Open banking creates a secure platform allowing third-party developers to access financial data through APIs, fostering innovation and personalized services. Digital banking offers fully online financial transactions and account management via mobile apps or websites, streamlining customer experience. Explore how open banking and digital banking transform the future of financial services.
Why it is important
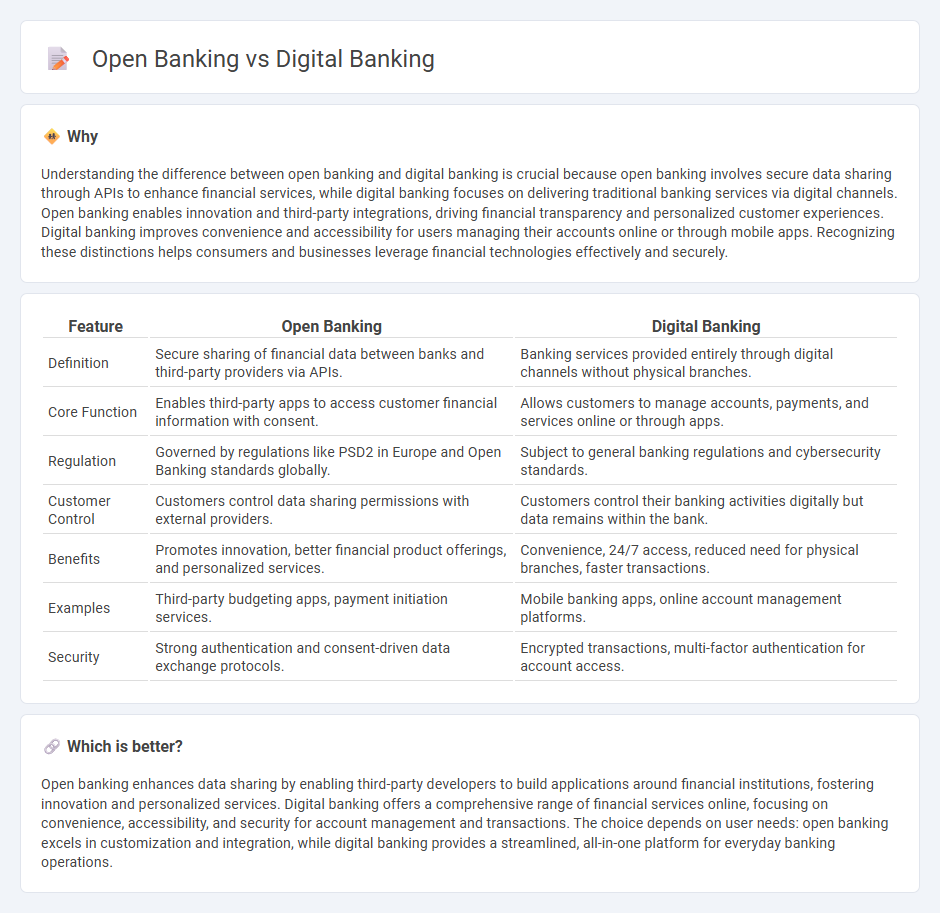
Understanding the difference between open banking and digital banking is crucial because open banking involves secure data sharing through APIs to enhance financial services, while digital banking focuses on delivering traditional banking services via digital channels. Open banking enables innovation and third-party integrations, driving financial transparency and personalized customer experiences. Digital banking improves convenience and accessibility for users managing their accounts online or through mobile apps. Recognizing these distinctions helps consumers and businesses leverage financial technologies effectively and securely.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Open Banking | Digital Banking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Secure sharing of financial data between banks and third-party providers via APIs. | Banking services provided entirely through digital channels without physical branches. |
| Core Function | Enables third-party apps to access customer financial information with consent. | Allows customers to manage accounts, payments, and services online or through apps. |
| Regulation | Governed by regulations like PSD2 in Europe and Open Banking standards globally. | Subject to general banking regulations and cybersecurity standards. |
| Customer Control | Customers control data sharing permissions with external providers. | Customers control their banking activities digitally but data remains within the bank. |
| Benefits | Promotes innovation, better financial product offerings, and personalized services. | Convenience, 24/7 access, reduced need for physical branches, faster transactions. |
| Examples | Third-party budgeting apps, payment initiation services. | Mobile banking apps, online account management platforms. |
| Security | Strong authentication and consent-driven data exchange protocols. | Encrypted transactions, multi-factor authentication for account access. |
Which is better?
Open banking enhances data sharing by enabling third-party developers to build applications around financial institutions, fostering innovation and personalized services. Digital banking offers a comprehensive range of financial services online, focusing on convenience, accessibility, and security for account management and transactions. The choice depends on user needs: open banking excels in customization and integration, while digital banking provides a streamlined, all-in-one platform for everyday banking operations.
Connection
Open banking and digital banking are interconnected through the use of APIs that enable secure data sharing between financial institutions and third-party providers. This collaboration enhances customer experience by offering personalized financial services, seamless payment solutions, and improved account aggregation features. Digital banking platforms leverage open banking frameworks to increase innovation, foster competition, and expand access to diverse financial products.
Key Terms
APIs
Digital banking integrates traditional financial services within online platforms, enabling customers to manage accounts, transfer funds, and access loans via secure web or mobile apps. Open banking leverages APIs to allow third-party developers to build applications that access banks' data securely, fostering innovation and personalized financial services. Explore how API-driven open banking is transforming the future of finance.
Customer Data Access
Digital banking primarily provides customers access to their own financial information within a single institution through online platforms, emphasizing secure account management and transaction capabilities. Open banking expands this access by enabling third-party providers to retrieve and use customer data across multiple banks via APIs, fostering personalized financial services and enhanced data sharing control. Discover how these evolving banking models transform customer data access and empower financial innovation.
Third-Party Providers
Third-Party Providers (TPPs) play a crucial role in open banking by granting secure access to customer financial data through APIs, enabling innovative financial services beyond traditional digital banking platforms. Unlike digital banking, which primarily offers bank-owned online services, open banking empowers TPPs to create personalized products such as budgeting tools, payment initiation services, and account aggregators. Explore how TPPs are revolutionizing customer experience and financial ecosystems by clicking here to learn more.
Source and External Links
Digital Banking: 2025 Market Overview, Trends & Insights - Digital banking digitizes traditional banking services to serve customers via online channels, with trends including mobile banking growth, digital-only banks, AI integration, and expanding digital payments.
Digital banking - Wikipedia - Digital banking encompasses online and mobile banking plus middleware, enabling automation and seamless service delivery across platforms with full banking functionalities and security compliance.
Digital Banking - UNFCU - UNFCU Digital Banking offers secure global account access, allowing users to manage accounts, transfer money, apply for loans, control cards, and receive fraud alerts through a single platform accessible from computers and mobile devices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com