Sustainable investing focuses on directing capital towards companies and projects that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term positive impacts alongside financial returns. Community investing targets underserved or low-income communities by funding local projects, businesses, and organizations to stimulate economic growth and improve quality of life. Discover more about how these distinct strategies contribute to ethical finance and societal progress.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainable investing and community investing is crucial for aligning financial goals with ethical values and social impact. Sustainable investing focuses on companies with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term ecological and societal benefits. Community investing directs capital to underserved communities, supporting local development and economic inclusion. This knowledge enables investors to make informed decisions that balance profitability with responsible social outcomes.
Comparison Table
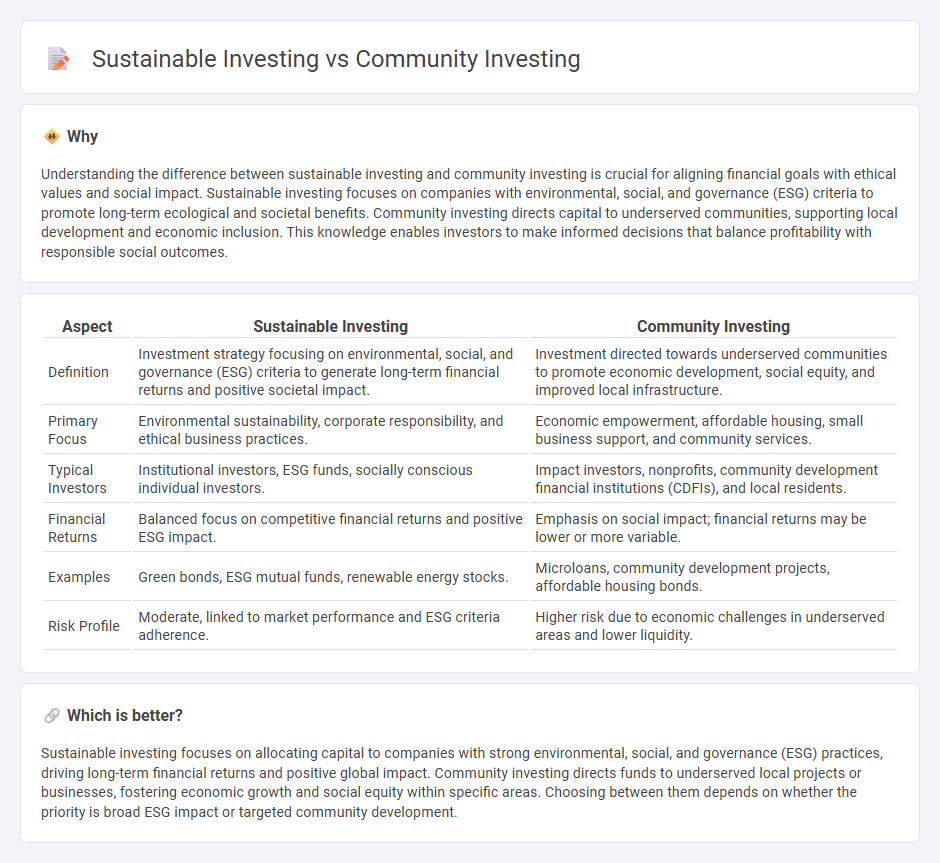
| Aspect | Sustainable Investing | Community Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment strategy focusing on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term financial returns and positive societal impact. | Investment directed towards underserved communities to promote economic development, social equity, and improved local infrastructure. |
| Primary Focus | Environmental sustainability, corporate responsibility, and ethical business practices. | Economic empowerment, affordable housing, small business support, and community services. |
| Typical Investors | Institutional investors, ESG funds, socially conscious individual investors. | Impact investors, nonprofits, community development financial institutions (CDFIs), and local residents. |
| Financial Returns | Balanced focus on competitive financial returns and positive ESG impact. | Emphasis on social impact; financial returns may be lower or more variable. |
| Examples | Green bonds, ESG mutual funds, renewable energy stocks. | Microloans, community development projects, affordable housing bonds. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate, linked to market performance and ESG criteria adherence. | Higher risk due to economic challenges in underserved areas and lower liquidity. |
Which is better?
Sustainable investing focuses on allocating capital to companies with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices, driving long-term financial returns and positive global impact. Community investing directs funds to underserved local projects or businesses, fostering economic growth and social equity within specific areas. Choosing between them depends on whether the priority is broad ESG impact or targeted community development.
Connection
Sustainable investing prioritizes environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to generate long-term value while fostering positive societal impact. Community investing channels capital into underserved areas, promoting economic development through accessible banking, affordable housing, and small business support. Both strategies align by directing financial resources toward projects that advance social equity and environmental stewardship within local communities.
Key Terms
Social Impact
Community investing directs capital to underserved communities, fostering affordable housing, small businesses, and essential social services, thereby generating measurable local social impact. Sustainable investing incorporates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria to promote long-term positive outcomes, including social equity, but with a broader scope beyond immediate community needs. Explore how aligning your investment strategy with specific social goals can enhance both impact and financial returns.
Environmental Criteria
Community investing targets funding for local projects that promote affordable housing, small businesses, and economic development in underserved areas, directly supporting social and environmental improvements at a grassroots level. Sustainable investing incorporates environmental criteria by selecting companies with strong practices in carbon reduction, resource efficiency, and pollution control to mitigate climate change and protect natural ecosystems. Explore comprehensive insights on how each investment strategy advances environmental goals and drives positive impact.
Underserved Communities
Community investing directs capital to underserved communities to stimulate economic growth, support small businesses, and enhance affordable housing opportunities. Sustainable investing integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, often prioritizing underserved populations but with a broader focus on ecological impact and corporate responsibility. Explore how targeted investments can drive social equity and environmental stewardship in underserved areas.
Source and External Links
Impact in Place: Emerging Sources of Community Investment - Discusses innovative community investing initiatives that promote racial equity and support small businesses through partnerships with financial institutions and community funds.
Community Investment Trusts - Small Business Anti-Displacement - Explains community investment trusts as for-profit entities that enable neighborhood residents to pool resources to buy community-owned real estate, fostering local wealth-building and long-term stability for small businesses.
The community investment fund: An efficient, scalable vehicle for tax-incentivized place-based investment - Proposes community investment funds (CIFs) as vehicles allowing tax-incentivized, scalable investments focused on low-income communities, combining various capital sources to support community development with flexible investment and return terms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com