Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using real and fabricated information to open fraudulent bank accounts and conduct illicit activities. Mule accounts are legitimate accounts manipulated by fraudsters or unwitting individuals to launder money or facilitate unauthorized transactions. Explore the differences and mitigation strategies for synthetic identity fraud versus mule accounts to strengthen your banking security.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between synthetic identity fraud and mule accounts is crucial for banking security and fraud prevention. Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fictitious identities by combining real and fake information to open fraudulent accounts, whereas mule accounts are legitimate accounts used unwittingly or willingly to launder stolen funds. Recognizing these distinct threats enables banks to implement targeted detection strategies and comply with regulatory requirements. Effective differentiation helps minimize financial losses and protects customer integrity.
Comparison Table
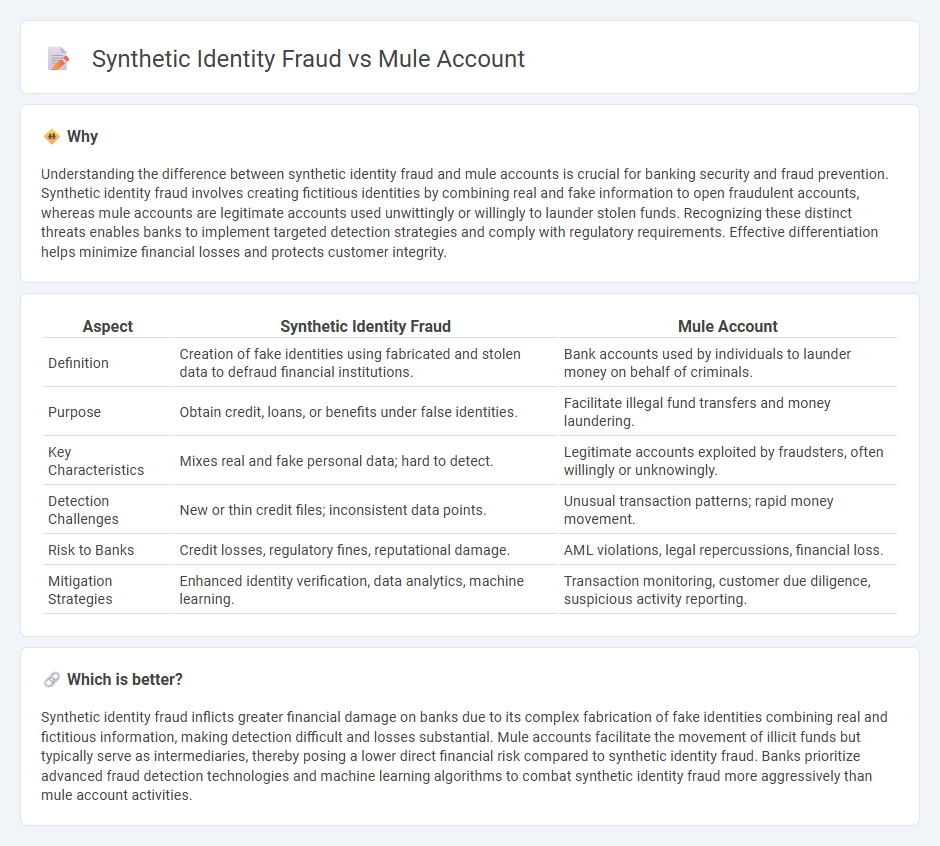
| Aspect | Synthetic Identity Fraud | Mule Account |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creation of fake identities using fabricated and stolen data to defraud financial institutions. | Bank accounts used by individuals to launder money on behalf of criminals. |
| Purpose | Obtain credit, loans, or benefits under false identities. | Facilitate illegal fund transfers and money laundering. |
| Key Characteristics | Mixes real and fake personal data; hard to detect. | Legitimate accounts exploited by fraudsters, often willingly or unknowingly. |
| Detection Challenges | New or thin credit files; inconsistent data points. | Unusual transaction patterns; rapid money movement. |
| Risk to Banks | Credit losses, regulatory fines, reputational damage. | AML violations, legal repercussions, financial loss. |
| Mitigation Strategies | Enhanced identity verification, data analytics, machine learning. | Transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, suspicious activity reporting. |
Which is better?
Synthetic identity fraud inflicts greater financial damage on banks due to its complex fabrication of fake identities combining real and fictitious information, making detection difficult and losses substantial. Mule accounts facilitate the movement of illicit funds but typically serve as intermediaries, thereby posing a lower direct financial risk compared to synthetic identity fraud. Banks prioritize advanced fraud detection technologies and machine learning algorithms to combat synthetic identity fraud more aggressively than mule account activities.
Connection
Synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities using a combination of real and fabricated information, which fraudsters use to open mule accounts. Mule accounts serve as intermediaries to receive and transfer illicit funds, masking the true origin and ownership of the money. Banks implement advanced analytics and identity verification technologies to detect these interconnected schemes and prevent financial losses.
Key Terms
Money Laundering
Mule accounts are often used in money laundering schemes to transfer illicit funds through legitimate banking channels, while synthetic identity fraud involves creating fake identities to open accounts used for layering and disguising the origins of dirty money. Both tactics pose significant risks to financial institutions' anti-money laundering (AML) efforts and require sophisticated detection tools leveraging AI and behavioral analytics. Explore effective strategies to identify and prevent these fraudulent money laundering methods.
Identity Fabrication
Mule accounts are legitimate accounts controlled by fraudsters to launder money or facilitate scams, whereas synthetic identity fraud involves creating entirely fabricated identities by combining real and fake information. Identity fabrication in synthetic fraud is complex, leveraging stolen Social Security numbers mixed with fictitious personal details to bypass traditional verification systems. Explore more on how identity fabrication tactics evolve and impact fraud prevention strategies.
Account Holder Verification
Account holder verification plays a crucial role in distinguishing mule accounts from synthetic identity fraud, as mule accounts involve real individuals who unwittingly or fraudulently facilitate money laundering or illicit transactions using their legitimate identities. In contrast, synthetic identity fraud combines fabricated and stolen personal information to create a non-existent but seemingly legitimate account holder, making verification more challenging due to the mixture of real and fake data. Explore advanced strategies to enhance account holder verification and effectively combat both mule account activities and synthetic identity fraud.
Source and External Links
Mule Account - Kount - A mule account is a bank or financial account used by criminals to transfer or launder illicit funds, often without the account holder's knowledge, with the account holder either tricked or complicit in the scheme.
Mule accounts and money laundering: How to eliminate blindspots - Mule accounts are used in the placement phase of money laundering to integrate illicit funds into the financial system and are characterized by suspicious transactional behaviors like rapid fund movements and unusual transfers.
Detecting Mule Accounts with Behavioral Biometrics - BioCatch - Mule accounts often involve accounts opened with stolen or synthetic identities and can be detected using behavioral biometrics along with monitoring transaction velocity and unusual transfer patterns.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com