batches, which is cost-effective but involves some credit risk and delayed finality compared to gross settlement.
Net Settlement - Overview, How It Works, Types, and Example - Corporate Finance Institute - A system where banks track daily transactions and use a clearinghouse to exchange information and settle the net difference, either bilaterally or multilaterally, ensuring only the net amount is transferred between participating banks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com