Fraud orchestration integrates multiple security tools and data sources to detect and prevent banking fraud in real time, streamlining threat response across channels. Payment authentication focuses specifically on verifying the identity of users during transactions to ensure secure, authorized payments. Explore deeper strategies and technologies driving effective fraud management and secure payment processes.
Why it is important
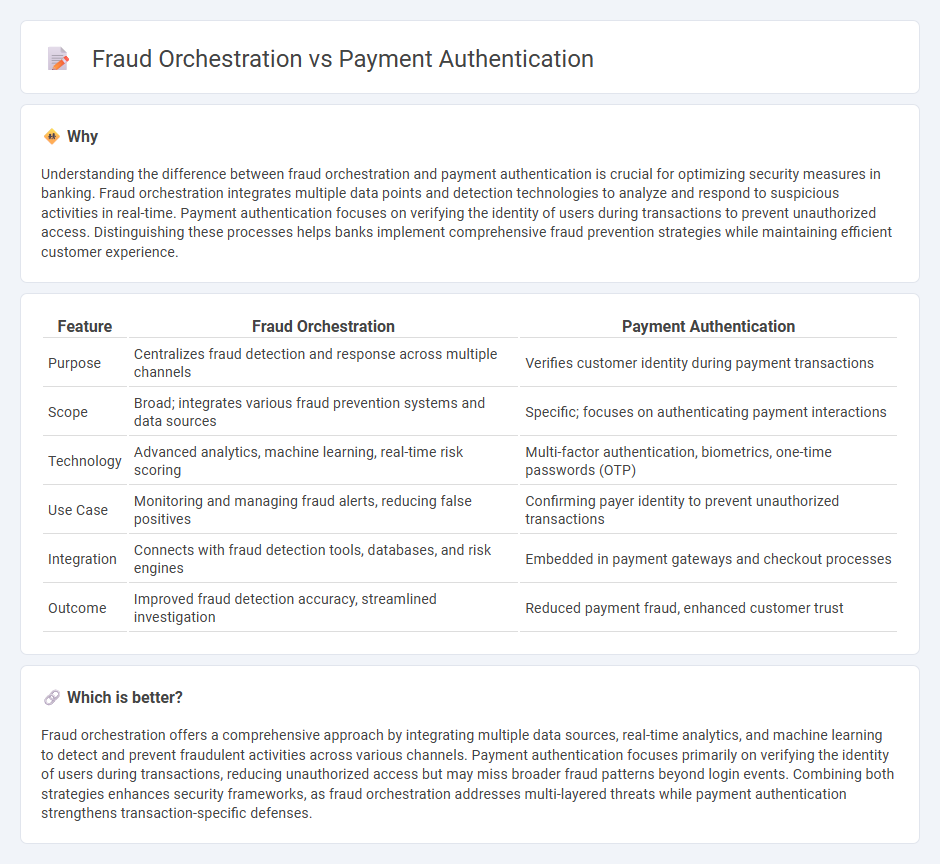
Understanding the difference between fraud orchestration and payment authentication is crucial for optimizing security measures in banking. Fraud orchestration integrates multiple data points and detection technologies to analyze and respond to suspicious activities in real-time. Payment authentication focuses on verifying the identity of users during transactions to prevent unauthorized access. Distinguishing these processes helps banks implement comprehensive fraud prevention strategies while maintaining efficient customer experience.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fraud Orchestration | Payment Authentication |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Centralizes fraud detection and response across multiple channels | Verifies customer identity during payment transactions |
| Scope | Broad; integrates various fraud prevention systems and data sources | Specific; focuses on authenticating payment interactions |
| Technology | Advanced analytics, machine learning, real-time risk scoring | Multi-factor authentication, biometrics, one-time passwords (OTP) |
| Use Case | Monitoring and managing fraud alerts, reducing false positives | Confirming payer identity to prevent unauthorized transactions |
| Integration | Connects with fraud detection tools, databases, and risk engines | Embedded in payment gateways and checkout processes |
| Outcome | Improved fraud detection accuracy, streamlined investigation | Reduced payment fraud, enhanced customer trust |
Which is better?
Fraud orchestration offers a comprehensive approach by integrating multiple data sources, real-time analytics, and machine learning to detect and prevent fraudulent activities across various channels. Payment authentication focuses primarily on verifying the identity of users during transactions, reducing unauthorized access but may miss broader fraud patterns beyond login events. Combining both strategies enhances security frameworks, as fraud orchestration addresses multi-layered threats while payment authentication strengthens transaction-specific defenses.
Connection
Fraud orchestration integrates multiple data sources and analytics to detect suspicious transaction patterns in real-time, enhancing the effectiveness of payment authentication processes. Payment authentication methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or biometrics rely on fraud orchestration systems to dynamically adjust security protocols based on risk scores generated from behavioral and device analytics. This interconnected approach reduces fraudulent transactions, improves regulatory compliance, and strengthens overall transaction security within the banking industry.
Key Terms
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) enhances payment authentication by requiring users to provide two distinct forms of verification, such as a password and a one-time code sent via SMS or generated by an app, significantly reducing unauthorized access. Fraud orchestration integrates 2FA within a broader framework that combines real-time risk assessment, device fingerprinting, and behavioral analytics to dynamically adjust security measures and prevent sophisticated fraud attempts. Explore how combining payment authentication with fraud orchestration optimizes security protocols and minimizes transaction fraud.
Transaction Monitoring
Payment authentication verifies the identity of users during a transaction, reducing unauthorized access and ensuring secure payment processing. Fraud orchestration integrates multiple monitoring systems to analyze transaction patterns in real-time, detecting suspicious activities and minimizing false positives. Explore more insights on how transaction monitoring enhances both payment authentication and fraud orchestration strategies.
Behavioral Analytics
Behavioral analytics in payment authentication enhances security by analyzing user patterns to verify identity and detect anomalies during transactions. In fraud orchestration, behavioral analytics integrates multiple data sources and applies real-time risk scoring to prevent sophisticated fraud attacks across channels. Explore how leveraging behavioral analytics can revolutionize your payment security strategy and fraud prevention frameworks.
Source and External Links
Understanding Payment Authentication: A Guide for 2024 | GR4VY - Payment authentication verifies the identity of the person initiating a transaction using methods like passwords, biometrics, OTPs, or behavioral analytics to secure payments and enhance customer trust.
Payment Authentication | Payments Explained - EBANX - It confirms a customer's identity by verifying at least one factor such as knowledge (passwords, PINs), inherence (biometrics like face or voice), ownership (tokens or keys), or user location to prevent payment fraud.
Optimizing payment authentication rates: a merchant's guide - Primer - Payment authentication ensures online transactions are legitimate by requiring customers to validate their identity using two of these factors: something they own (device), something they are (biometrics), or something they know (password or PIN), with 3D Secure being a prominent protocol for this purpose.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com