Cloud core banking leverages scalable cloud infrastructure to deliver flexible, cost-effective financial services with enhanced data accessibility and security. Microservices-based core banking architecture breaks down complex banking functions into independent, modular services, enabling faster development and seamless integration of new features. Explore the key differences and benefits of these architectures to understand their impact on modern banking innovation.
Why it is important
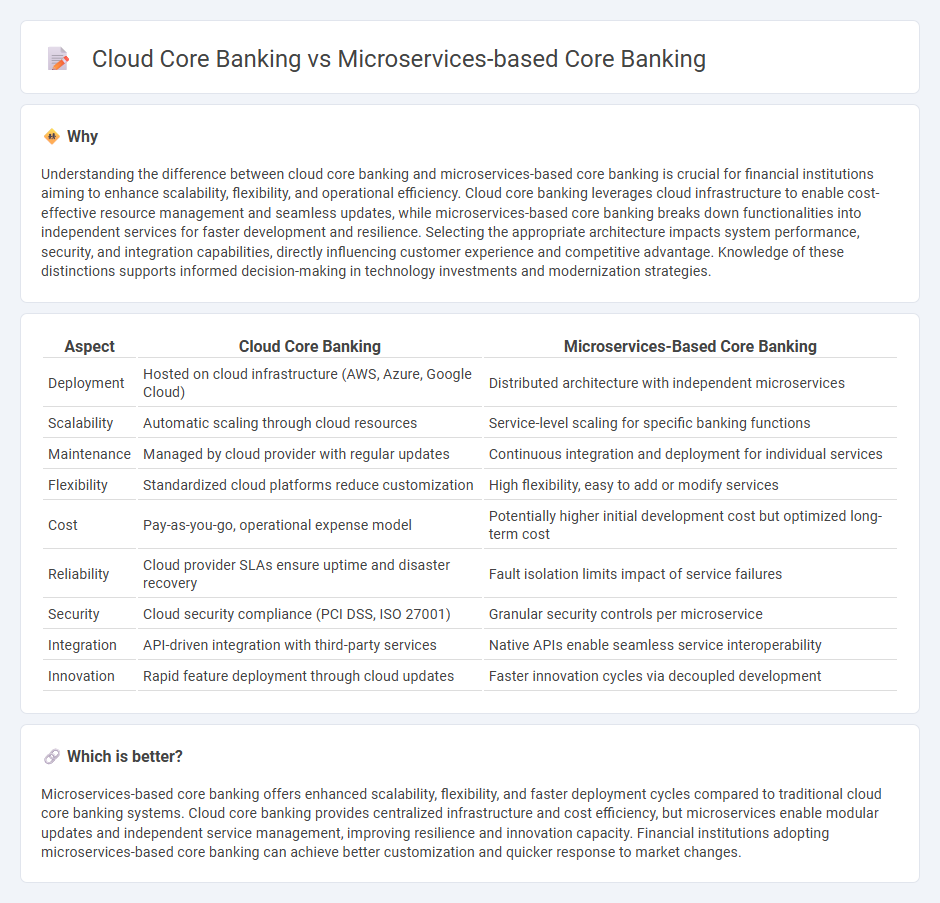
Understanding the difference between cloud core banking and microservices-based core banking is crucial for financial institutions aiming to enhance scalability, flexibility, and operational efficiency. Cloud core banking leverages cloud infrastructure to enable cost-effective resource management and seamless updates, while microservices-based core banking breaks down functionalities into independent services for faster development and resilience. Selecting the appropriate architecture impacts system performance, security, and integration capabilities, directly influencing customer experience and competitive advantage. Knowledge of these distinctions supports informed decision-making in technology investments and modernization strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cloud Core Banking | Microservices-Based Core Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Hosted on cloud infrastructure (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) | Distributed architecture with independent microservices |
| Scalability | Automatic scaling through cloud resources | Service-level scaling for specific banking functions |
| Maintenance | Managed by cloud provider with regular updates | Continuous integration and deployment for individual services |
| Flexibility | Standardized cloud platforms reduce customization | High flexibility, easy to add or modify services |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go, operational expense model | Potentially higher initial development cost but optimized long-term cost |
| Reliability | Cloud provider SLAs ensure uptime and disaster recovery | Fault isolation limits impact of service failures |
| Security | Cloud security compliance (PCI DSS, ISO 27001) | Granular security controls per microservice |
| Integration | API-driven integration with third-party services | Native APIs enable seamless service interoperability |
| Innovation | Rapid feature deployment through cloud updates | Faster innovation cycles via decoupled development |
Which is better?
Microservices-based core banking offers enhanced scalability, flexibility, and faster deployment cycles compared to traditional cloud core banking systems. Cloud core banking provides centralized infrastructure and cost efficiency, but microservices enable modular updates and independent service management, improving resilience and innovation capacity. Financial institutions adopting microservices-based core banking can achieve better customization and quicker response to market changes.
Connection
Cloud core banking leverages scalable cloud infrastructure to deliver banking services efficiently, while microservices-based core banking decomposes applications into modular components for flexibility and rapid deployment. The integration of microservices within cloud-based core banking platforms enables agile development, seamless updates, and improved fault isolation, enhancing overall system resilience and customer experience. Financial institutions adopting this combination benefit from scalable, cost-effective solutions that accelerate innovation and support real-time processing.
Key Terms
**Microservices-based core banking:**
Microservices-based core banking architecture decomposes banking functions into independent, modular services, enhancing scalability, flexibility, and faster deployment cycles. This approach enables seamless integration with third-party applications and supports continuous delivery, reducing downtime and fostering innovation. Explore further to understand how microservices optimize core banking transformations.
APIs
Microservices-based core banking leverages modular, independently deployable services that enhance scalability, flexibility, and rapid innovation, enabling precise API orchestration for seamless integration with external financial services. Cloud core banking platforms prioritize scalable infrastructure, automatic updates, and cost efficiency, using APIs to facilitate real-time data exchange and multi-channel connectivity across cloud environments. Explore the strategic advantages and API-driven capabilities of both architectures to optimize your banking technology stack.
Service orchestration
Microservices-based core banking leverages independently deployable services allowing granular service orchestration that enhances scalability and resilience through containerization and API gateways. Cloud core banking platforms integrate microservices with cloud-native capabilities such as automated scaling, managed service meshes, and advanced orchestration tools like Kubernetes for seamless deployment and real-time monitoring. Explore detailed comparisons and implementation strategies to optimize service orchestration in core banking systems.
Source and External Links
Microservices-Based Banking Systems: Enabling Innovation ... - BICon - Microservices-based core banking architectures encapsulate each banking capability into independent services like payments, accounts, fraud detection, lending, and notifications, enabling agility, scalability, real-time processing, and continuous innovation through domain-driven microservices communicating over APIs in cloud-native environments.
The Role of Microservices in Modernizing Core Banking Systems - Microservices allow faster updates, independent scaling, and reduced downtime in core banking systems, enhancing security via isolation, facilitating real-time data processing, and enabling seamless integration with third-party APIs through API gateways for better customer experience and ecosystem partnerships.
Why microservices are the future of banking - Thought Machine - Microservices dramatically improve scalability and cost-efficiency in core banking by allowing individual scaling of services to meet peak demands, ease of updating with zero downtime, and risk reduction, thus overcoming limitations of traditional monolithic mainframes and legacy systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com