Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized ledger technology to enable secure, transparent, and fast cross-border money transfers with reduced fees and real-time tracking. Hawala, an informal value transfer system popular in South Asia and the Middle East, operates through trust-based networks without physical movement of cash or formal banking channels. Explore the advantages and challenges of each system to understand their impact on global banking and remittance landscapes.
Why it is important
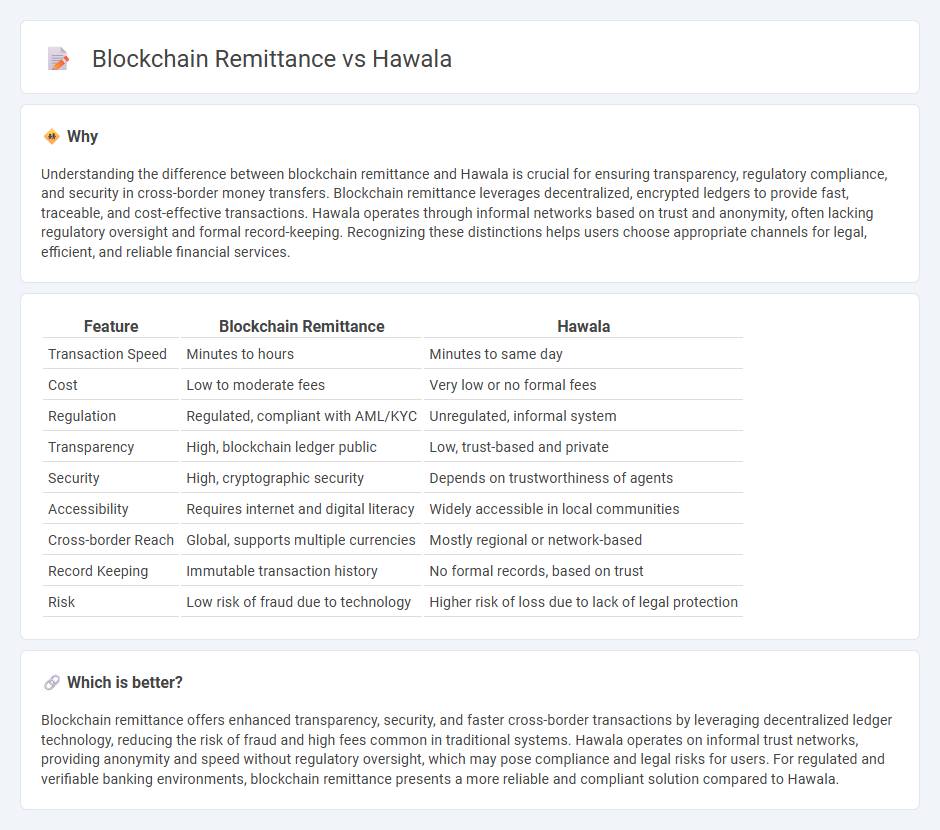
Understanding the difference between blockchain remittance and Hawala is crucial for ensuring transparency, regulatory compliance, and security in cross-border money transfers. Blockchain remittance leverages decentralized, encrypted ledgers to provide fast, traceable, and cost-effective transactions. Hawala operates through informal networks based on trust and anonymity, often lacking regulatory oversight and formal record-keeping. Recognizing these distinctions helps users choose appropriate channels for legal, efficient, and reliable financial services.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Blockchain Remittance | Hawala |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to hours | Minutes to same day |
| Cost | Low to moderate fees | Very low or no formal fees |
| Regulation | Regulated, compliant with AML/KYC | Unregulated, informal system |
| Transparency | High, blockchain ledger public | Low, trust-based and private |
| Security | High, cryptographic security | Depends on trustworthiness of agents |
| Accessibility | Requires internet and digital literacy | Widely accessible in local communities |
| Cross-border Reach | Global, supports multiple currencies | Mostly regional or network-based |
| Record Keeping | Immutable transaction history | No formal records, based on trust |
| Risk | Low risk of fraud due to technology | Higher risk of loss due to lack of legal protection |
Which is better?
Blockchain remittance offers enhanced transparency, security, and faster cross-border transactions by leveraging decentralized ledger technology, reducing the risk of fraud and high fees common in traditional systems. Hawala operates on informal trust networks, providing anonymity and speed without regulatory oversight, which may pose compliance and legal risks for users. For regulated and verifiable banking environments, blockchain remittance presents a more reliable and compliant solution compared to Hawala.
Connection
Blockchain remittance and Hawala both facilitate cross-border money transfers by bypassing traditional banking systems, offering faster, cost-effective solutions. Blockchain technology enhances transparency and security through decentralized ledgers, addressing the trust issues inherent in Hawala's informal, trust-based network. The integration of blockchain can modernize Hawala practices by digitizing transactions while preserving its core principle of trust and community reliance.
Key Terms
Intermediaries
Hawala remittance relies heavily on trusted intermediaries known as hawaladars who facilitate informal value transfers without traditional banking systems. Blockchain remittance eliminates intermediaries by utilizing decentralized ledger technology, ensuring transparency and reducing transaction costs. Explore how each system's role of intermediaries affects speed, security, and regulatory compliance.
Transparency
Hawala operates through a trusted network of brokers and informal trust systems, which inherently lacks transparency and official records, making it difficult to trace transactions. Blockchain remittance uses decentralized ledgers and cryptographic protocols to ensure every transaction is publicly verifiable, immutable, and transparent, enhancing accountability and reducing fraud. Explore how transparency differences impact the efficiency and security of cross-border money transfers.
Traceability
Hawala relies on informal trust-based networks without digital records, making traceability challenging and regulatory oversight limited. Blockchain remittance uses a decentralized ledger system that records every transaction transparently and immutably, enhancing compliance and auditability. Explore how traceability in these systems impacts global remittance security and efficiency.
Source and External Links
Is Hawala Legal in the United States? - Hawala is an informal money transfer system based on trust and interpersonal networks, widely used by migrant workers to send remittances, but it is considered illegal in the United States as it operates outside formal financial regulation.
The Hawala System: A Risky Alternative to Traditional Banking - Hawala, also known as hundi, is an ancient, informal value transfer system relying on hawaladars who facilitate remittances without formal financial institutions, existing largely outside regulatory oversight but sometimes regulated in countries like the UAE and the UK.
Misplaced Blame: Islam, Terrorism and the Origins of Hawala - Hawala is a historic and global money transfer system that predates modern banking, originating in the Middle East and Indian subcontinent, operating based on trust and persisting despite state efforts to regulate it, with complex cultural and economic roots.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com