Account aggregation consolidates financial data from multiple sources into a single platform, enhancing visibility and decision-making for users. Loan origination involves the entire process of applying for and approving loans, focusing on credit assessment and risk management. Explore the differences to understand which banking service best suits your financial needs.
Why it is important
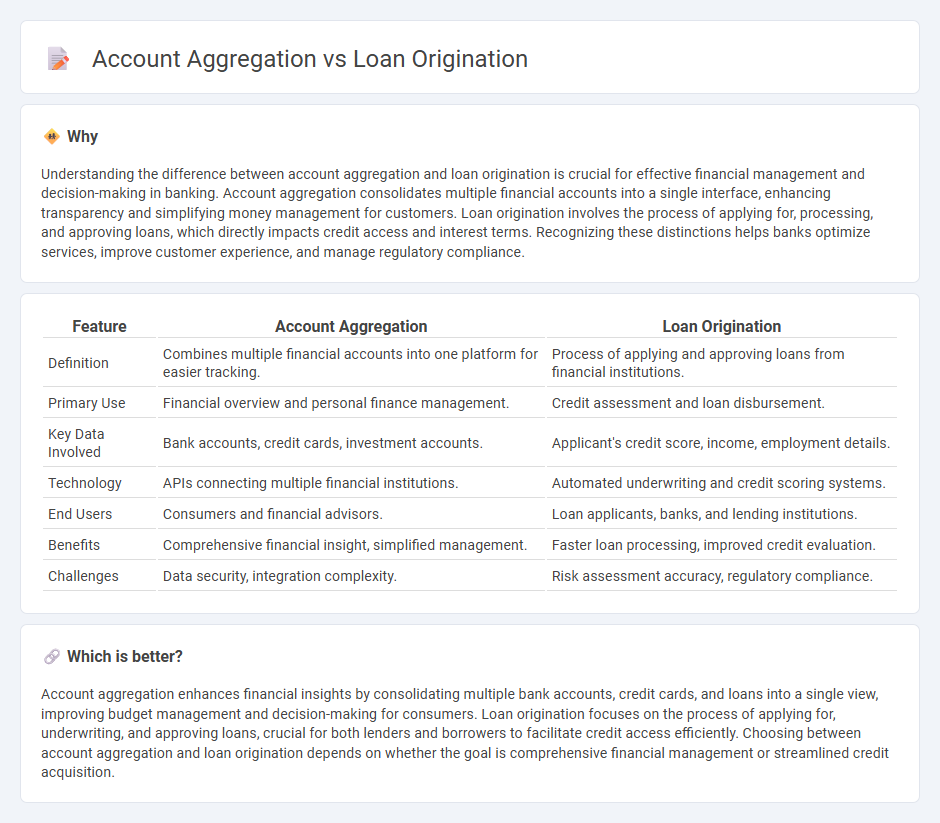
Understanding the difference between account aggregation and loan origination is crucial for effective financial management and decision-making in banking. Account aggregation consolidates multiple financial accounts into a single interface, enhancing transparency and simplifying money management for customers. Loan origination involves the process of applying for, processing, and approving loans, which directly impacts credit access and interest terms. Recognizing these distinctions helps banks optimize services, improve customer experience, and manage regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Account Aggregation | Loan Origination |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines multiple financial accounts into one platform for easier tracking. | Process of applying and approving loans from financial institutions. |
| Primary Use | Financial overview and personal finance management. | Credit assessment and loan disbursement. |
| Key Data Involved | Bank accounts, credit cards, investment accounts. | Applicant's credit score, income, employment details. |
| Technology | APIs connecting multiple financial institutions. | Automated underwriting and credit scoring systems. |
| End Users | Consumers and financial advisors. | Loan applicants, banks, and lending institutions. |
| Benefits | Comprehensive financial insight, simplified management. | Faster loan processing, improved credit evaluation. |
| Challenges | Data security, integration complexity. | Risk assessment accuracy, regulatory compliance. |
Which is better?
Account aggregation enhances financial insights by consolidating multiple bank accounts, credit cards, and loans into a single view, improving budget management and decision-making for consumers. Loan origination focuses on the process of applying for, underwriting, and approving loans, crucial for both lenders and borrowers to facilitate credit access efficiently. Choosing between account aggregation and loan origination depends on whether the goal is comprehensive financial management or streamlined credit acquisition.
Connection
Account aggregation consolidates financial data from multiple accounts into a single platform, enabling lenders to have a comprehensive view of a borrower's financial health. This comprehensive data enhances the loan origination process by improving credit risk assessment and enabling personalized loan offerings. Streamlined access to aggregated account information accelerates loan approval times and reduces the likelihood of defaults.
Key Terms
**Loan Origination:**
Loan origination is the comprehensive process by which a financial institution evaluates, approves, and funds a borrower's loan application, incorporating credit assessment, risk analysis, and regulatory compliance. Advanced technologies like AI-driven credit scoring and automated document verification streamline loan origination, reducing processing time and improving accuracy. Explore how these innovations transform lending efficiency and borrower experience.
Underwriting
Loan origination streamlines underwriting by automating credit assessment and risk evaluation through borrower data integration, enhancing decision accuracy and processing speed. Account aggregation consolidates financial information from multiple sources, providing underwriters a comprehensive view of applicant cash flows and transaction history for improved risk analysis. Explore how advanced data aggregation tools improve underwriting effectiveness in lending processes.
Credit Scoring
Loan origination involves the process of evaluating and approving borrower applications, heavily relying on credit scoring to assess creditworthiness and minimize default risk. Account aggregation consolidates financial data from multiple accounts to provide a comprehensive view of a borrower's financial status, enhancing the accuracy of credit scoring models. Explore how integrating advanced credit scoring techniques in both loan origination and account aggregation can optimize lending decisions.
Source and External Links
Loan Originations and Onboarding - FICO - Loan origination is the multi-stage process a borrower undergoes when applying for a loan, including application submission, document verification, credit evaluation and underwriting, approval/denial decision, and finally loan disbursement and closing.
What Is The Mortgage Loan Origination Process? | Bankrate - The mortgage loan origination process typically takes 30-60 days and includes preapproval, loan application, financial vetting, appraisal, and receiving a loan estimate to compare offers before final approval.
Loan Origination Process Explained (And How to Improve Efficiency) - The loan origination process includes pre-qualification, loan application (often online), processing, underwriting, quality control, and funding, with strong emphasis on creditworthiness and compliance checks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com